| Citation: |
Hua Chen, Renjie Gong, Xu Cheng, Yulin Zhang, Zhong Gao, Guiliang Guo, Yuepeng Yan. A 220-1100 MHz low phase-noise frequency synthesizer with wide-band VCO and selectable I/Q divider[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(12): 125006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/125006
****
H Chen, R J Gong, X Cheng, Y L Zhang, Z Gao, G L Guo, Y P Yan. A 220-1100 MHz low phase-noise frequency synthesizer with wide-band VCO and selectable I/Q divider[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(12): 125006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/125006.
|
A 220-1100 MHz low phase-noise frequency synthesizer with wide-band VCO and selectable I/Q divider
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/125006
More Information
-
Abstract
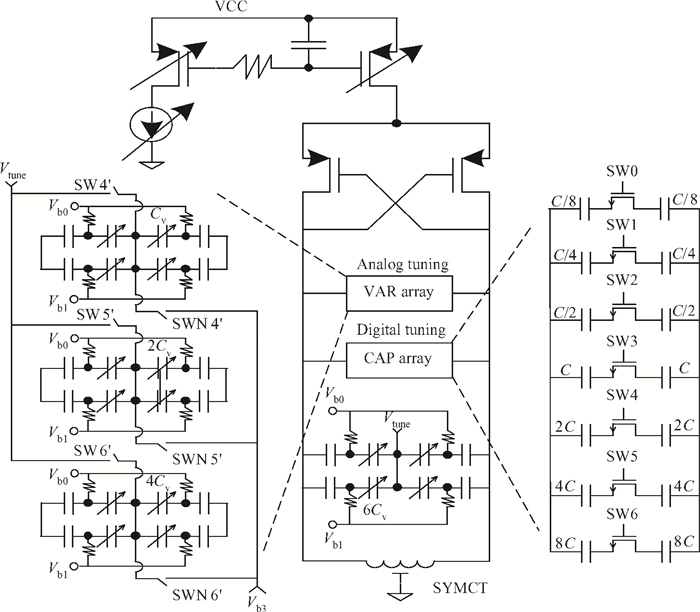
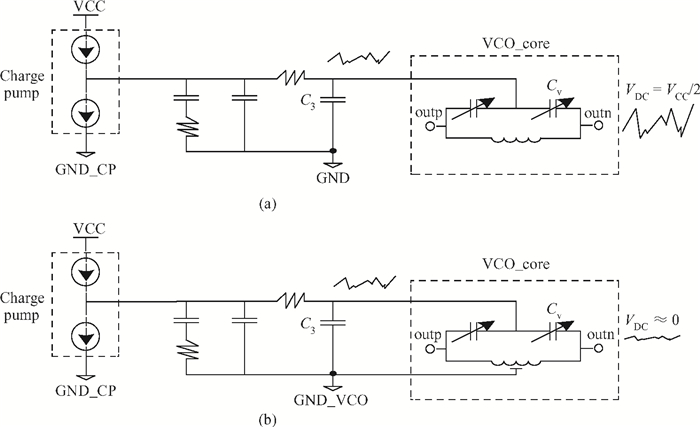
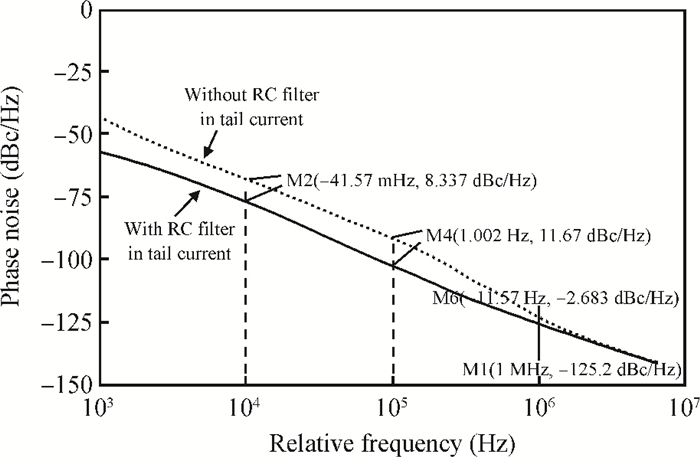
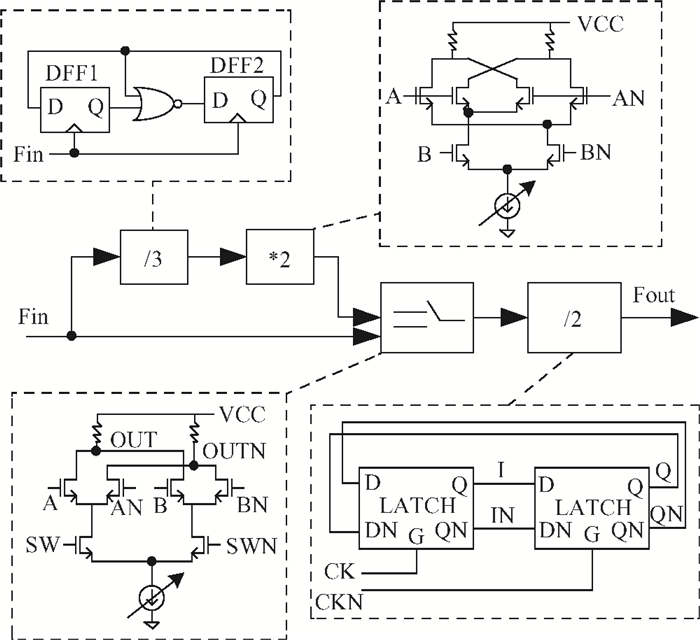
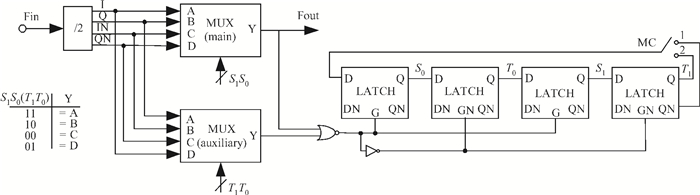
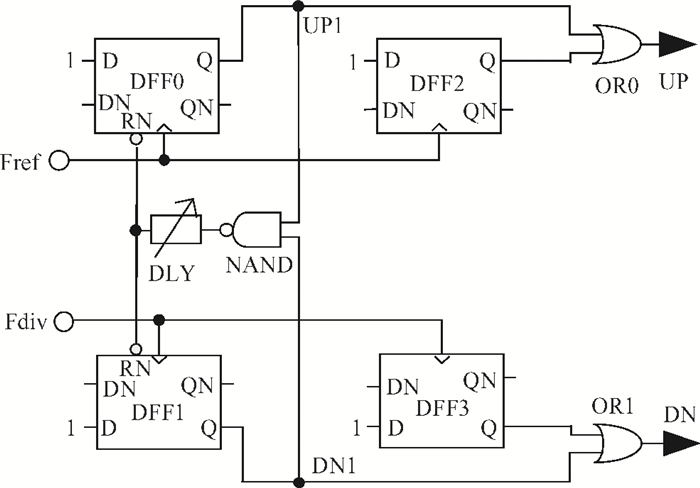
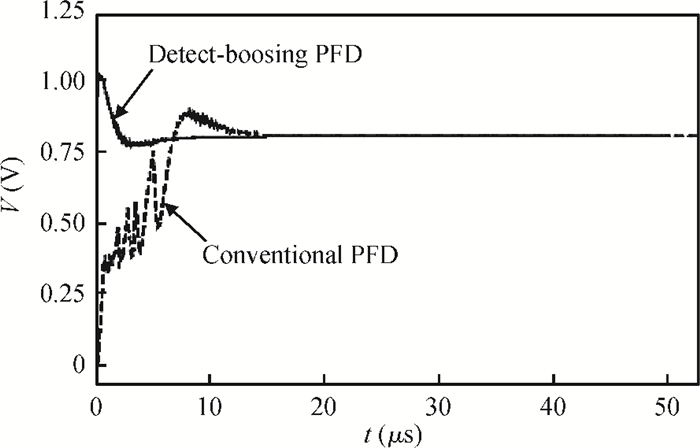
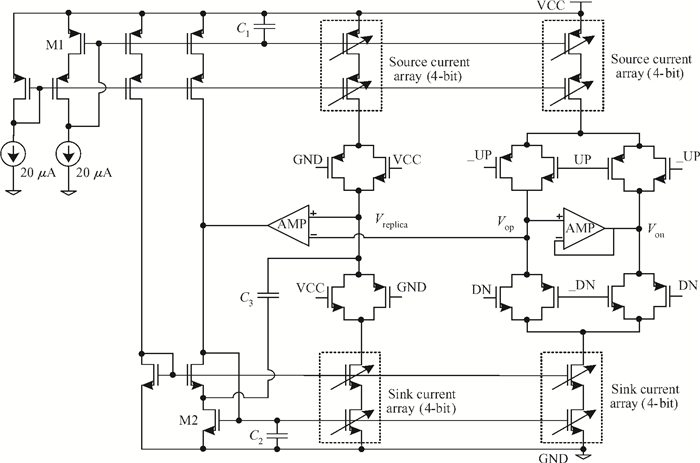
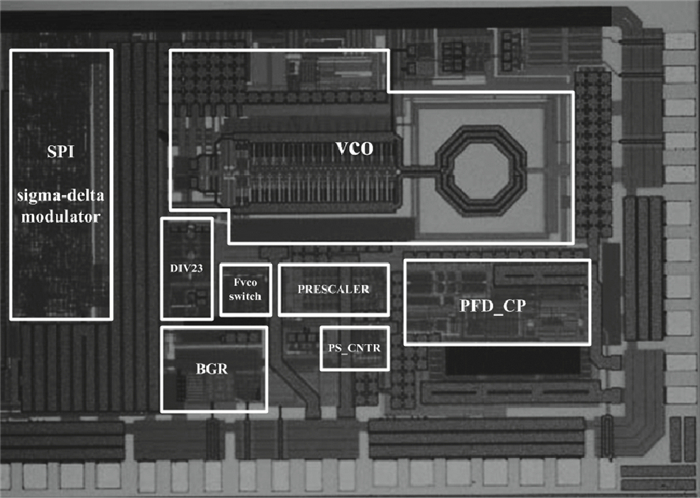
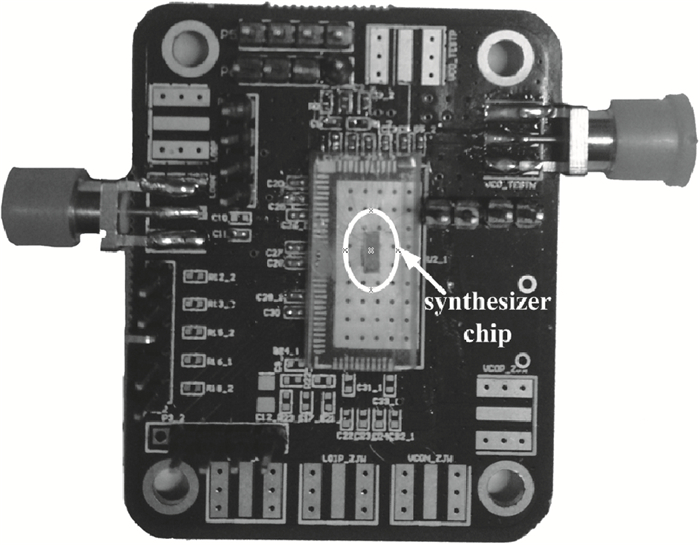
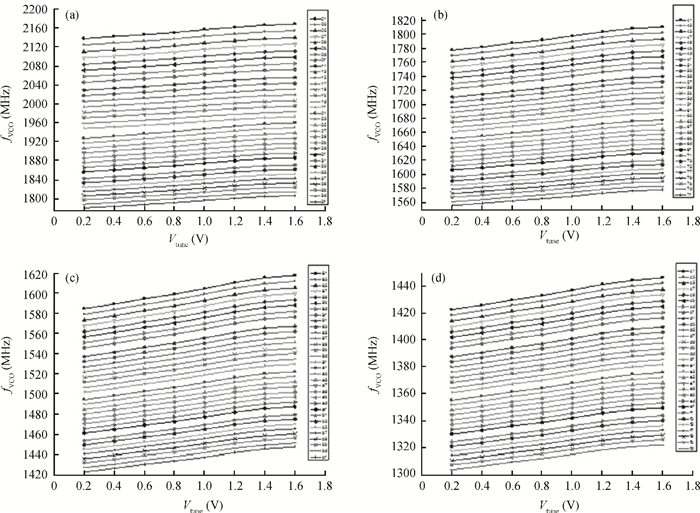
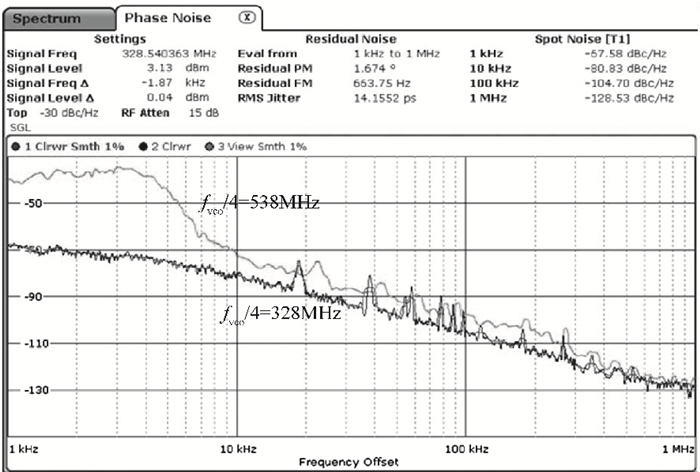
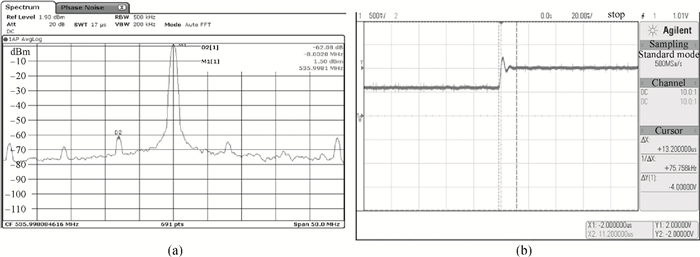
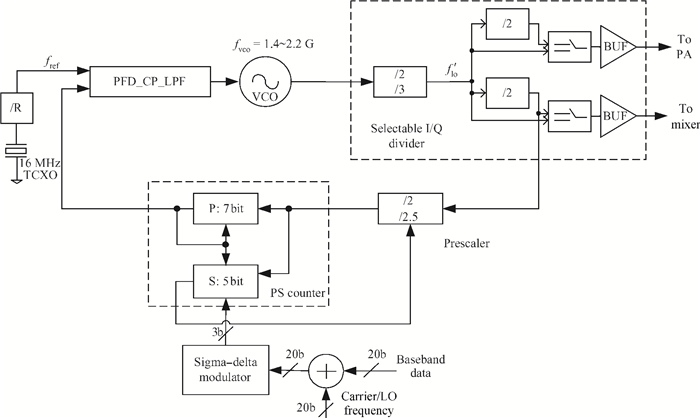
This paper presents a low phase-noise fractional-N frequency synthesizer which provides an in-phase/quadrature-phase (I/Q) signal over a frequency range of 220-1100 MHz for wireless networks of industrial automation (WIA) applications. Two techniques are proposed to achieve the wide range. First, a 1.4-2.2 GHz ultralow gain voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is adopted by using 128 tuning curves. Second, a selectable I/Q divider is employed to divide the VCO frequency by 2 or 3 or 4 or 6. Besides, a phase-switching prescaler is proposed to lower PLL phase noise, a self-calibrated charge pump is used to suppress spur, and a detect-boosting phase frequency detector is adopted to shorten settling time. With a 200 kHz loop bandwidth, lowest measured phase noise is -106 dBc/Hz at a 10 kHz offset and -131 dBc/Hz at a 1 MHz offset. Fabricated in the TSMC 0.18 μm CMOS process, the synthesizer occupies a chip area of 1.2 mm2, consumes only 15 mW from the 1.8 V power supply, and settles within 13.2 μs. The synthesizer is optimized for the WIA applications, but can also be used for other short-range wireless communications, such as 433, 868, 916 MHz ISM band applications. -
References
[1] IEEE 802. 15. 4(2006 version): Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs)[2] China's wireless industry coalition. Industrial wireless networking standard first part of the WIA: WIA for process automation system structure and communications specifications, 2008[3] Ussmueller T, Jung M, Weigel R. Synthesizer concepts for FMCW based locatable wireless sensor nodes. IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop on Wireless Sensing, Local Positioning, 2009:1 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=5307860&[4] Li Z, Cao Q, Qi X, et al. Design of a low power 5-GHz frequency synthesizer for WSN applications. IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), 2012:228 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6401669[5] Cheng S, Zhang K, Lu W, et al. A 2.4-GHz spur-cancelled fractional-N frequency synthesizer with PFD/DAC structure for WSN application. IEEE 7th International Conference on ASIC, 2007:696 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4415726/[6] Zhao B, Yang H, Wang H. A low-power fast-settling bond-wire frequency synthesizer with a dynamic-bandwidth scheme. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2012:1367 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.711.2700[7] Yan D L, Hui T T, Zhao B, et al. A low-power FSK modulator using fractional-N synthesizer for wireless sensor network application. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium, 2006:4 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1651121[8] Qi Nan, Chen Fan, Zhang Lingwei, et al. A reconfigurable multi-mode multi-band transmitter with integrated frequency synthesizer for short-range wireless communication. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(9):095008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095008[9] Berny A D, Niknejad A M, Meyer R G. A 1.8-GHz LC VCO with 1.3-GHz tuning range and digital amplitude calibration. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(4):909 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.842851[10] Ahn T, Moon J, Moon Y. A fractional-N frequency synthesizer with a wide-band small gain-fluctuation VCO for mobile DTV applications. International Conference on ASIC Proceedings, 2007[11] Hauspie D, Park E C, Craninckx J. Wideband VCO with simultaneous switching of frequency band, active core, and varactor size. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(7):1472 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.899105[12] Lu L, Chen J, Yuan L, et al. An 18-mW 1.175-2-GHz frequency synthesizer with constant bandwidth for DVB-T tuners. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2009, 57(4):928 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2009.2014449[13] Kim J, Shin J, Kim S, et al. A wide-band CMOS LC VCO with linearized coarse tuning characteristics. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ:Express Briefs, 2008, 55(5):399 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2007.914896[14] Osmany S A, Herzel F, Scheytt J C. An integrated 0.6-4.6 GHz, 5-7 GHz, 10-14 GHz, and 20-28 GHz frequency synthesizer for software-defined radio applications. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(9):1657 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2051476[15] Kim J, Lee S J, Kim S, et al. A 54-862-MHz CMOS transceiver for TV-band white-space device applications. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2011, 59(4):966 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2010.2103089[16] Razavi B. RF microelectronics. 2nd ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2012[17] Perrott M H, Tewksbury Ⅲ T L, Sodini C G. A 27-mW CMOS fractional-N synthesizer using digital compensation for 2.5-Mb/s GFSK modulation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1997, 32(12):2048 doi: 10.1109/4.643663[18] Moon Y J, Roh Y S, Jeong C Y, et al. A 4.39-5.26 GHz LC-tank CMOS voltage-controlled oscillator with small VCO-gain variation. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2009, 19(8):524 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2009.2024846[19] Mira J, Divel T, Ramet S, et al. Distributed MOS varactor biasing for VCO gain equalization in 0.13μm CMOS technology. Digest of Papers, IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium, 2004:131 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1320548[20] Kim J, Plouchart J O, Zamdmer N, et al. A 44 GHz differentially tuned VCO with 4 GHz tuning range in 0.12μm SOI CMOS. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, 2005, 1:416 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1494046[21] Heng C H, Song B S. A 1.8-GHz CMOS fractional-N frequency synthesizer with randomized multiphase VCO. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(6):848 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.811872[22] Razavi B. Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits. New York: McGRAW-Hill, 2001[23] Lu L, Gong Z, Liao Y, et al. A 975-to-1960 MHz fast-locking fractional-N synthesizer with adaptive bandwidth control and 4/4.5 prescaler for digital TV tuners. ISSCC, 2009:396 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4977475[24] Jian H Y, Xu Z, Wu Y C, et al. A fractional-N PLL for multiband (0.8-6 GHz) communications using binary-weighted D/A differentiator and offset-frequency Δ -Σ modulator. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(4):768 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2040232[25] Hsu M T, Chiu C T. A low power 10 GHz current reused VCO using negative resistance enhancement technique. IEEE Asia Pacific Microwave Conference, 2009:2276 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5385436/[26] Yang C Y, Chang C H, Lin J M, et al. A 0.6 V 10 GHz CMOS VCO using a negative-Gm back-gate tuned technique. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2011, 21(3):163 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2010.2102011[27] Tsai P K, Liu C Y, Huang T H. A CMOS voltage controlled oscillator and frequency tripler for 22-27 GHz local oscillator generation. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2011, 21(9):492 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2011.2163060[28] Wang T P, Li C C. A 0.4-V 1.08-mW 12-GHz high-performance VCO in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), 2012:207 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6175356/[29] Wu Q, Quach T, Mattamana A, et al. Design of wide tuning-range mm-wave VCOs using negative capacitance. IEEE Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium (CSICS), 2012:1 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?tp= & arnumber=6340077 & url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fstamp%2Fstamp.jsp%3Farnumber%3D6340077[30] Tsai P K, Huang T H. Integration of current-reused VCO and frequency tripler for 24-GHz low-power phase-locked loop applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ:Express Briefs, 2012, 59(4):199 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2012.2188459[31] Wu Q, Elabd S, Quach T K, et al. A-189 dBc/Hz FOM T wide tuning range Ka-band VCO using tunable negative capacitance and inductance redistribution. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), 2013:199 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=6569560[32] Wang T P, Yan Y M. A low-voltage low-power wide-tuning-range hybrid class-AB/class-B VCO with robust start-up and high-performance FOM. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2014, 62:521 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2014.2300443 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: