| Citation: |
Xinliang Chen, Congbo Yan, Xinhua Geng, Dekun Zhang, Changchun Wei, Ying Zhao, Xiaodan Zhang. Modified textured surface MOCVD-ZnO:B transparent conductive layers for thin-film solar cells[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(4): 043002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/043002
****
X L Chen, C B Yan, X H Geng, D K Zhang, C C Wei, Y Zhao, X D Zhang. Modified textured surface MOCVD-ZnO:B transparent conductive layers for thin-film solar cells[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(4): 043002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/043002.
|
Modified textured surface MOCVD-ZnO:B transparent conductive layers for thin-film solar cells
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/043002
More Information
-
Abstract
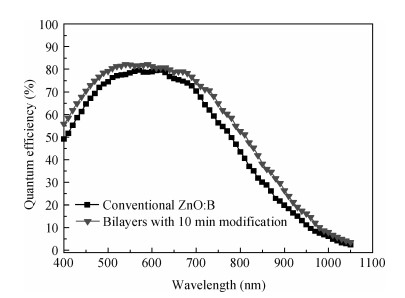
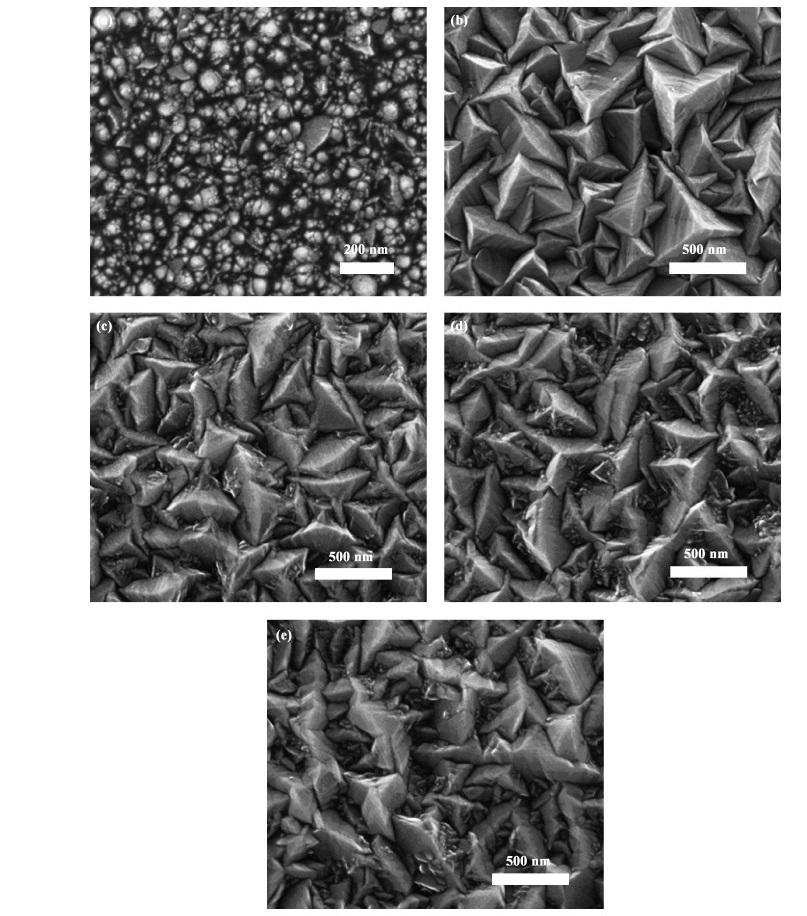
Modified textured surface boron-doped ZnO (ZnO:B) transparent conductive layers for thin-film solar cells were fabricated by low-pressure metal organic chemical vapor deposition (LP-MOCVD) on glass substrates. These modified textured surface ZnO:B thin films included two layers. The first ZnO:B layer, which has a pyramid-shaped texture, was deposited under conventional growth conditions, and the second layer, which has a sphere-like structure, at a relatively lower growth temperature. Typical bi-layer ZnO:B thin films exhibit a high electron mobility of 27.6 cm2/(V· s) due to improved grain boundary states. For bi-layer ZnO:B, the haze value increases and the total transmittance decreases with the increasing film thickness of the second modification layer. When applied in hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon (μc-Si:H) thin-film solar cells, the modified textured surface ZnO:B layers present relatively higher conversion efficiency than conventional ZnO:B films. -
References
[1] Shah A V, Schade H, Vanecek M, et al. Thin-film silicon solar cell technology. Prog Photovolt:Res and Appl, 2004, 12:113 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-159X[2] Hoffmann W, Pellkofer T. Thin films in photovoltaics:technologies and perspectives. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520:4094 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.04.146[3] Hsu C M, Battaglia C, Pahud C, et al. High-efficiency amorphous silicon solar cell on a periodic nanocone back reflector. Adv Energy Mater, 2012, 2:628 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201100514[4] Müller J, Rech B, Springer J, et al. TCO and light trapping in silicon thin film solar cells. Sol Energy, 2004, 77:917 doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2004.03.015[5] Yan B, Yue G, Sivec L, et al. Innovative dual function nc-SiOx:H layer leading to a > 16% efficient multi-junction thin-film silicon solar cell. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99:113512 doi: 10.1063/1.3638068[6] Janthong B, Hongsingthong A, Krajangsang T, et al. Novel a-Si:H/μc-Si:H tandem cell with lower optical loss. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2012, 358:2478 doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.01.060[7] Ruske F, Jacobs C, Sittinger V, et al. Large area ZnO:Al films with tailored light scattering properties for photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515:8695 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2007.03.107[8] Ding L, Boccard M, Bugnon G, et al. Highly transparent ZnO bilayers by LP-MOCVD as front electrodes for thin-film micromorph silicon solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2012, 98:331 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2011.11.033[9] Bugnon G, Parascandolo G, Söderström T, et al. A new view of microcrystalline silicon:the role of plasma processing in achieving a dense and stable absorber material for photovoltaic applications. Adv Funct Mater, 2012, 22:3665 doi: 10.1002/adfm.v22.17[10] Hongsingthong A, Krajangsang T, Fujioka H, et al. Improvement of short-circuit current in silicon-based thin film solar cells using ZnO films with very high haze value. 26th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, DOI:10.4229/26thEUPVSEC2011-3AV.2.9[11] Kluth O, Rech B, Houben L, et al. Texture etched ZnO:Al coated glass substrates for silicon based thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films, 1999, 351:247 doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(99)00085-1[12] Hongsingthong A, Yunaz I A, Miyajima S, et al. Preparation of ZnO thin films using MOCVD technique with D2O/H2O gas mixture for use as TCO in silicon-based thin film solar cells. Sol Energy MaterSol Cells, 2011, 95:171 doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2010.04.025[13] Chen X L, Li L N, Wang F, et al. Natively textured surface aluminum-doped zinc oxide transparent conductive layers for thin film solar cells via pulsed direct-current reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520:5392 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2012.03.120[14] Owen J I, Zhang W, Köhl D, et al. Study on the in-line sputtering growth and structural properties of polycrystalline ZnO:Al on ZnO and glass. J Cryst Growth, 2012, 344:12 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2012.01.043[15] Hüpkes J, Owen J I, Pust S E, et al. Chemical etching of zinc oxide for thin-film silicon solar cells. Chem Phys Phys Chem, 2012, 13:66 doi: 10.1002/cphc.201100738[16] Chen X L, Geng X H, Xue J M, et al. Temperature-dependent growth of zinc oxide thin films grown by metal organic chemical vapor deposition. J Cryst Growth, 2006, 296:43 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.08.028[17] Python M, Vallat-Sauvain E, Bailat J, et al. Relation between substrate surface morphology and microcrystalline silicon solar cell performance. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2008, 354:2258 doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.09.084[18] Moriya Y, Krajangsang T, Sichanugrist P, et al. Development of high-efficiency tandem silicon solar cells on W-textured zinc oxide-coated soda-lime glass substrates. Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), DOI:10.1109/PVSC.2012.6318219.[19] Chen X L, Xue J M, Sun J, et al. Growth of textured ZnO thin films and their front electrodes for application in solar cells. Chin J Semicond, 2007, 28:1072 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-BDTX200707013.htm[20] Jiang X, Jia C L, Szyszka B. Manufacture of specific structure of aluminum-doped zinc oxide films by patterning the substrate surface. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 80:3090 doi: 10.1063/1.1473683[21] Yan C B, Chen X L, Wang F, et al. Textured surface ZnO:B/(hydrogenated gallium-doped ZnO) and (hydrogenated gallium-doped ZnO)/ZnO:B transparent conductive oxide layers for Si-based thin film solar cells. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 521:249 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.10.203[22] Shah A. Thin-film silicon solar cells. Swiss EPFL Press, 2010 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: