| Citation: |
Yanbin Luo, Jian Shi, Chengyan Ma, Yebing Gan, Min Qian. A high linearity SiGe HBT LNA for GPS receiver[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(4): 045001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/045001
****
Y B Luo, J Shi, C Y Ma, Y B Gan, M Qian. A high linearity SiGe HBT LNA for GPS receiver[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(4): 045001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/045001.
|
-
Abstract
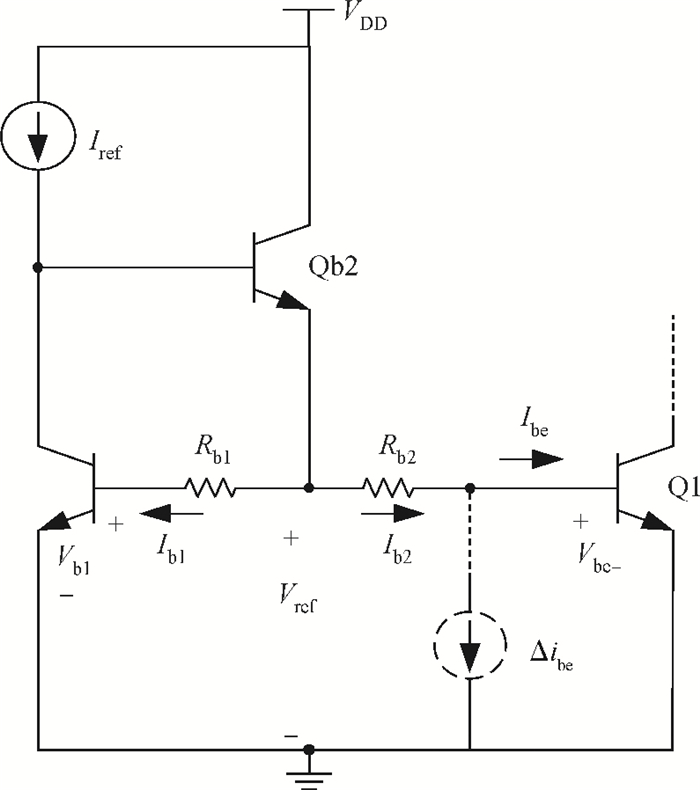
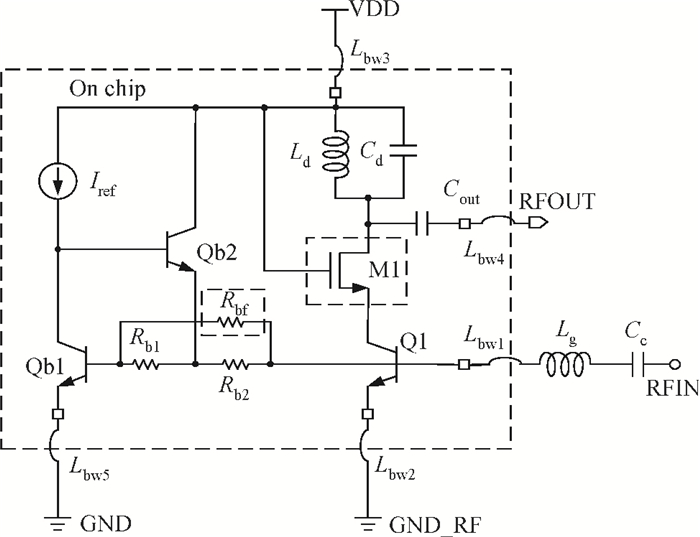
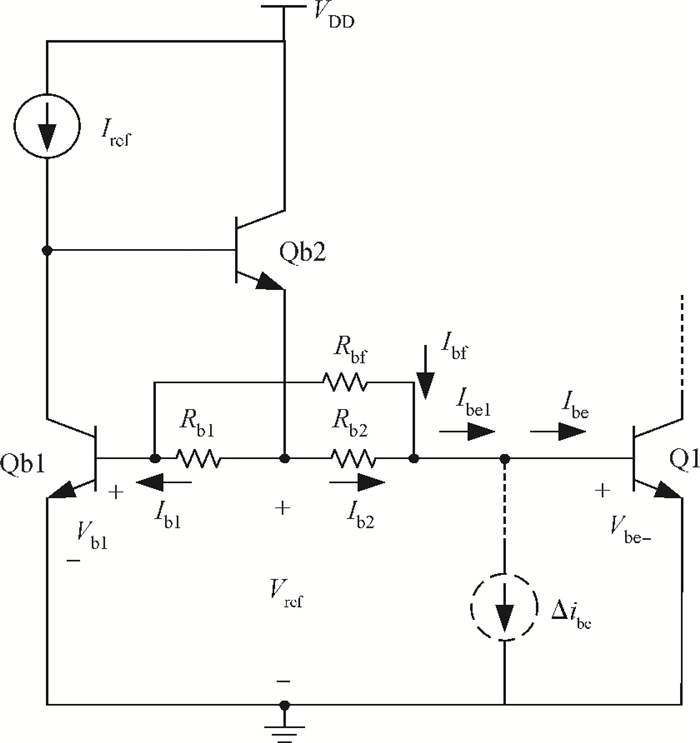
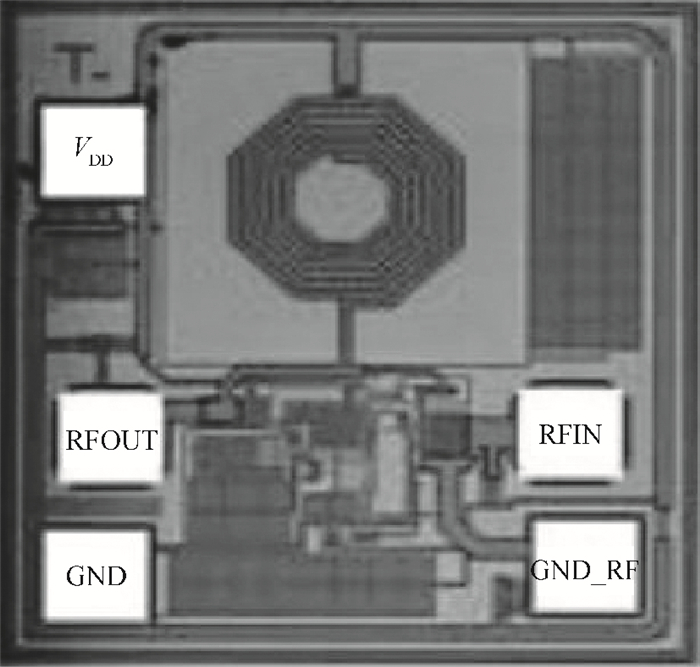
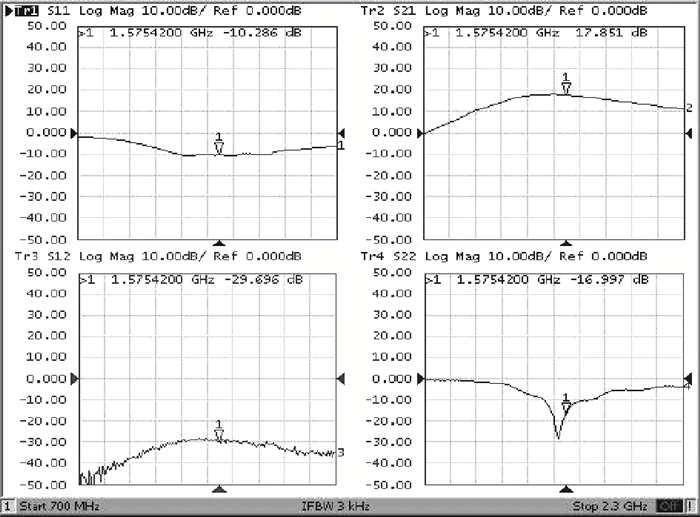
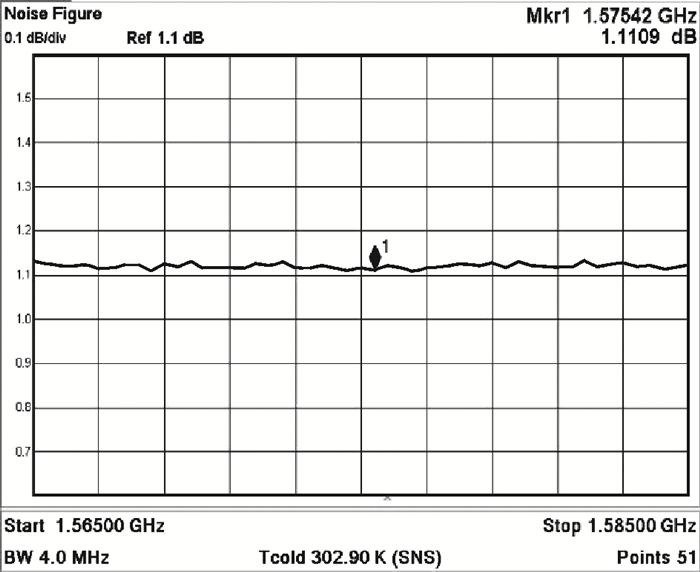
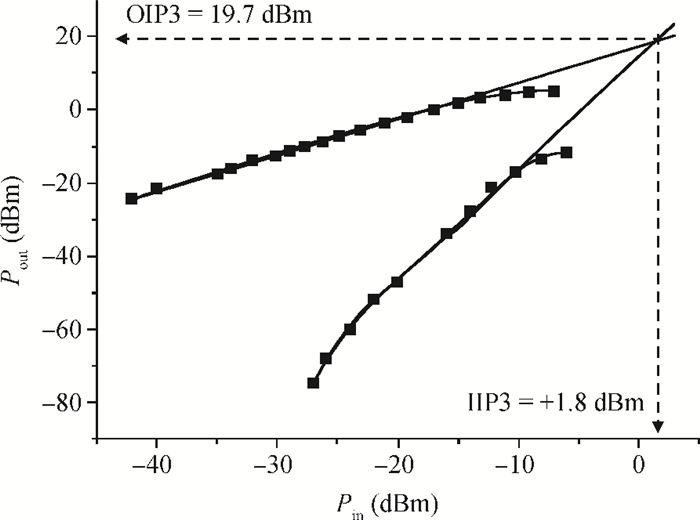
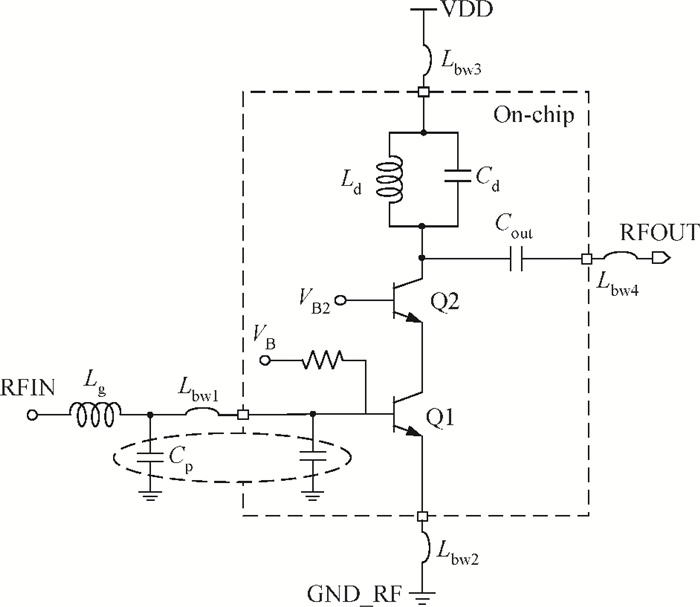
A high linearity 1.575 GHz SiGe:HBT low noise amplifier (LNA) for global positioning system applications is described. The bipolar cascoded with an MOSFET LNA was fabricated in a commercial 0.18 μm SiGe BiCMOS process. A resistor bias feed circuit with a feedback resistor was designed for the LNA input transistor to improve its intermodulation and compression performance. The packaged chip tested on board has displayed a noise figure of 1.11 dB, a power gain of 18 dB, an output 1 dB compression point of +7.8 dBm and an input third-order intercept point of +1.8 dBm. The chip occupies a 500×560 μm2 area and consumes 3.6 mA from a 2.85 V power supply.-
Keywords:
- LNA,
- noise figure,
- high linearity,
- OP1dB,
- ⅡP3,
- SiGe HBT
-
References
[1] Agarwal A, Chandel G S, Biswas A. A 1.575 GHz BiCMOS GPS low noise amplifier for low power application. Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems, 2004:179 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1398197[2] Poh J C H, Cheng P, Thrivikraman T K, et al. High gain, high linearity, L-band SiGe low noise amplifier with fully-integrated matching network. Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems (SiRF), 2010:69 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5422953/[3] Liang Q Q, Niu G F, Cressler J D, et al. Geometry and bias current optimization for SiGe HBT cascode low-noise amplifiers. IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, 2002, 1:517 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/abstractKeywords.jsp?arnumber=1012078[4] Sivonen P, Kangasmaa S, Parssinen A. Analysis of packaging effects and optimization in inductively degenerated common-emitter low-noise amplifiers. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2003, 51(4):1220 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2003.809633[5] Ma P X, Racanelli M, Zheng J, et al. A novel bipolar-MOSFET low-noise amplifier (BiFET LNA), circuit configuration, design methodology, and chip implementation. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2003, 51(11):2175 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2003.818581[6] Ko J S, Kim H S, Ko B K, et al. Effect of bias scheme on intermodulation distortion and its use for the design of PCS Tx driver. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium, 2000:105 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=854427[7] Taniguchi E, Ikushima T, Itoh K, et al. A dual bias-feed circuit design for SiGe HBT low-noise linear amplifier. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2003, 51(2):414 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2002.807835[8] Leitner T. A high linearity LNA with modified resistor biasing. Asia Pacific Microwave Conference, 2009:160 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5384407/[9] Zhou Renjie, Xiang Yong, Wang Hong, et al. A sub-1-dB noise figure monolithic GNSS LNA. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(9):095010 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095010[10] Kang B, Yu J, Shin H, et al. Design and analysis of a cascode bipolar low-noise amplifier with capacitive shunt feedback under power-constraint. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2011, 59(6):1539 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2136355[11] Im D. A +9 dBm output P1dB active feedback CMOS wideband LNA for SAW-less receivers. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ:Express Briefs, 2013, 60(7):377 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2013.2261174 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: