| Citation: |
Youtao Zhang, Xiaopeng Li, Min Zhang, Wei Cheng, Xinyu Chen. A 83 GHz InP DHBT static frequency divider[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(4): 045004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/045004
****
Y T Zhang, X P Li, M Zhang, W Cheng, X Y Chen. A 83 GHz InP DHBT static frequency divider[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(4): 045004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/045004.
|
-
Abstract
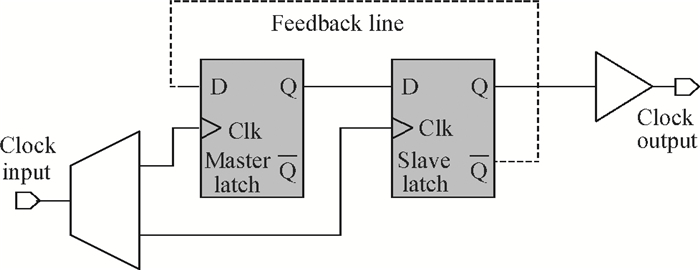
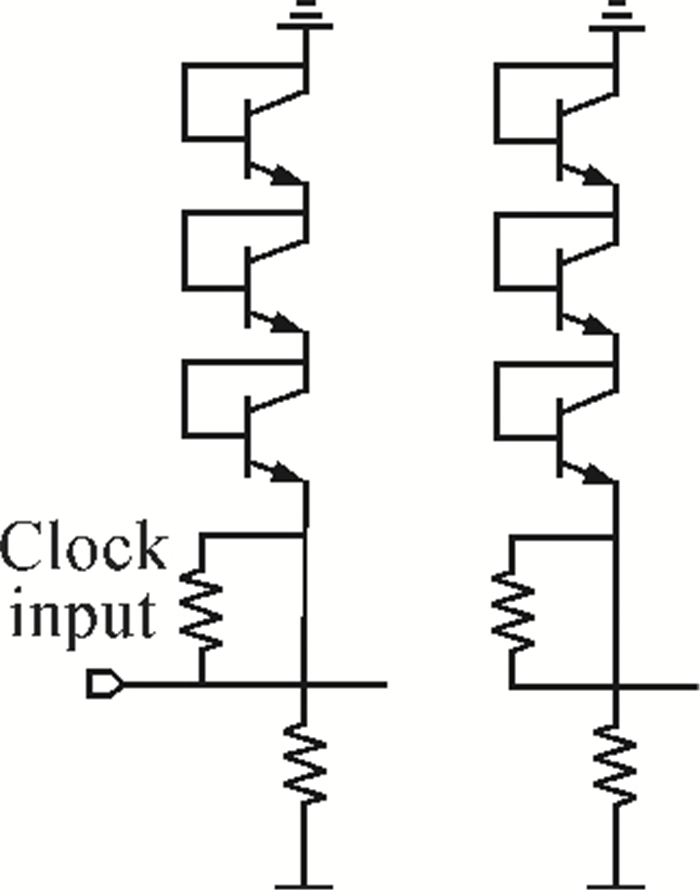
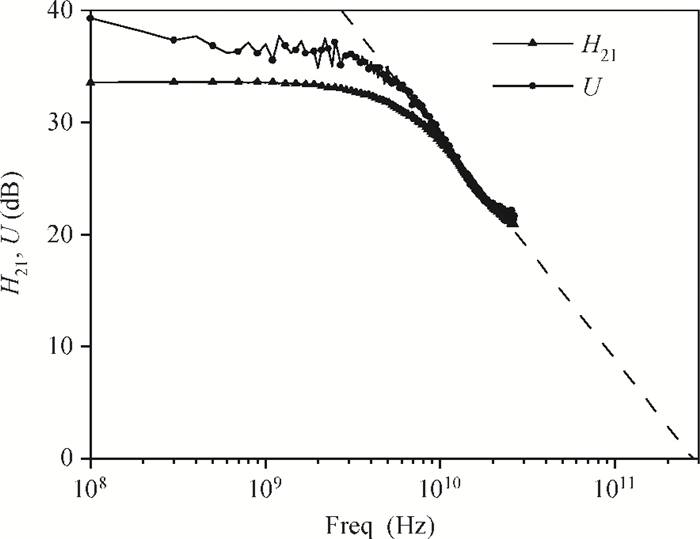
A static frequency divider is presented using 0.7 μm InP DHBTs with 280 GHz 1ft/fmax. The divider is based on ECL master-slave D-flip-flop topology with 30 HBTs and 20 resistors with a chip size 0.62×0.65 mm2. The circuits use peaking inductance as a part of the loads to maximize the highest clock rate. Momentum simulation is used to accurately characterize the effect of the clock feedback lines at the W band. Test results show that the divider can operate from 1 GHz up to 83 GHz. Its phase noise is 139 dBc/Hz with 100 kHz offset. The power dissipation of divider core is 350 mW.-
Keywords:
- high-speed,
- static frequency divider,
- InP DHBT
-
References
[1] Trotta S, Knapp H, Meister T, et al. 110-GHz, static frequency divider in SiGe bipolar technology. IEEE Compound Semiconductor IC Symposium, 2005:291 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1576599[2] Urteaga M, Pierson R, Rowell P, et al. Advanced InP DHBT process for high speed LSI circuits. IEEE Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2008:1 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4703058/[3] Monier C, Scott D, D'Amore M, et al. High-speed InP HBT technology for advanced mixed signal and digital applications. IEEE IEDM Digest, 2007:671 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4419033[4] D'Amore M, Monier C, Lin S, et al. A 0.25μm InP DHBT 200 GHz+static frequency divider. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(10):1992 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2058171[5] He G, Howard J, Le M, et al. Self-aligned InP DHBT with ft and fmax over 300 GHz in a new manufacturable technology. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2004, 25(8):520 doi: 10.1109/LED.2004.832528[6] Griffith Z, Urteaga M, Pieraon R, et al. A 204.8 GHz static divide-by-8 frequency divider in 250 nm InP HBT. IEEE Symposium on Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuits. 2010:1 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5619684&searchWithin%3Dp_Authors%3A.QT.Rodwell%2C+M.+J.+W..QT.[7] Zhao Yan, Cheng Wei, Wang Yuan, et al. A submicron InGaAs/InP double heterojunction bipolar transistor with ft and fmax of 280 GHz. International Conference on Precision Mechanical Instruments and Measurement Technology, 2013:3665 http://www.scientific.net/AMM.347-350.1673[8] Su Yongbo, Jin Zhi, Cheng Wei, et al. An InGaAs/InP 40 GHz CML static frequency divider. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(3):035008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/3/035008 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: