| Citation: |
Linxi Dong, Quan Yu, Jinyan Bao, Jiaping Tao. Analysis of reliability factors of MEMS disk resonator under the strong inertial impact[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(7): 074014. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/074014
****
L X Dong, Q Yu, J Y Bao, J P Tao. Analysis of reliability factors of MEMS disk resonator under the strong inertial impact[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(7): 074014. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/074014.
|
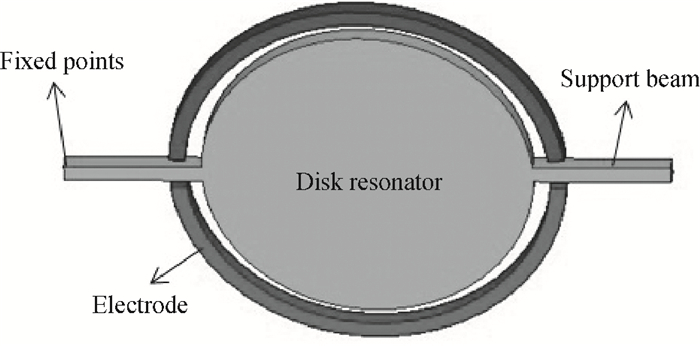
Analysis of reliability factors of MEMS disk resonator under the strong inertial impact
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/074014
More Information
-
Abstract
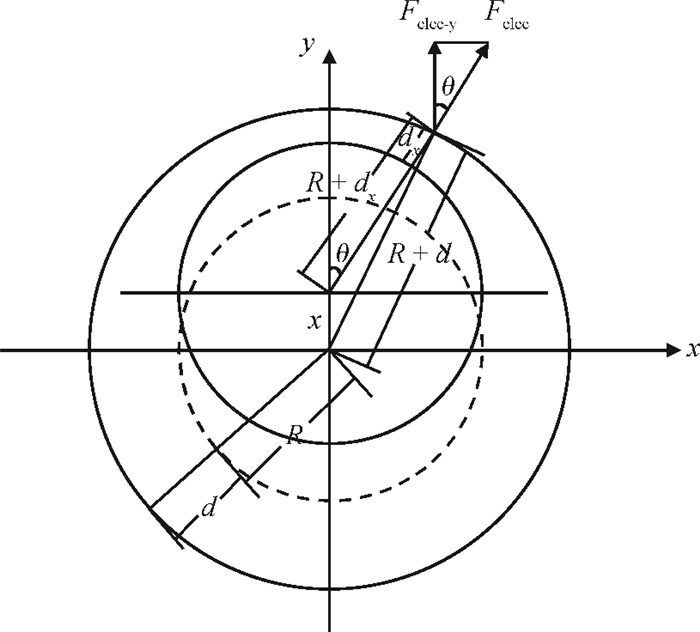
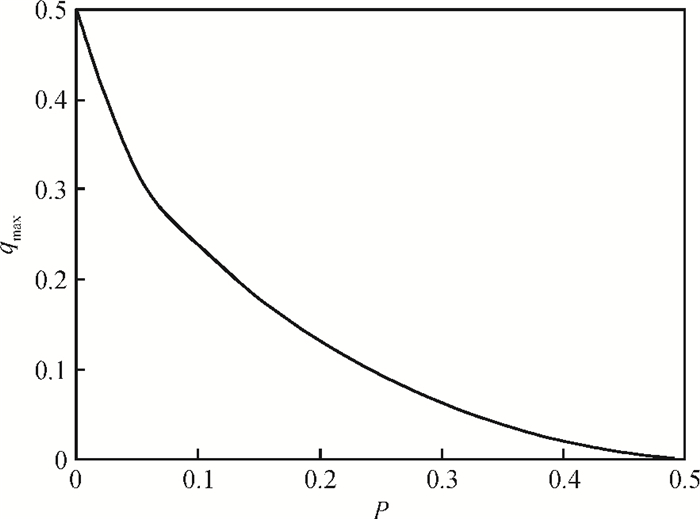
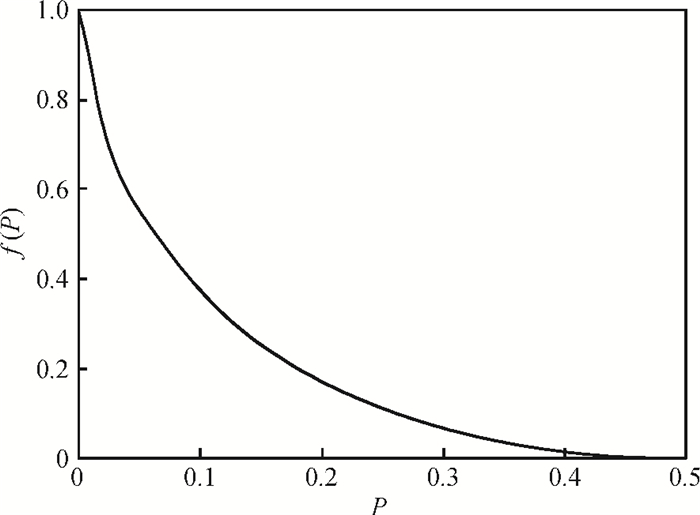
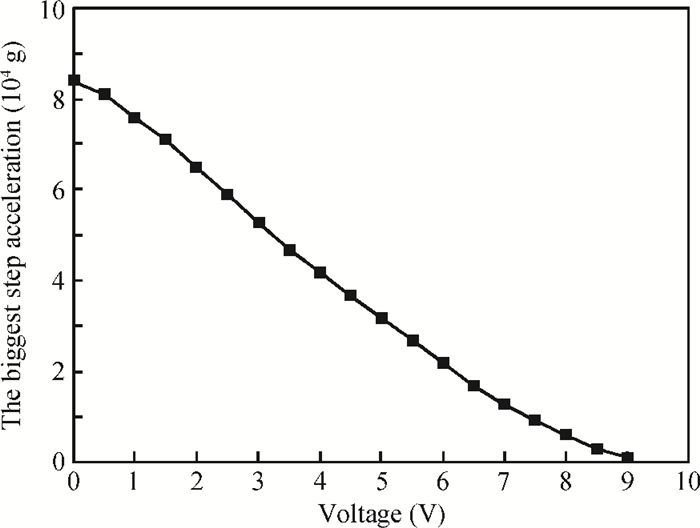
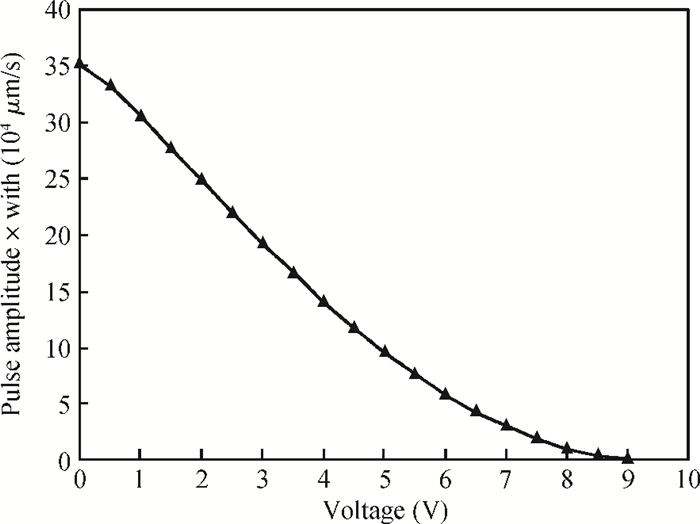
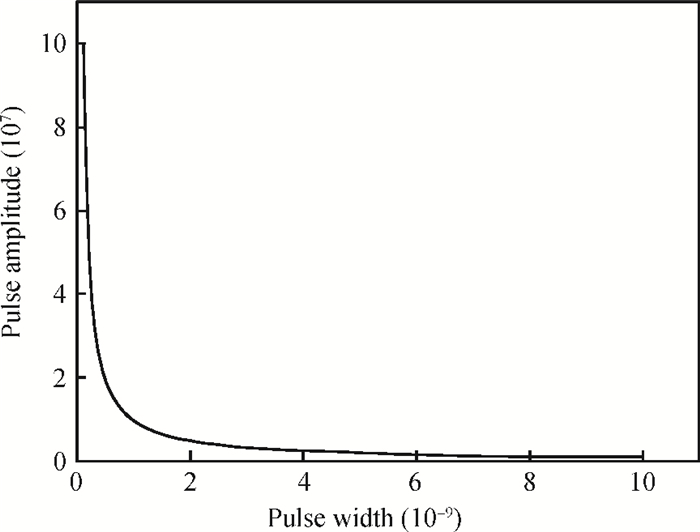
Increasing the bias voltage is a method of reducing the motional resistance of the capacitive disk resonator to match the impedance of the RF circuit. But there are few reports on the study of reliable working range of bias voltage under the shock and vibration environment. Therefore, the reliability of disk resonator under the step and pulse acceleration impact respectively is systematically analyzed in this paper. By the expression of the biggest inertial acceleration the disk can bear under the reliable condition, the maximal reliable range curves of the disk resonator under the dynamic impact environment are obtained. According to the actual sizes of disk in the literature, it can be seen that when a step shock of 13000 g is supplied, the reliability range is reduced to 75% compared with the original state. For the pulse shock, the reliability range is related to the pulse amplitude and time width. Research of this paper can provide the basis for the selection of bias voltage of disk resonator under the inertial shock.-
Keywords:
- MEMS resonator,
- inertial impact,
- bias voltage,
- reliability
-
References
[1] Nguyen C T C. MEMS technologies for communications. Nanotechnology Conference and Trade Show (Nanotech 2003), 2003: 723[2] Li Yingliang, Pan Wu. MEMS resonators and filters in RF system. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2004, 12(1): 47[3] Li Li, Zhao Zhengping, Zhang Zhiguo. Development of a MEMS-based RF low-phase -noise voltage controlled oscillator. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2006, 27(5): 900[4] Jia Yingxi, Zhao Zhengping, Yang Yongjun. SOI-based radial-contour-mode micromechanical disk resonator. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(11): 115001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/11/115001[5] Gu Hongming, Lü Miao, Liang Chunguang. MEMS class E amplifier. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2003, 24(4): 401 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-BDTX200304013.htm[6] Akgul M, Nguyen C T C. Voltage-controlled tuning to optimize MEMS resonator array-composite output power. Frequency Control and the European Frequency and Time Forum (FCS), 2011: 1[7] Demirci M U, Nguyen C T C. Mechanically corner-coupled square microresonator array for reduced series motional resistance. J Microelectromechan Syst, 2006: 1419 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/home.jsp[8] Dong Linxi, Sun Lingling, Xu Xiaoliang. Effect of inertial shock on RF MEMS capacitive switches property in low vacuum. Journal of Semiconductors, 2007, 28(4): 507 http://www.jos.ac.cn/bdtxbcn/ch/reader/view_abstract_new.aspx?volume=28&start_page=507[9] Clark J R, Hsu W T, Abdelmoneum M A, et al. High-Q UHF micromechanical radial-contour mode disk resonators. J Microelectromechan Syst, 2005, 14(6): 1298 doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2005.856675[10] Naing T L, Rocheleau T O, Ren Z. Vibration-insensitive 61-MHz micromechanical disk reference oscillator. IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (FCS), 2012: 1 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6243738/?arnumber=6243738&punumber%3D6238031[11] Dong Yonggui, Zhang Qi. Double parameter detection method of resonant sensor pulse. Journal of Tsinghua University, 2009, (5): 6603 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0263224110002629[12] Alsaleem F M, Younis M I, Ouakad H M. On the nonlinear resonances and dynamic pull-in of electrostatically actuated resonators. J Micromechan Microeng, 2009, 19(4): 045013 doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/19/4/045013[13] Wang Binglei, Zhou Shenjie, Zhao Junfeng. The size effect research of MEMS microstructure under electrostatic excitation. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2011, 32(6): 541[14] Dong Qiaohua, Liao Xiaoping, Huang Qingan. Analysis of pull-in voltage of RF MEMS switches. Journal of Semiconductors, 2008, 29(1): 163 http://www.jos.ac.cn/bdtxbcn/ch/reader/view_abstract_new.aspx?volume=29&start_page=163[15] Xu Lin, Fang Yuming, Xi Junjian. The dynamic pull-in phenomenon in parallel-plate electrostatic microactuator. Semicond Technol, 2012, 37(3): 176[16] Bao Minhang, Sun Yuancheng, Sun Yiping. Reliable operation conditions of capacitive inertial sensor for step and shock signals. The Eighth Sensitive Element and Sensor Academic Conference Proceedings, 2003: 112 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924424704001578[17] Bao Minhang. Analysis and design principles of MEMS devices. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005: 44 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA73467762[18] Yang Lin, Wei Changli. Enhancement of micromechanical resonator manufacturing precision via mechanically-coupled arraying. Joint Meeting of the European Frequency and Time Forum and the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFCS 2009), 2009: 58 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5168142/[19] Li Shengshian, Lin Yuwei, Ren Zeying. An MSI micromechanical differential disk-array filter. Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, 2007: 307 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4300130/?reload=true&arnumber=4300130&filter%3DAND(p_IS_Number:4300056)[20] Li Shengshian, Lin Yuwei, Ren Zeying. A micromechanical parallel-class disk-array filter. Frequency Control Symposium, Joint with the 21st European Frequency and Time Forum, 2007: 1356 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/home.jsp[21] Lin Y, Lee S, Li S. Series-resonant VHF micromechanical resonator reference oscillators. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(12): 2477 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.837086 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: