| Citation: |
Shangqing Ren, Bo Tang, Hao Xu, Weichun Luo, Zhaoyun Tang, Yefeng Xu, Jing Xu, Dahai Wang, Junfeng Li, Jiang Yan, Chao Zhao, Dapeng Chen, Tianchun Ye, Wenwu Wang. Characterization of positive bias temperature instability of NMOSFET with high-k/metal gate last process[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(1): 014007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/1/014007
****
S Q Ren, B Tang, H Xu, W C Luo, Z Y Tang, Y F Xu, J Xu, D H Wang, J F Li, J Yan, C Zhao, D P Chen, T C Ye, W W Wang. Characterization of positive bias temperature instability of NMOSFET with high-k/metal gate last process[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(1): 014007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/1/014007.
|
Characterization of positive bias temperature instability of NMOSFET with high-k/metal gate last process
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/1/014007
More Information
-
Abstract
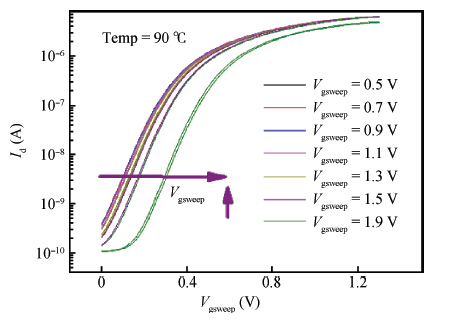
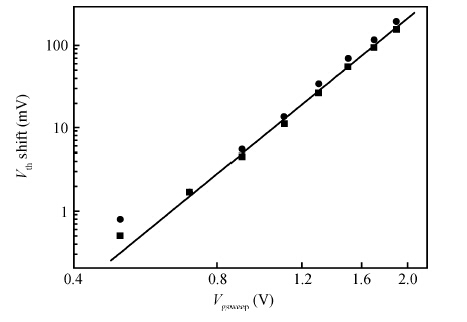
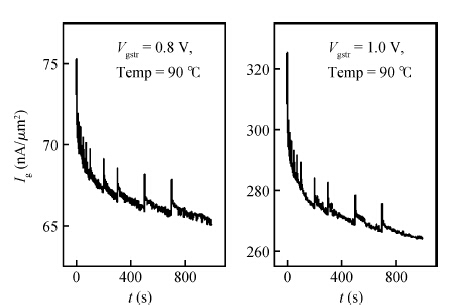
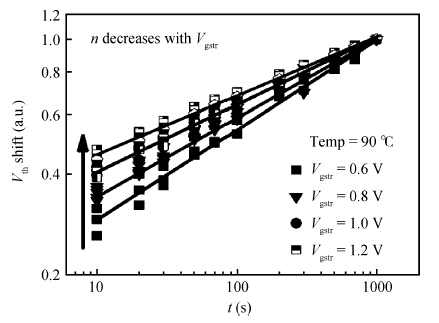
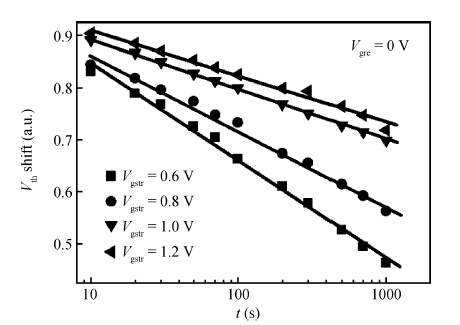
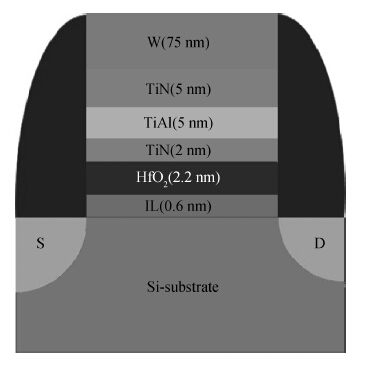
Positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) characteristics and degradation mechanisms of NMOSFET with high-k/metal gate last process have been systematically investigated. The time evolution of threshold voltage shift during PBTI stress still follows a power law. However, the exponent n decreases from 0.26 to 0.16 linearly as the gate stress voltage increases from 0.6 to 1.2 V. There is no interface state generation during stress because of the negligible sub-threshold swing change. Moreover, the activation energy is 0.1 eV, which implies that electrons directly tunnel into high-k bulk and are trapped by pre-existing traps resulting into PBTI degradation. During recovery the threshold voltage shift is linear in lgt, and a mathematical model is proposed to express threshold voltage shift. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: