| Citation: |
Xinhai Yu, Changchun Chai, Liping Qiao, Yintang Yang, Yang Liu, Xiaowen Xi. Modeling and analysis of the HPM pulse-width upset effect on CMOS inverter[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(5): 054011. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/5/054011
****
X H Yu, C C Chai, L P Qiao, Y T Yang, Y Liu, X W Xi. Modeling and analysis of the HPM pulse-width upset effect on CMOS inverter[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(5): 054011. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/5/054011.
|
Modeling and analysis of the HPM pulse-width upset effect on CMOS inverter
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/5/054011
More Information
-
Abstract
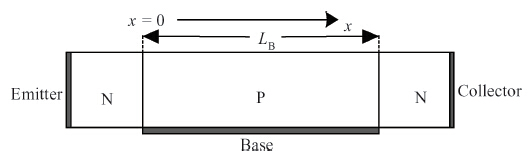
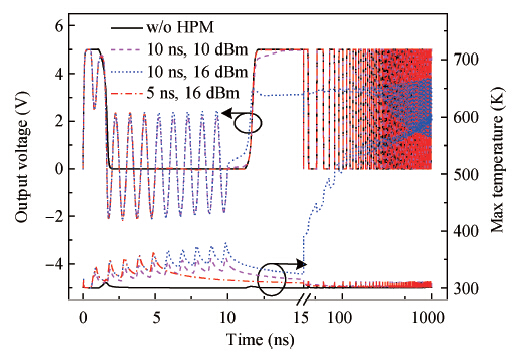
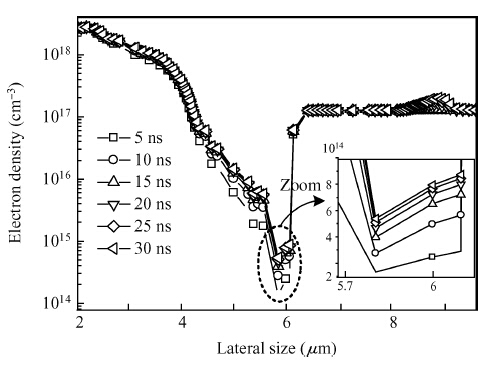
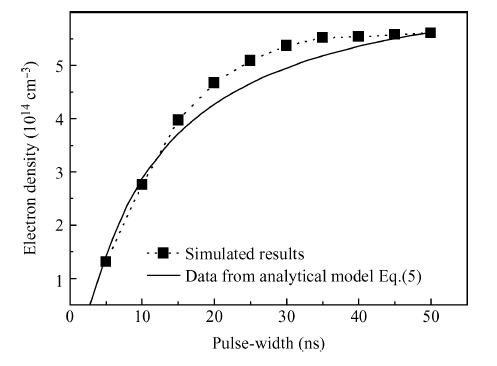
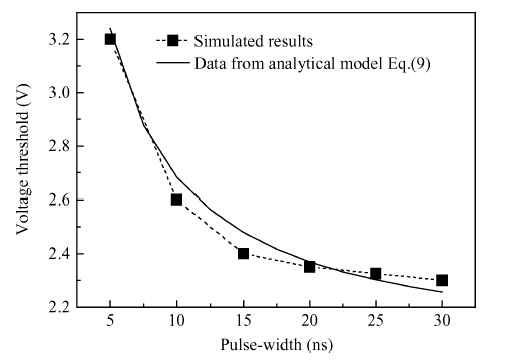
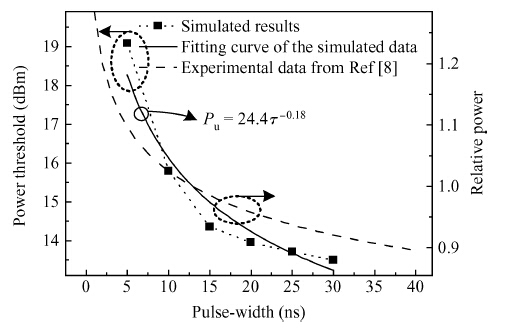
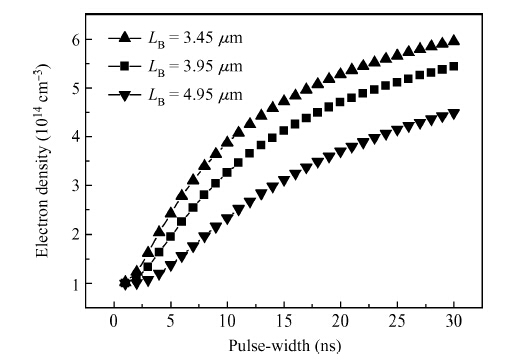
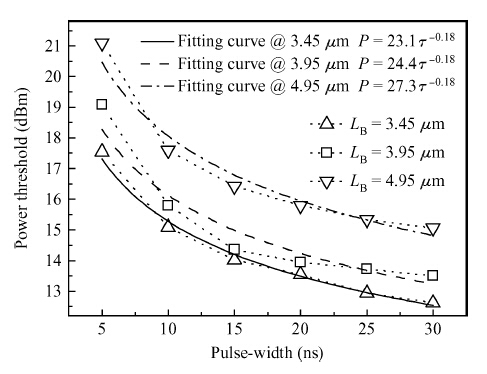
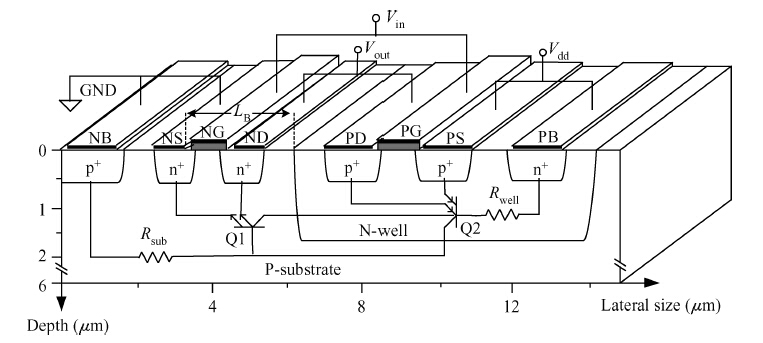
We derive analytical models of the excess carrier density distribution and the HPM (high-power microwave) upset susceptibility with dependence of pulse-width, which are validated by the simulated results and experimental data. Mechanism analysis and model derivation verify that the excess carriers dominate the current amplification process of the latch-up. Our results reveal that the excess carrier density distribution in P-substrate behaves as pulse-width dependence. The HPM upset voltage threshold Vp decreases with the incremental pulse-width, while there is an inflection point which is caused because the excess carrier accumulation in the P-substrate will be suppressed over time. For the first time, the physical essence of the HPM pulse-width upset effect is proposed to be the excess carrier accumulation effect. Validation concludes that the Vp model is capable of giving a reliable and accurate prediction to the HPM upset susceptibility of a CMOS inverter, which simultaneously considers technology information, ambient temperature, and layout parameters. From the model, the layout parameter LB has been demonstrated to have a significant impact on the pulse-width upset effect: a CMOS inverter with minor LB is more susceptible to HPM, which enables us to put forward hardening measures for inverters that are immune from the HPM upset. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: