| Citation: |
Haiyang Zhao, Lei Zhang, Sizhu Shao, Jianfeng Ding, Xin Fu, Lin Yang. Multistage second-order microring-resonator filters with box-like spectral responses and relaxed fabrication tolerances[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(11): 114009. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/11/114009
****
H Y Zhao, L Zhang, S Z Shao, J F Ding, X Fu, L Yang. Multistage second-order microring-resonator filters with box-like spectral responses and relaxed fabrication tolerances[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(11): 114009. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/11/114009.
|
Multistage second-order microring-resonator filters with box-like spectral responses and relaxed fabrication tolerances
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/11/114009
More Information
-
Abstract
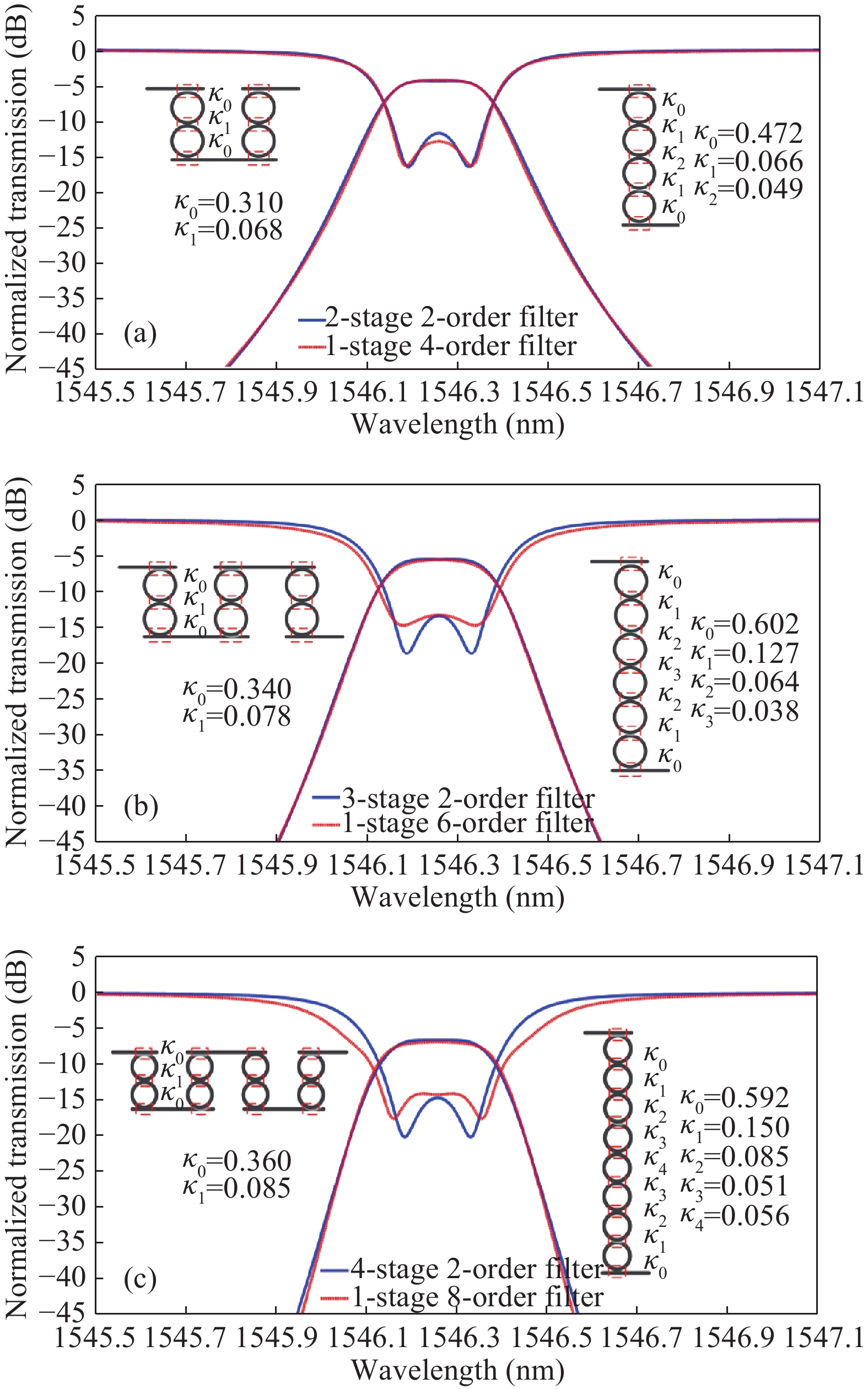
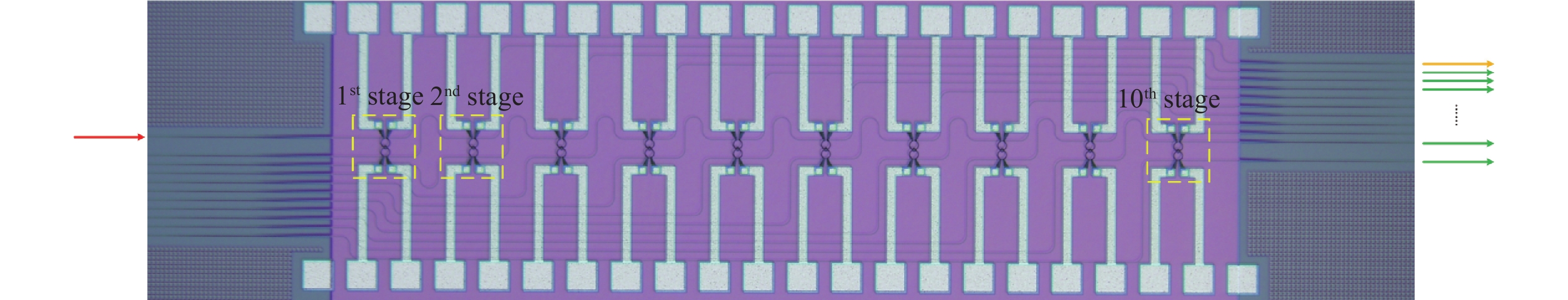
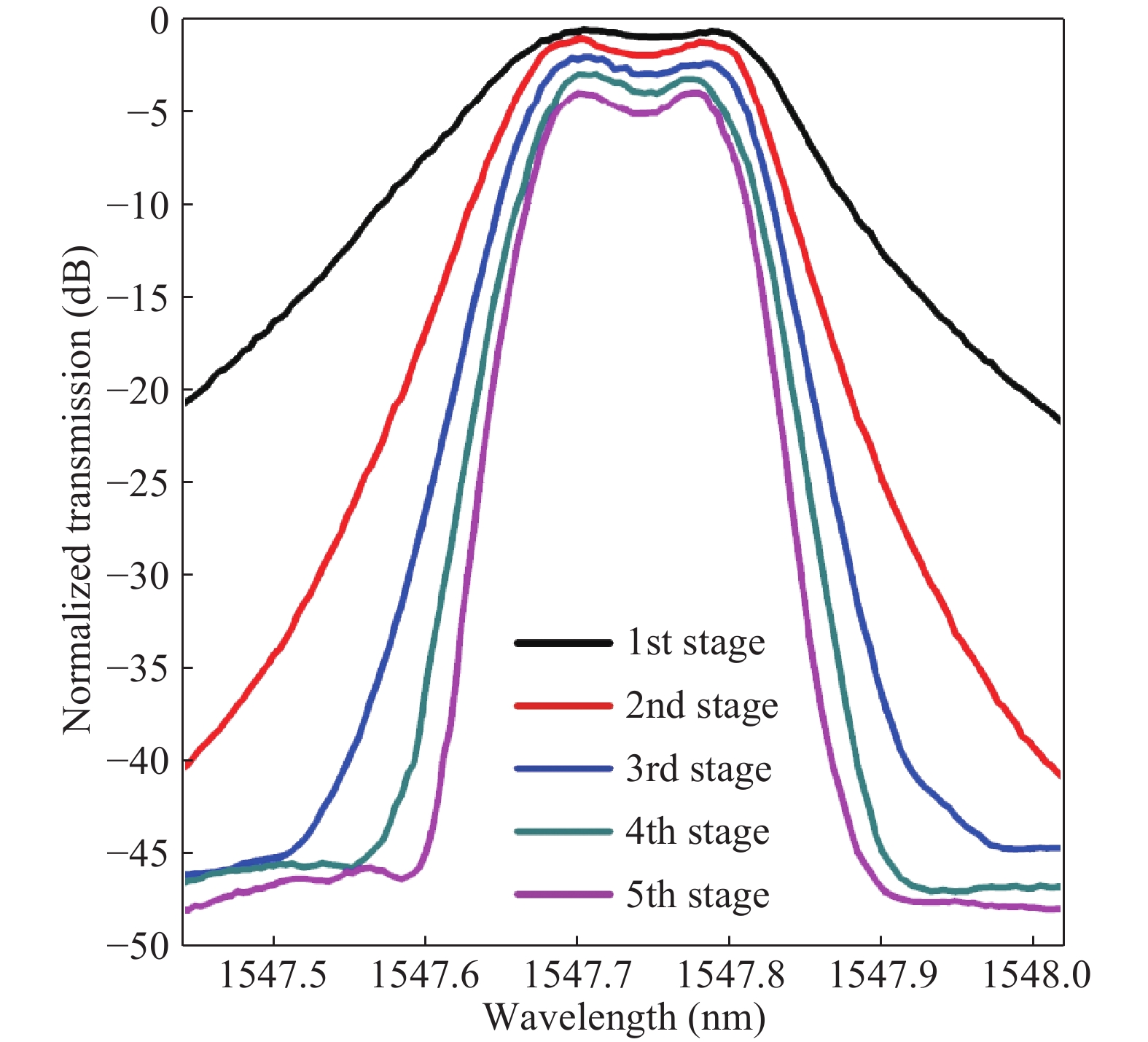
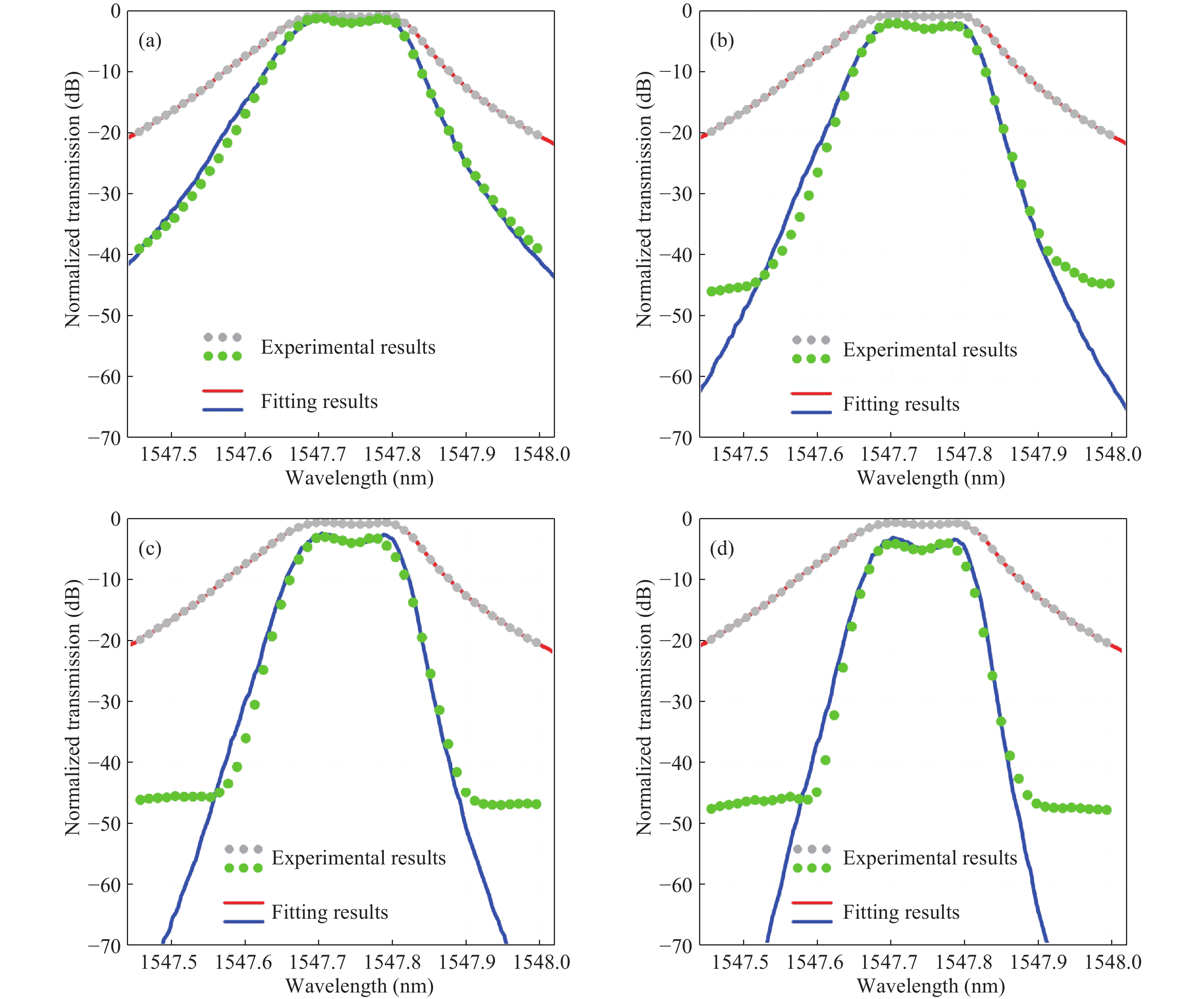
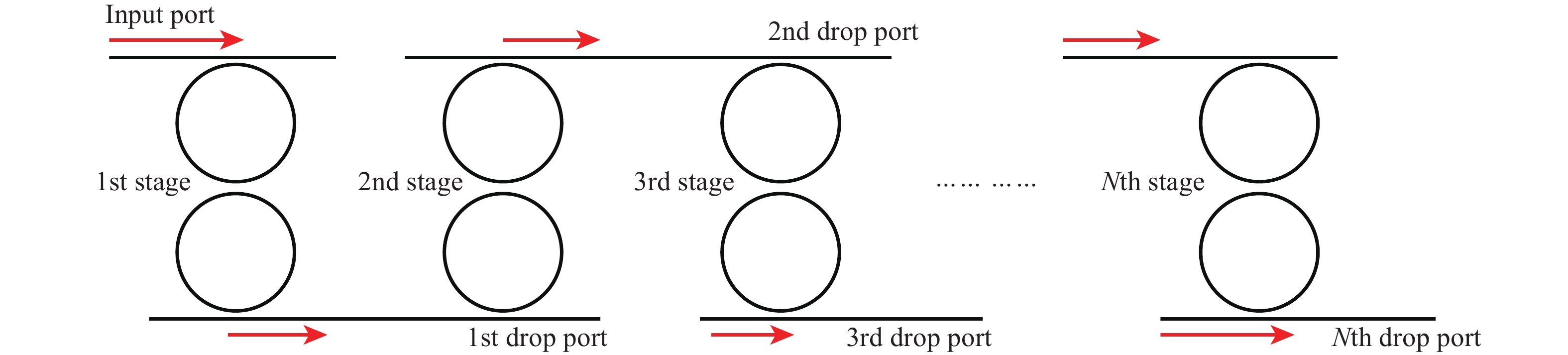
We demonstrate an optical filter based on multistage second-order microring resonators (MRs) with box-like spectral responses. Compared with single-stage high-order optical filters with the same number of MRs, the demonstrated structure has comparable performances in the aspects of passband flatness, rolling-off slope and insertion loss. Moreover, the architecture relaxes the fabrication tolerance, electrical wiring and tuning difficulty since there are only two MRs in each stage. We experimentally demonstrate this kind of optical filter with five stages, which shows a 3-dB bandwidth of ~17 GHz, a rolling-off slope of ~5 dB/GHz and an on-chip insertion loss of ~6 dB. -
References
[1] Park S J, Lee C H, Jeong K T, et al. Fiber-to-the-home services based on wavelength-division-multiplexing passive optical network. J Lightw Technol, 2004, 22(11): 2582 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2004.834504[2] Luo Y Q, Zhou X P, Effenberger F, et al. Time- and wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network (TWDM-PON) for next-generation PON stage 2 (NG-PON2). J Lightw Technol, 2013, 31(4): 587 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2012.2215841[3] Brackett C A. Dense wavelength division multiplexing networks: principles and applications. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 1990, 8(6): 948 doi: 10.1109/49.57798[4] Kuznetsov M. Cascaded coupler Mach-Zehnder channel dropping filters for wavelength-division-multiplexed optical systems. J Lightw Technol, 1994, 12(2): 226 doi: 10.1109/50.350600[5] Kewitsch A S, Rakuljic G A, Willems P A, et al. All-fiber zero-insertion-loss add–drop filter for wavelength-division multiplexing. Opt Lett, 1998, 23(2): 106 doi: 10.1364/OL.23.000106[6] Sadot D, Boimovich E. Tunable optical filters for dense WDM networks. IEEE Commun Mag, 1998, 36(12): 50 doi: 10.1109/35.735877[7] Grover R, Van V, Ibrahim T A, et al. Parallel-cascaded semiconductor microring resonators for high-order and wide-FSR filters. J Lightw Technol, 2002, 20(5): 872[8] Melloni A, Costa R, Monguzzi P, et al. Ring-resonator filters in silicon oxynitride technology for dense wavelength-division multiplexing systems. Opt Lett, 2003, 28(17): 1567 doi: 10.1364/OL.28.001567[9] Little B E, Chu S T, Haus H A, et al. Microring resonator channel dropping filters. J Lightw Technol, 1997, 15(6): 872[10] Hryniewicz J V, Absil P P, Little B E, et al. Higher order filter response in coupled microring resonators. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2000, 12(3): 320 doi: 10.1109/68.826927[11] Popovic M A, Barwicz T, Watts M R, et al. Multistage high-order microring-resonator add–drop filters. Opt Lett, 2006, 31(17): 2571 doi: 10.1364/OL.31.002571[12] Xia F N, Rooks M, Sekaric L, et al. Ultra-compact high order ring resonator filters using submicron silicon photonic wires for onchip optical interconnects. Opt Express, 2007, 15(19): 11934 doi: 10.1364/OE.15.011934[13] Chen L, Sherwood-Droz N, Lipson M. Compact bandwidth-tunable microring resonators. Opt Lett, 2007, 32(22): 3361 doi: 10.1364/OL.32.003361[14] Ong J R, Kumar R, Mookherjea S. Ultra-high-contrast and tunable-bandwidth filter using cascaded high-order silicon microring filters. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2013, 25(16): 320[15] Headley W R, Reed G T, Howe S. Polarization-independent optical racetrack resonators using rib waveguides on silicon-on-insulator. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85(23): 5523 doi: 10.1063/1.1827337[16] Chen P X, Chen S T, Guan X W, et al. High-order microring resonators with bent couplers for a box-like filter response. Opt Lett, 2014, 39(21): 6304 doi: 10.1364/OL.39.006304[17] Zhang Z, Huang B J, Zhang Z Y, et al. Microwave photonic filter with reconfigurable and tunable bandpass response using integrated optical signal processor based on microring resonator. Opt Eng, 2013, 52(12): 127102 doi: 10.1117/1.OE.52.12.127102[18] Ding Y H, Pu M H, Liu L, et al. Bandwidth and wavelength-tunable optical bandpass filter based on silicon microring-MZI structure. Opt Express, 2011, 19(7): 6462 doi: 10.1364/OE.19.006462[19] Huang C J, Zuo Y H, Cheng B W, et al. Si-based thermal-optical resonant-cavity tunable filter. Chin J Semicond, 2003, 24(12): 1312[20] Hu T, Wang W J, Qiu C, et al. Thermally tunable filters based on third-order microring resonators for WDM applications. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2012, 24(6): 524 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2012.2182988[21] Wheeler J A. On the mathematical description of light nuclei by the method of resonating group structure. Phys Rev, 1937, 52(11): 1107 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.52.1107 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: