| Citation: |
Linfeng Wang, Qiao Meng, Hao Zhi, Fei Li. A 10 bit 200 MS/s pipeline ADC using loading-balanced architecture in 0.18 μm CMOS[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(7): 075003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/7/075003
****
L F Wang, Q Meng, H Zhi, F Li. A 10 bit 200 MS/s pipeline ADC using loading-balanced architecture in 0.18 μm CMOS[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(7): 075003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/7/075003.
|
A 10 bit 200 MS/s pipeline ADC using loading-balanced architecture in 0.18 μm CMOS
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/7/075003
More Information
-
Abstract
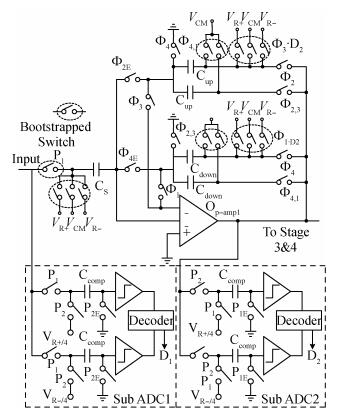
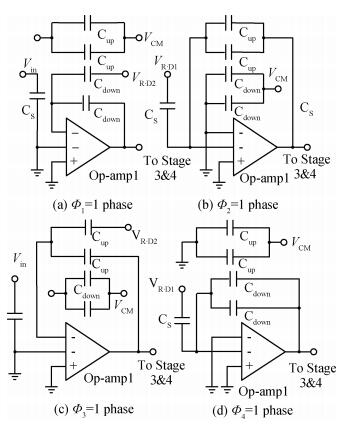
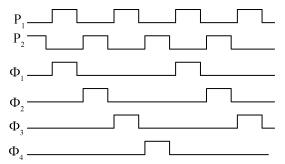
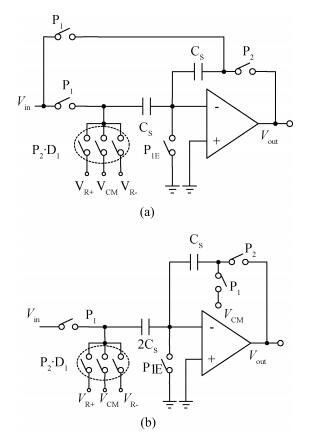
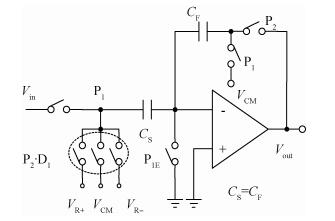
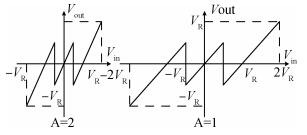
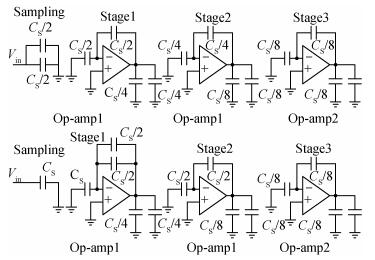
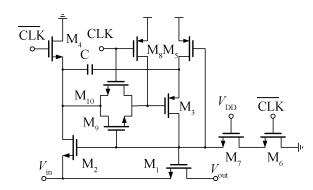
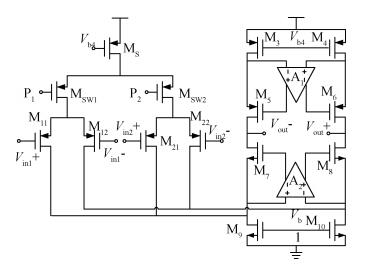
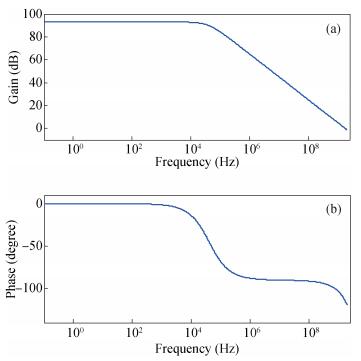
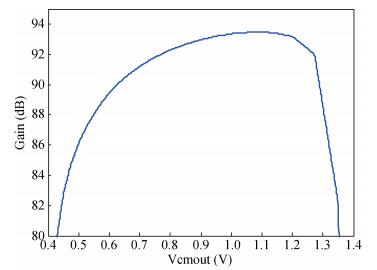
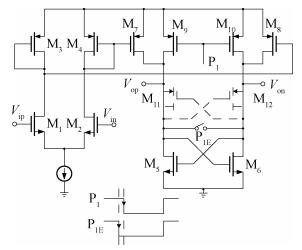
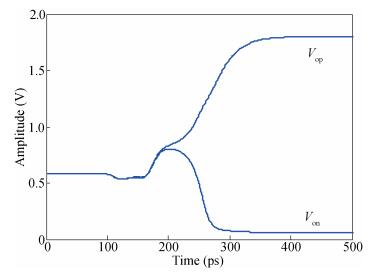
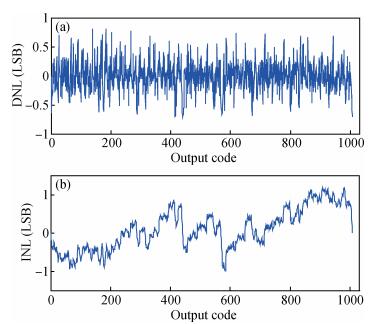
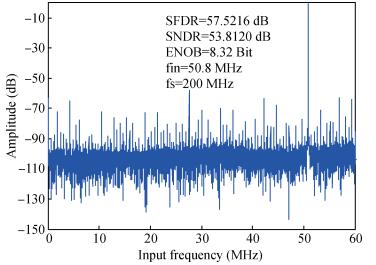
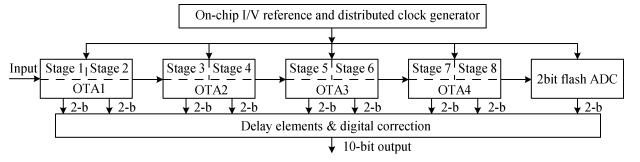
A new loading-balanced architecture for high speed and low power consumption pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is presented in this paper. The proposed ADC uses SHA-less, op-amp and capacitor-sharing technique, capacitor-scaling scheme to reduce the die area and power consumption. A new capacitor-sharing scheme was proposed to cancel the extra reset phase of the feedback capacitors. The non-standard inter-stage gain increases the feedback factor of the first stage and makes it equal to the second stage, by which, the load capacitor of op-amp shared by the first and second stages is balanced. As for the fourth stage, the capacitor and op-amp no longer scale down. From the system's point of view, all load capacitors of the shared OTAs are balanced by employing a loading-balanced architecture. The die area and power consumption are optimized maximally. The ADC is implemented in a 0.18 μm 1P6M CMOS technology, and occupies a die area of 1.2×1.2 mm2. The measurement results show a 55.58 dB signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio (SNDR) and 62.97 dB spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) with a 25 MHz input operating at a 200 MS/s sampling rate. The proposed ADC consumes 115 mW at 200 MS/s from a 1.8 V supply.-
Keywords:
- pipeline ADC,
- loading-balanced,
- op-amp sharing,
- SHA-Less,
- MDAC,
- scaling down
-
References
[1] Manish B, Chris B, Jeff W, et al. A 180 MS/s 162 Mb/s wideband three-channel baseband and MAC processor for 802.11a/b/g. IEEE Int Solid-State Circuits Conf, 2005, 24: 454 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1494065[2] Chi H L, Paul J, Stephen H, et al. A four-channel time-interleaved ADC with digital calibration of inter-channel timing and memory error. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2101, 45: 2091 http://www.oalib.com/references/7785716[3] John P K, Paul J H, Stephen H L, et al. Digital background calibration for memory effects in pipelined analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 2006, 53: 511 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2005.858760[4] Siddharth D, Larry S, Dan K, et al. A 16 b 125 MS/s 385 mW 78.8 dB SNR CMOS pipeline ADC. IEEE Int Solid-State Circuits Conf, 2009, 2: 86 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221117118_A_16b_125MSs_385mW_787dB_SNR_CMOS_pipeline_ADC[5] Wang X F, Zhang H, Zhang J, et al. A SHA-less 14 bit 100 MS/s pipelined ADC with comparator offset cancellation in background. J Semicond, 2016, 37(3): 035002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/3/035002[6] Hussein A, Marc S, Roger P, et al. Split ADC digital background calibration for high speed SHA-less pipeline ADCs. IEEE Int Sympos Circuits Syst (ISCAS), 2014: 1143 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271471758_Split_ADC_digital_background_calibration_for_high_speed_SHA-less_pipeline_ADCs[7] Ping L H, Wan P Y, Victor L, et al. SHA-less pipelined ADC converting 10th nyquist band with in-situ clock-skew calibration. Custom Integr Circuits Conf (CICC), 2010: 3 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224240943_SHA-Less_Pipelined_ADC_With_In_Situ_Background_Clock-Skew_Calibration[8] Dong Y C. Design techniques for a pipelined ADC without using a front-end sample-and-hold amplifier. IEEE Trans Circuit Syst, 2004, 51(11): 2123 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2004.836842[9] Chen H, He L, Deng H, et al. A high-performance bootstrap switch for low voltage switched-capacitor circuits. IEEE Int Sympos Integr Circuits (ISIC), 2014: 484 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286746382_A_high-performance_bootstrap_switch_for_low_voltage_switched-capacitor_circuits[10] Mehr I, Singer L. A 55 mW, 10-bit 40 Msample/s Nyquist-rate CMOS ADC. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2000, 35(3): 318 doi: 10.1109/4.826813[11] Gamauf C, Nemecek A, Promitzer G. Design and characterization of a 10 bit pipeline ADC for 100 MSps in 0.18 μ m CMOS. IEEE Int Conf VLSI Des, 2014: 1 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6946311/[12] Zhou J, Xu L L, Li F L, et al. A 10-bit 120-MS/s pipeline ADC with improved switch and layout scaling strategy. J Semicond, 2015, 36(8): 085008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/8/085008[13] Chang S S, Gil C A. A 10 bit 100 MS/s dual-channel pipelined ADC using dynamic memory effect cancellation technique. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 2011, 58(5): 274 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2011.2149130[14] Ji P L, Gabriele M, Matthew C, et al. A 10 b 170 MS/s pipelined ADC featuring 84 dB SFDR without calibration. IEEE Sympos VLSI Circuits, 2006 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224650262_A_10b_170MSs_CMOS_Pipelined_ADC_Featuring_84dB_SFDR_without_Calibration[15] Tomohiro N, Katsuhiko M, Junichiro A, et al. A 10 bit 200 MS/s pipeline A/D converter for high-speed video signal digitizer. IEEE Solid State Circuits Conf ASSCC, 2006: 31 https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.ieee-art-000004197583 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: