| Citation: |
Wei Luo, Tai Li, Yongde Li, Houjin Wang, Ye Yuan, Shangfeng Liu, Weiyun Wang, Qi Wang, Junjie Kang, Xinqiang Wang. Watts-level ultraviolet-C LED integrated light sources for efficient surface and air sterilization[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(7): 072301. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/7/072301
****
W Luo, T Li, Y D Li, H J Wang, Y Yuan, S F Liu, W Y Wang, Q Wang, J J Kang, X Q Wang. Watts-level ultraviolet-C LED integrated light sources for efficient surface and air sterilization[J]. J. Semicond, 2022, 43(7): 072301. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/7/072301
|
Watts-level ultraviolet-C LED integrated light sources for efficient surface and air sterilization
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/7/072301
More Information
-
Abstract
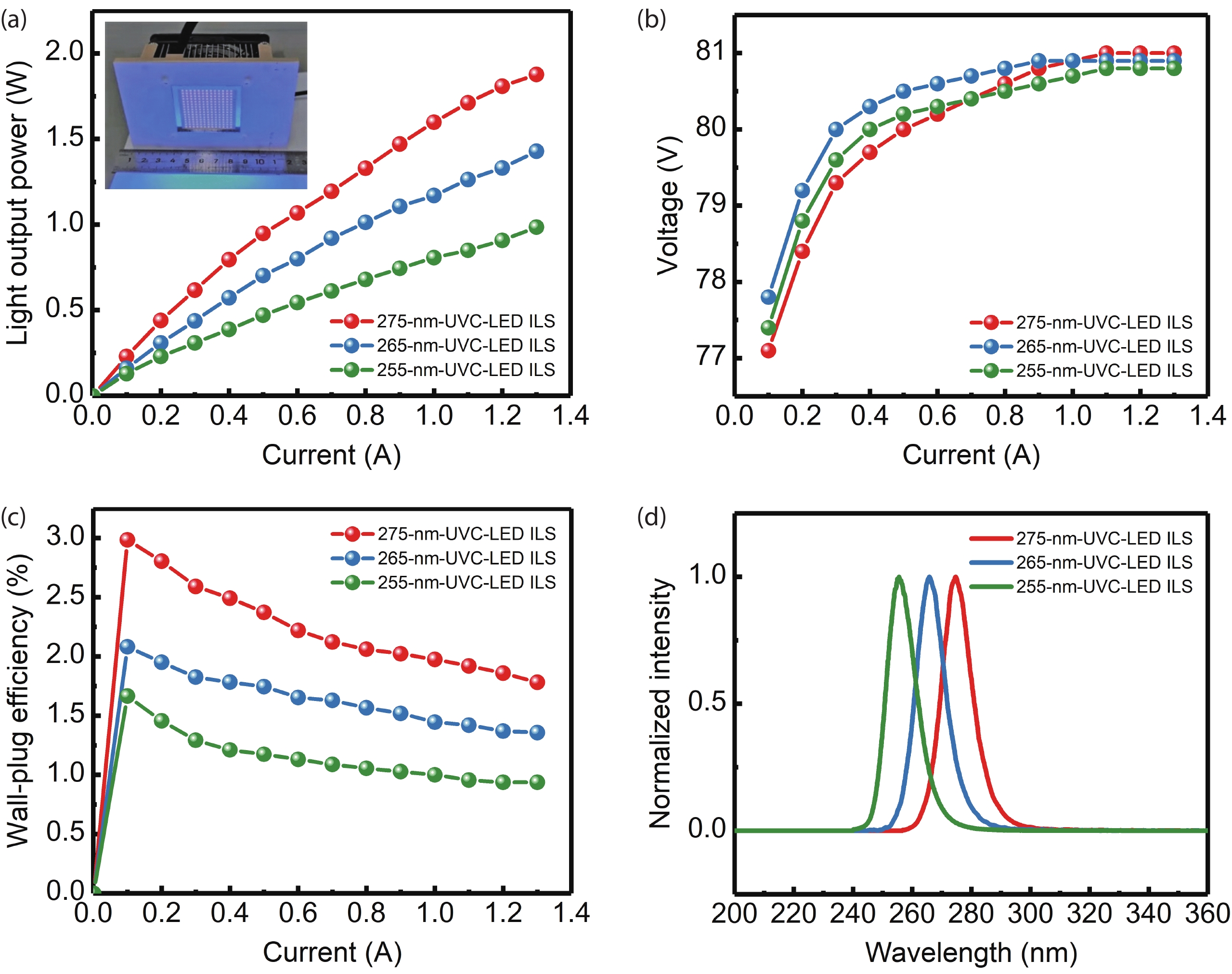
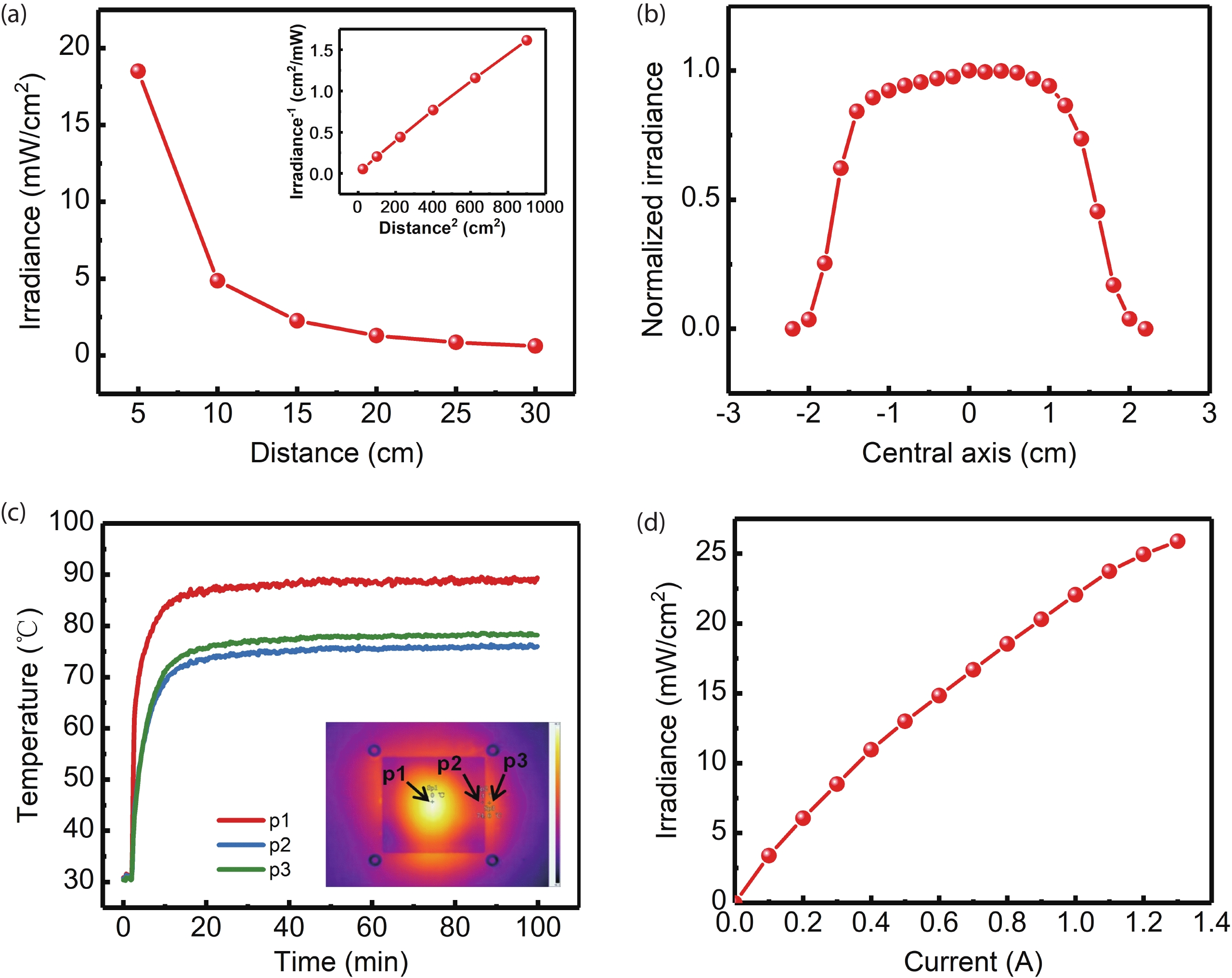
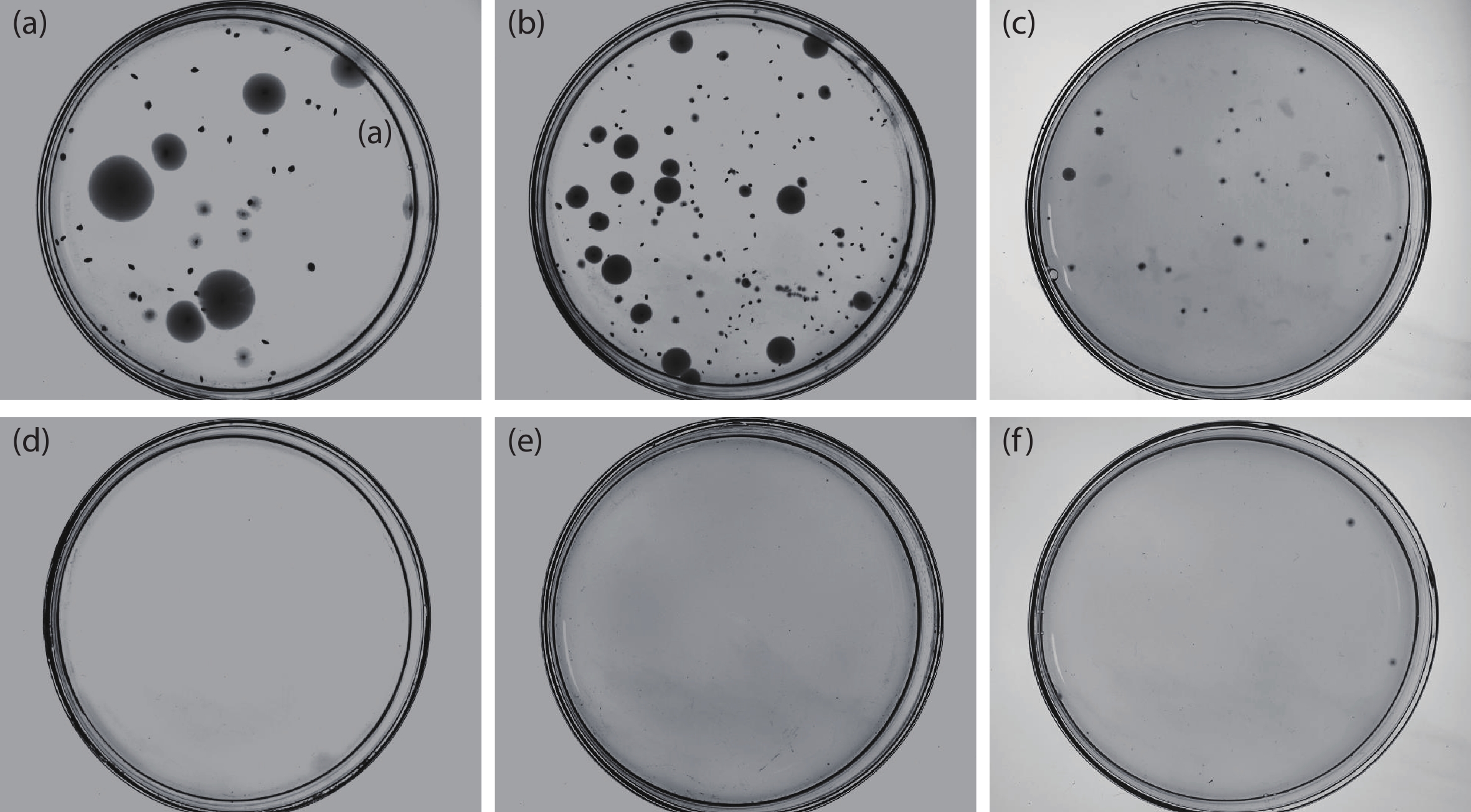
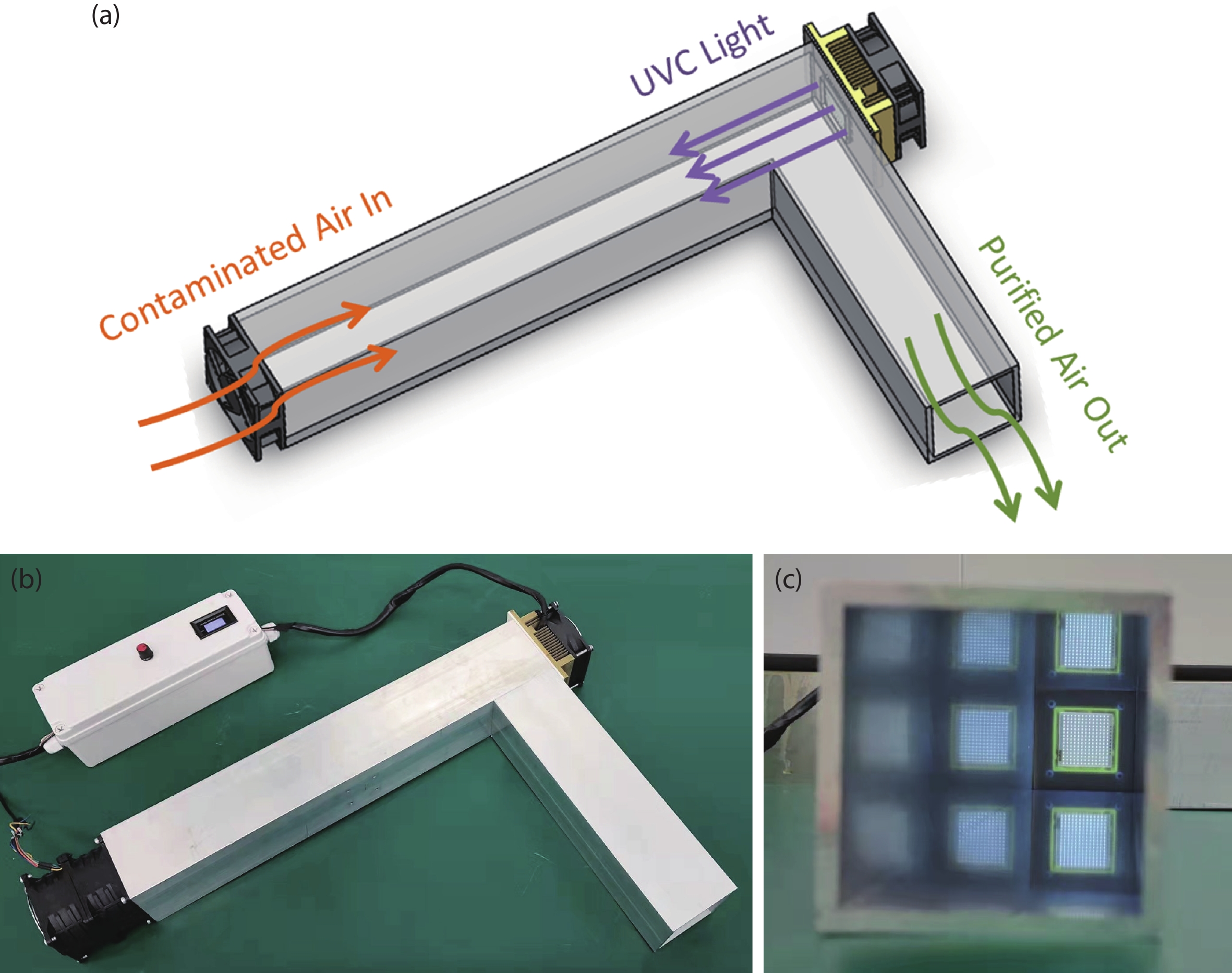
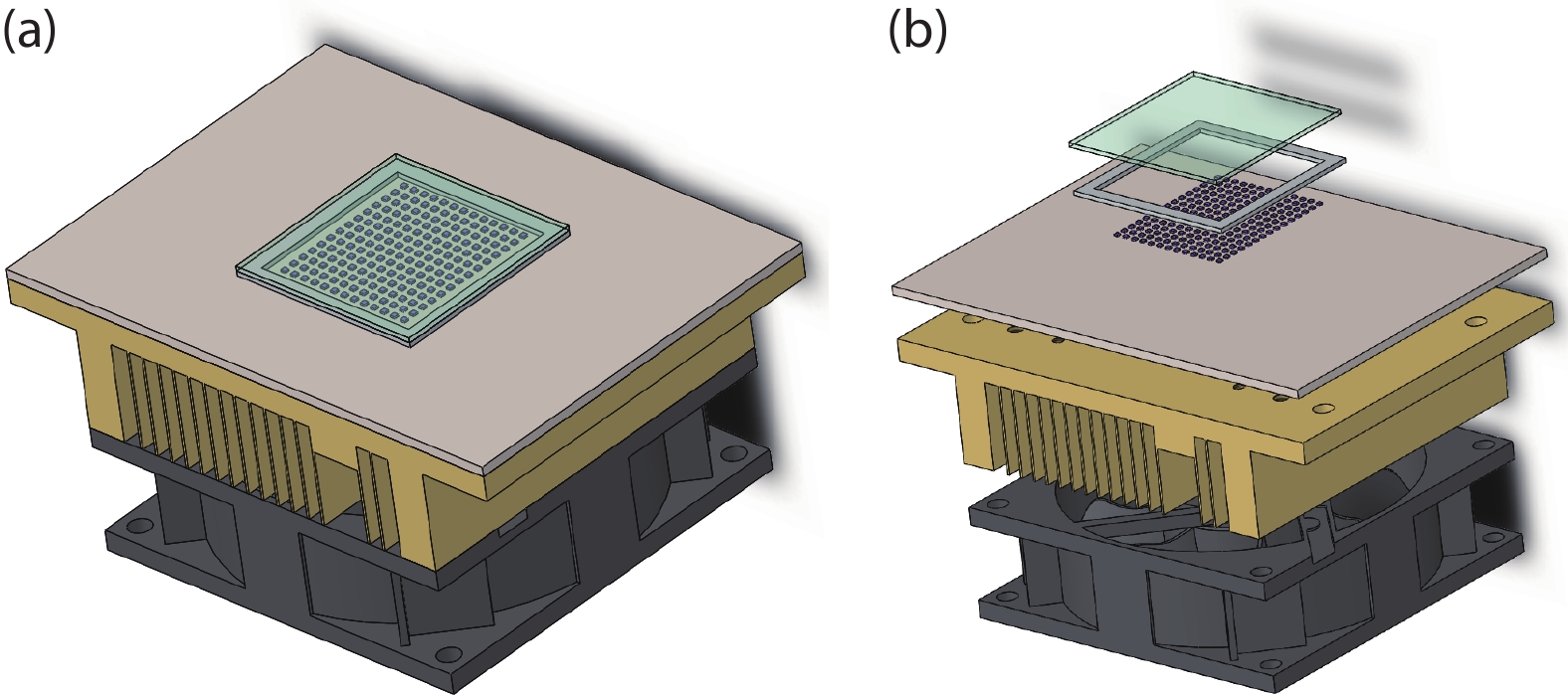
With the epidemic of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infection, AlGaN-based ultraviolet-C light emitting diodes (UVC-LEDs) have attracted widespread attention for their sterilization application. However, the sterilization characters of high power integrated light sources (ILSs) haven’t been widely investigated before utilizing in public sanitary security. In this work, by integrating up to 195 UVC-LED chips, high power UVC-LED ILSs with a light output power (LOP) of 1.88 W were demonstrated. The UVC-LED ILSs were verified to have efficient and rapid sterilization capability, which have achieved more than 99.9% inactivation rate of several common pathogenic microorganisms within 1 s. In addition, the corresponding air sterilization module based on them was also demonstrated to kill more than 97% of Staphylococcus albus in the air of 20 m3 confined room within 30 min. This work demonstrates excellent sterilization ability of UVC-LED ILSs with high LOP, revealing great potential of UVC-LEDs in sterilization applications in the future. -
References
[1] Abbasi R, Jain R, Nelson K, et al. Polymeric films containing sodium chlorite that release disinfectant gas upon activation with UV light. Adv Funct Mater, 2019, 29(7), 1804851 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201804851[2] Ogata N, Sakasegawa M, Miura T, et al. Inactivation of airborne bacteria and viruses using extremely low concentrations of chlorine dioxide gas. Pharmacology, 2016, 97(5/6), 301 doi: 10.1159/000444503[3] Rauth A M. The physical state of viral nucleic acid and the sensitivity of viruses to ultraviolet light. Biophys J, 1965, 5(3), 257 doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(65)86715-7[4] Beck S E, Wright H B, Hargy T M, et al. Action spectra for validation of pathogen disinfection in medium-pressure ultraviolet (UV) systems. Water Res, 2015, 70, 27 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.11.028[5] Santos A L, Moreirinha C, Lopes D, et al. Effects of UV radiation on the lipids and proteins of bacteria studied by mid-infrared spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol, 2013, 47(12), 6306 doi: 10.1021/es400660g[6] Hijnen W, Beerendonk E, Medema G J. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo) cysts in water: a review. Water Res, 2006, 40(1), 3 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.030[7] Sarigiannis D, Karakitsios S, Antonakopoulou M, et al. Exposure analysis of accidental release of mercury from compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). Sci Total Environ, 2012, 435, 306 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.026[8] Schalk S, Adam V, Arnold E, et al. UV-lamps for disinfection and advanced oxidation-lamp types, technologies and applications. IUVA News, 2006, 8(1), 32[9] da Silveira Petruci J F, Fortes P R, Kokoric V, et al. Real-time monitoring of ozone in air using substrate-integrated hollow waveguide mid-infrared sensors. Sci Reports, 2013, 3(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/srep03174[10] Hirayama H, Maeda N, Fujikawa S, et al. Recent progress and future prospects of AlGaN-based high-efficiency deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2014, 53(10), 100209 doi: 10.7567/JJAP.53.100209[11] Li D, Jiang K, Sun X, et al. AlGaN photonics: recent advances in materials and ultraviolet devices. Adv Opt Photonics, 2018, 10(1), 43 doi: 10.1364/AOP.10.000043[12] Kneissl M, Seong T Y, Han J, et al. The emergence and prospects of deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode technologies. Nat Photonics, 2019, 13(4), 233 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0359-9[13] Taniyasu Y, Kasu M, Makimoto T. An aluminium nitride light-emitting diode with a wavelength of 210 nanometres. Nature, 2006, 441(7091), 325 doi: 10.1038/nature04760[14] Khan A, Balakrishnan K, Katona T. Ultraviolet light-emitting diodes based on group three nitrides. Nat Photonics, 2008, 2(2), 77 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.293[15] Nagasawa Y, Hirano A. A review of AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes on sapphire. Appl Sci, 2018, 8(8), 1264 doi: 10.3390/app8081264[16] Simon J, Protasenko V, Lian C, et al. Polarization-induced hole doping in wide–band-gap uniaxial semiconductor heterostructures. Science, 2010, 327(5961), 60 doi: 10.1126/science.1183226[17] Zhang L, Ding K, Yan J, et al. Three-dimensional hole gas induced by polarization in (0001)-oriented metal-face III-nitride structure. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97(6), 062103 doi: 10.1063/1.3478556[18] Ryu H Y, Choi I G, Choi H S, et al. Investigation of light extraction efficiency in AlGaN deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Express, 2013, 6(6), 062101 doi: 10.7567/APEX.6.062101[19] Li Y, Wang C, Zhang Y, et al. Analysis of TM/TE mode enhancement and droop reduction by a nanoporous n-AlGaN underlayer in a 290 nm UV-LED. Photonics Res, 2020, 8(6), 806 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.387607[20] Bowker C, Sain A, Shatalov M, et al. Microbial UV fluence-response assessment using a novel UV-LED collimated beam system. Water Res, 2011, 45(5), 2011 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.12.005[21] Bolton J R, Linden K G. Standardization of methods for fluence (UV dose) determination in bench-scale UV experiments. J Environ Eng, 2003, 129(3), 209 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2003)129:3(209)[22] Suzuki A, Emoto A, Shirai A, et al. Ultraviolet light-emitting diode (UV-LED) sterilization of citrus bacterial canker disease targeted for effective decontamination of citrus sudachi fruit. Biocontrol Sci, 2022, 27(1), 1 doi: 10.4265/bio.27.1[23] Lee Y W, Yoon H D, Park J H, et al. Application of 265-nm UVC LED lighting to sterilization of typical gram negative and positive bacteria. J Korean Physl Soc, 2018, 72(10), 1174 doi: 10.3938/jkps.72.1174[24] Huang S Y, Lin J C, Huang X Q, et al. Large-area 280 nm LED flexible sterilization light source with improved thermal performance. Optik, 2021, 248, 168109 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168109[25] Kim B S, Youm S, Kim Y K. Sterilization of harmful microorganisms in hydroponic cultivation using an ultraviolet LED light source. Sens Mater, 2020, 32(11), 3773 doi: 10.18494/SAM.2020.2979[26] Nunayon S S, Zhang H, Lai A C K. Comparison of disinfection performance of UVC-LED and conventional upper-room UVGI systems. Indoor Air, 2020, 30(1), 180 doi: 10.1111/ina.12619[27] Liu S, Luo W, Li D, et al. Sec-eliminating the SARS-CoV-2 by AlGaN based high power deep ultraviolet light source. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 31, 2008452 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202008452[28] Bormann M, Alt M, Schipper L, et al. Disinfection of SARS-CoV-2 contaminated surfaces of personal items with UVC-LED disinfection boxes. Viruses, 2021, 13(4), 598 doi: 10.3390/v13040598[29] Tamulaitis G, Mickevičius J, Kazlauskas K, et al. Efficiency droop in high-Al-content AlGaN/AlGaN quantum wells. Phys Status Solidi C, 2011, 8(7/8), 2130 doi: 10.1002/pssc.201000889[30] Yun J, Shim J I, Hirayama H. Analysis of efficiency droop in 280-nm AlGaN multiple-quantum-well light-emitting diodes based on carrier rate equation. Appl Phys Express, 2015, 8(2), 022104 doi: 10.7567/APEX.8.022104[31] Cho J, Schubert E F, Kim J K. Efficiency droop in light-emitting diodes: Challenges and countermeasures. Laser Photonics Rev, 2013, 7(3), 408 doi: 10.1002/lpor.201200025[32] Hu J, Zhang J, Zhang Y, et al. Enhanced performance of AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes with chirped superlattice electron deceleration layer. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2019, 14(1), 1 doi: 10.1186/s11671-018-2843-4[33] Bolton J R, Cotton C A. The ultraviolet disinfection handbook. Glacier Publishing Services, Inc., 2011[34] Rastogi R P, Kumar A, Tyagi M B, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage and repair. J Nucleic Acids, 2010, 90(6/7), 560 doi: 10.4061/2010/592980 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: