| Citation: |
Hengze Qu, Ziwei Lin, Ruijuan Guo, Xiyu Ming, Wenhan Zhou, Shiying Guo, Xiufeng Song, Shengli Zhang, Haibo Zeng. First-principle study of puckered arsenene MOSFET[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2020, 41(8): 082006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/8/082006
****
H Z Qu, Z W Lin, R J Guo, X Y Ming, W H Zhou, S Y Guo, X F Song, S L Zhang, H B Zeng, First-principle study of puckered arsenene MOSFET[J]. J. Semicond., 2020, 41(8): 082006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/8/082006.
|
First-principle study of puckered arsenene MOSFET
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/8/082006
More Information
-
Abstract
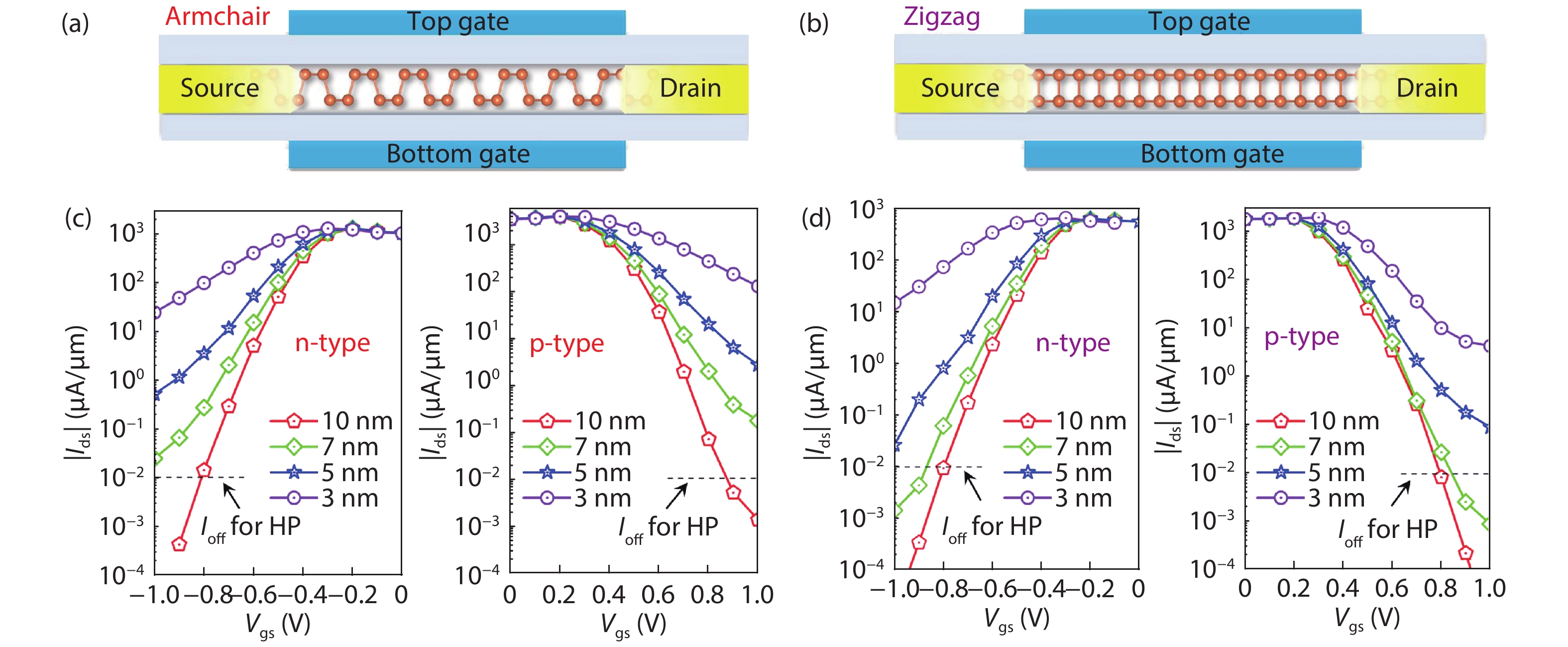
Two-dimensional material has been regarded as a competitive silicon-alternative with a gate length approaching sub-10 nm, due to its unique atomic thickness and outstanding electronic properties. Herein, we provide a comprehensively study on the electronic and ballistic transport properties of the puckered arsenene by the density functional theory coupled with nonequilibrium Green’s function formalism. The puckered arsenene exhibits an anisotropic characteristic, as effective mass for the electron/hole in the armchair and zigzag directions is 0.35/0.16 m0 and 1.26/0.32 m0. And it also holds a high electron mobility, as the highest value can reach 20 045 cm2V–1s–1. Moreover, the puckered arsenene FETs with a 10-nm channel length possess high on/off ratio above 105 and a steep subthreshold swing below 75 mV/dec, which have the potential to design high-performance electronic devices. Interestingly, the channel length limit for arsenene FETs can reach 7-nm. Furthermore, the benchmarking of the intrinsic arsenene FETs and the 32-bit arithmetic logic unit circuits also shows that the devices possess high switching speed and low energy dissipation, which can be comparable to the CMOS technologies and other CMOS alternatives. Therefore, the puckered arsenene is an attractive channel material in next-generation electronics. -
References
[1] Chau R, Doyle B, Datta S, et al. Integrated nanoelectronics for the future. Nat Mater, 2007, 6, 810 doi: 10.1038/nmat2014[2] Franklin A D. Nanomaterials in transistors: From high-performance to thin-film applications. Science, 2015, 349, aab2750 doi: 10.1126/science.aab2750[3] Desai S B, Madhvapathy S R, Sachid A B, et al. MoS2 transistors with 1-nanometer gate lengths. Science, 2016, 354, 99 doi: 10.1126/science.aah4698[4] Zhang S L, Guo S Y, Chen Z F, et al. Recent progress in 2D group-VA semiconductors: From theory to experiment. Chem Soc Rev, 2018, 47, 982 doi: 10.1039/C7CS00125H[5] Guo S Y, Zhang Y P, Ge Y Q, et al. 2D V-V binary materials: Status and challenges. Adv Mater, 2019, 31, 1902352 doi: 10.1002/adma.201902352[6] Zhou W H, Zhang S L, Guo S Y, et al. Designing sub-10-nm metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors via ballistic transport and disparate effective mass: The case of two-dimensional BiN. Phys Rev Appl, 2020, 13, 044066 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.13.044066[7] Cao W, Kang J H, Sarkar D, et al. 2D semiconductor FETs: Projections and design for sub-10 nm VLSI. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2015, 62, 3459 doi: 10.1109/TED.2015.2443039[8] Zhu Z L, Cai X L, Yi S, et al. Multivalency-driven formation of Te-based monolayer materials: A combined first-principles and experimental study. Phys Rev Lett, 2017, 119, 106101 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.106101[9] Zhou Z Q, Cui Y, Tan P H, et al. Optical and electrical properties of two-dimensional anisotropic materials. J Semicond, 2019, 40, 061001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/6/061001[10] Zhou W H, Chen J Y, Bai P X, et al. Two-dimensional pnictogen for field-effect transistors. Res Wash D C, 2019, 2019, 1046329 doi: 10.34133/2019/1046329[11] Novoselov K S, Mishchenko A, Carvalho A, et al. 2D materials and van der Waals heterostructures. Science, 2016, 353, aac9439 doi: 10.1126/science.aac9439[12] Wang S X, Yu Z H, Wang X R. Electrical contacts to two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides. J Semicond, 2018, 39, 124001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/12/124001[13] Schwierz F. Graphene transistors. Nat Nanotechnol, 2010, 5, 487 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.89[14] Tao L, Cinquanta E, Chiappe D, et al. Silicene field-effect transistors operating at room temperature. Nat Nanotechnol, 2015, 10, 227 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.325[15] Nourbakhsh A, Zubair A, Sajjad R N, et al. MoS2 field-effect transistor with sub-10 nm channel length. Nano Lett, 2016, 16, 7798 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03999[16] Qiao J S, Kong X H, Hu Z X, et al. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 4475 doi: 10.1038/ncomms5475[17] Zhang S L, Yan Z, Li Y F, et al. Atomically thin arsenene and antimonene: Semimetal –semiconductor and indirect-direct band-gap transitions. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2015, 54, 3112 doi: 10.1002/anie.201411246[18] Li L K, Yu Y J, Ye G J, et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat Nanotechnol, 2014, 9, 372 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.35[19] Wang X X, Hu Y, Mo J B, et al. Arsenene: A potential therapeutic agent for acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells by acting on nuclear proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2020, 59, 5151 doi: 10.1002/anie.201913675[20] Zhong M Z, Xia Q L, Pan L F, et al. Thickness-dependent carrier transport characteristics of a new 2D elemental semiconductor: Black arsenic. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 28, 1802581 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201802581[21] Wu X, Shao Y, Liu H, et al. Epitaxial growth and air-stability of monolayer antimonene on PdTe2. Adv Mater, 2017, 29, 1605407 doi: 10.1002/adma.201605407[22] Chen Y B, Chen C Y, Kealhofer R, et al. Black arsenic: A layered semiconductor with extreme in-plane anisotropy. Adv Mater, 2018, 30, 1800754 doi: 10.1002/adma.201800754[23] Pizzi G, Gibertini M, Dib E, et al. Performance of arsenene and antimonene double-gate MOSFETs from first principles. Nat Commun, 2016, 7, 12585 doi: 10.1038/ncomms12585[24] Quhe R G, Li Q H, Zhang Q X, et al. Simulations of quantum transport in sub-5-nm monolayer phosphorene transistors. Phys Rev Appl, 2018, 10, 024022 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.10.024022[25] Wang J, Cai Q, Lei J M, et al. Performance of monolayer blue phosphorene double-gate MOSFETs from the first principles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11, 20956 doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b02192[26] Wang Y Y, Huang P, Ye M, et al. Many-body effect, carrier mobility, and device performance of hexagonal arsenene and antimonene. Chem Mater, 2017, 29, 2191 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b04909[27] Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes forab initiototal-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54, 11169 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169[28] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 77, 3865 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865[29] Grimme S, Ehrlich S, Goerigk L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J Comput Chem, 2011, 32, 1456 doi: 10.1002/jcc.21759[30] Takagi S, Toriumi A, Iwase M, et al. On the universality of inversion layer mobility in Si MOSFET's: Part II-effects of surface orientation. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1994, 41, 2363 doi: 10.1109/16.337450[31] Atomistix Toolkit vertion 2019.03, Synopsys QuantumWise A/S[32] Datta S. Quantum transport: atom to transistor. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005[33] Gaddemane G, Vandenberghe W G, van de Put M L, et al. Theoretical studies of electronic transport in monolayer and bilayer phosphorene: A critical overview. Phys Rev B, 2018, 98, 115416 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.98.115416[34] Poncé S, Margine E R, Giustino F. Towards predictive many-body calculations of phonon-limited carrier mobilities in semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2018, 97, 121201 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.97.121201[35] International Roadmap for Devices and Systems, 2018 edition. https://irds.ieee.org/editions/2018 (accessed May 20, 2019)[36] Nikonov D E, Young I A. Overview of beyond-CMOS devices and a uniform methodology for their benchmarking. Proc IEEE, 2013, 101, 2498 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2013.2252317[37] Nikonov D E, Young I A. Benchmarking of beyond-CMOS exploratory devices for logic integrated circuits. IEEE J Explor Solid-State Comput Devices Circuits, 2015, 1, 3 doi: 10.1109/JXCDC.2015.2418033 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: