| Citation: |
Junyao Ji, Xinao Ji, Ziyu Zhou, Zhichao Dai, Xuhui Chen, Jie Zhang, Zheng Jiang, Hong Zhang. A 16-bit 18-MSPS flash-assisted SAR ADC with hybrid synchronous and asynchronous control logic[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(6): 062201. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120049
****
J Y Ji, X A Ji, Z Y Zhou, Z C Dai, X H Chen, J Zhang, Z Jiang, and H Zhang, A 16-bit 18-MSPS flash-assisted SAR ADC with hybrid synchronous and asynchronous control logic[J]. J. Semicond., 2024, 45(6), 062201 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120049
|
A 16-bit 18-MSPS flash-assisted SAR ADC with hybrid synchronous and asynchronous control logic
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/23120049
More Information
-
Abstract
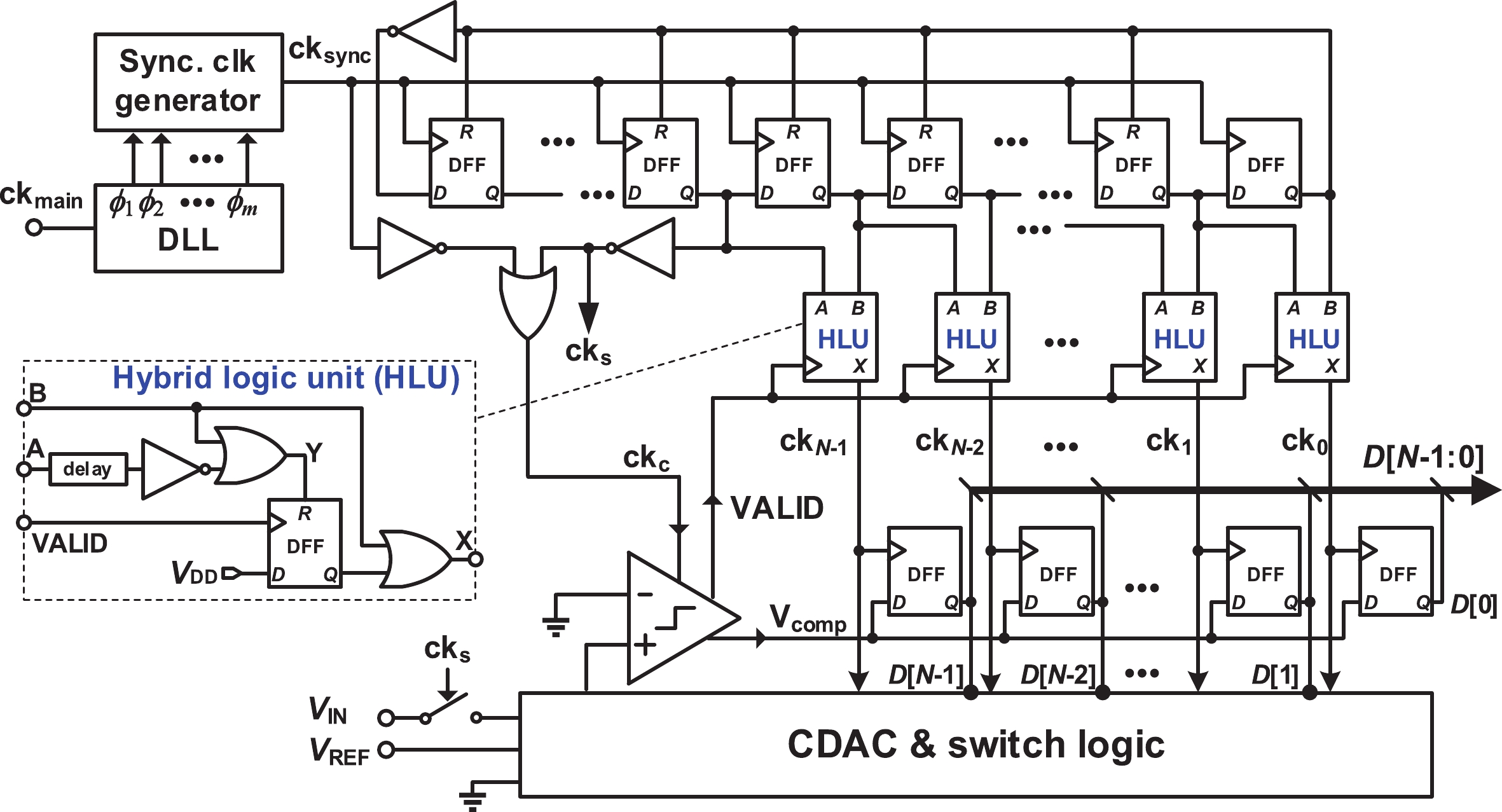
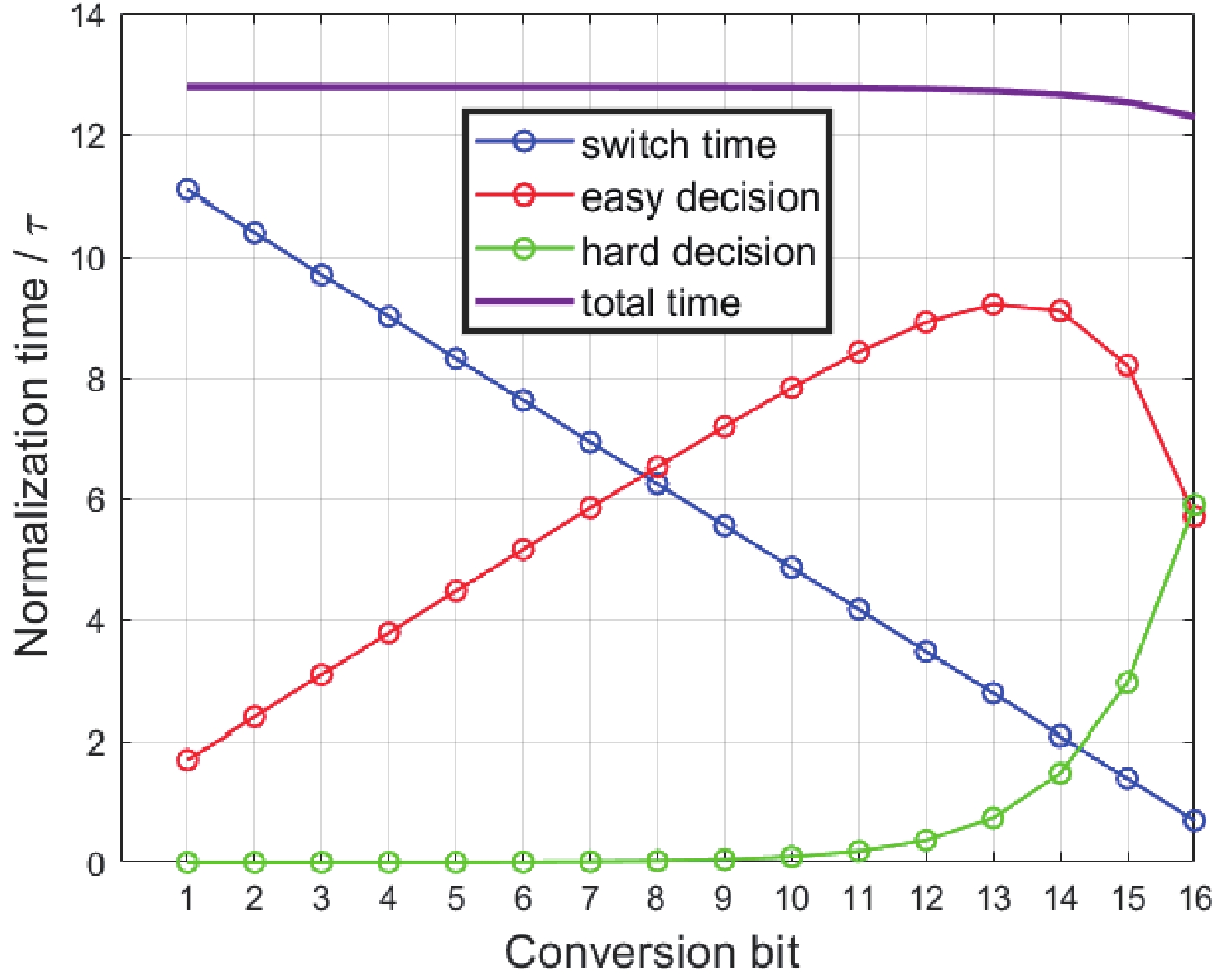
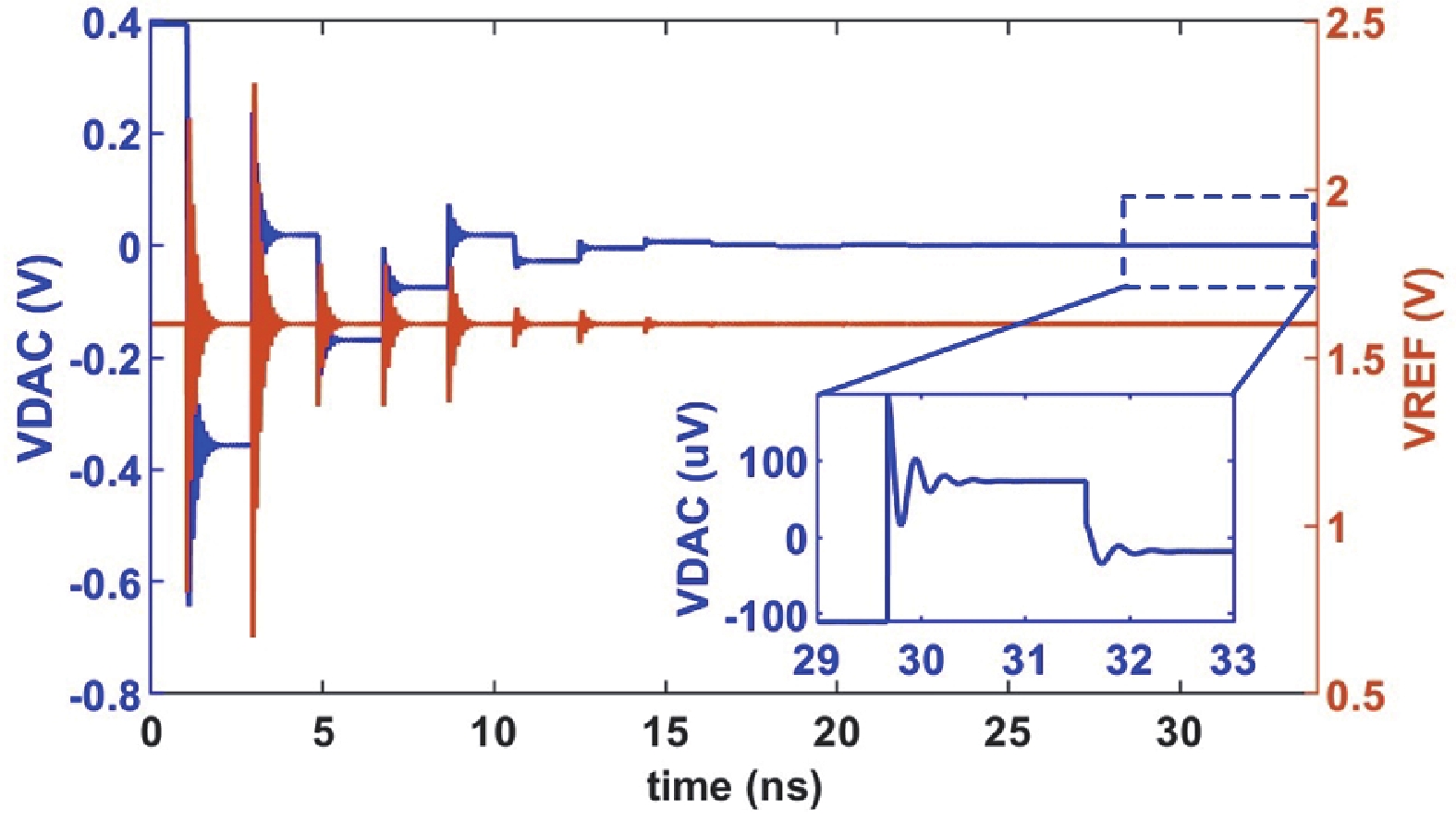
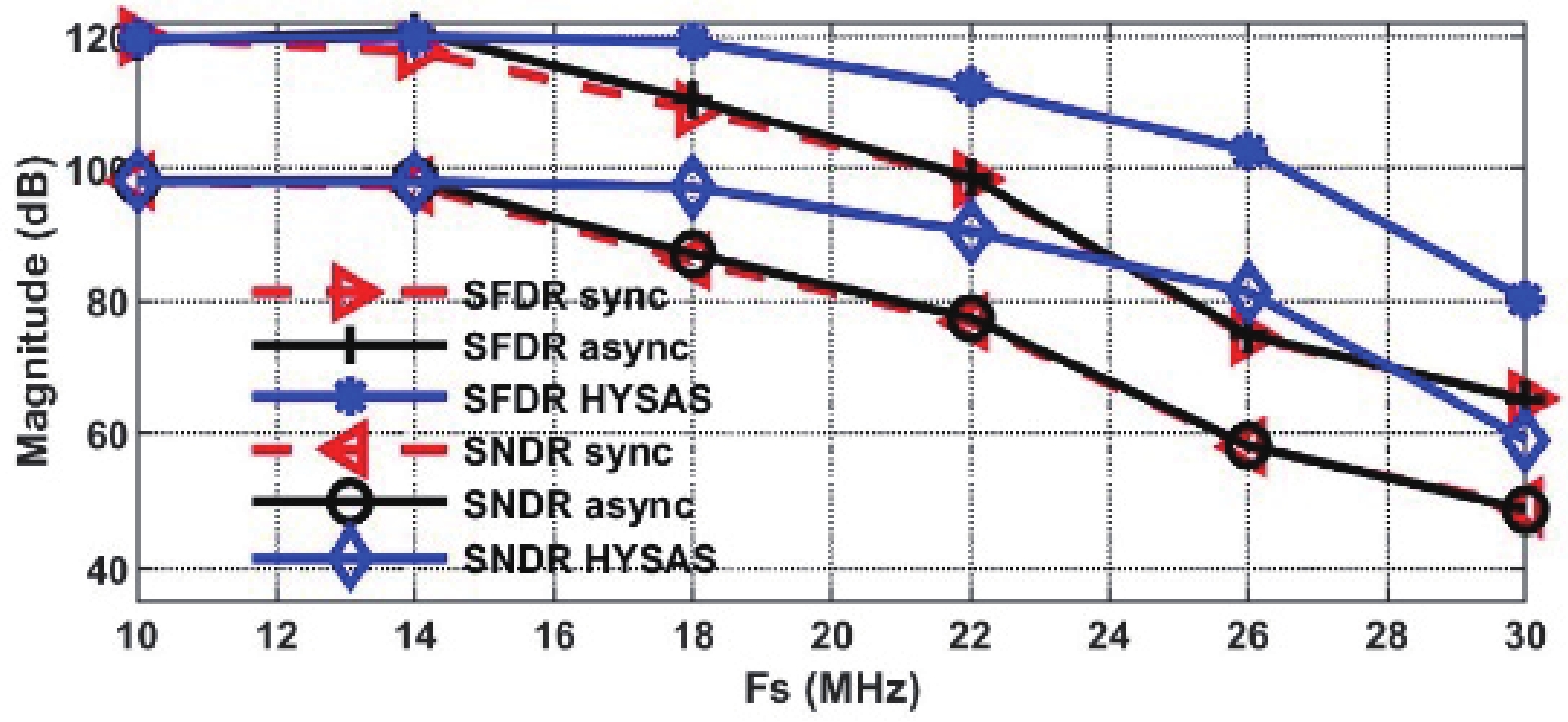
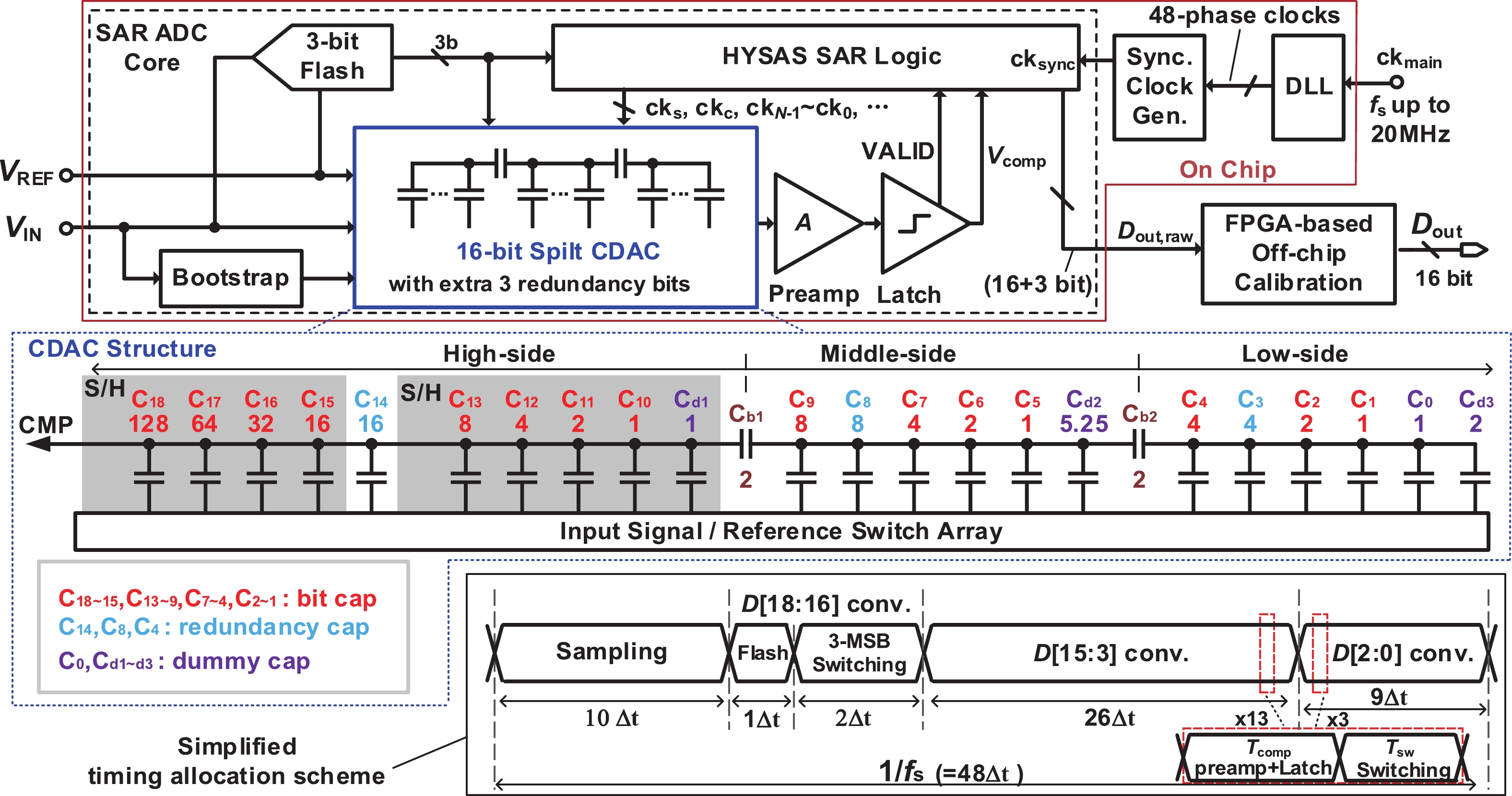
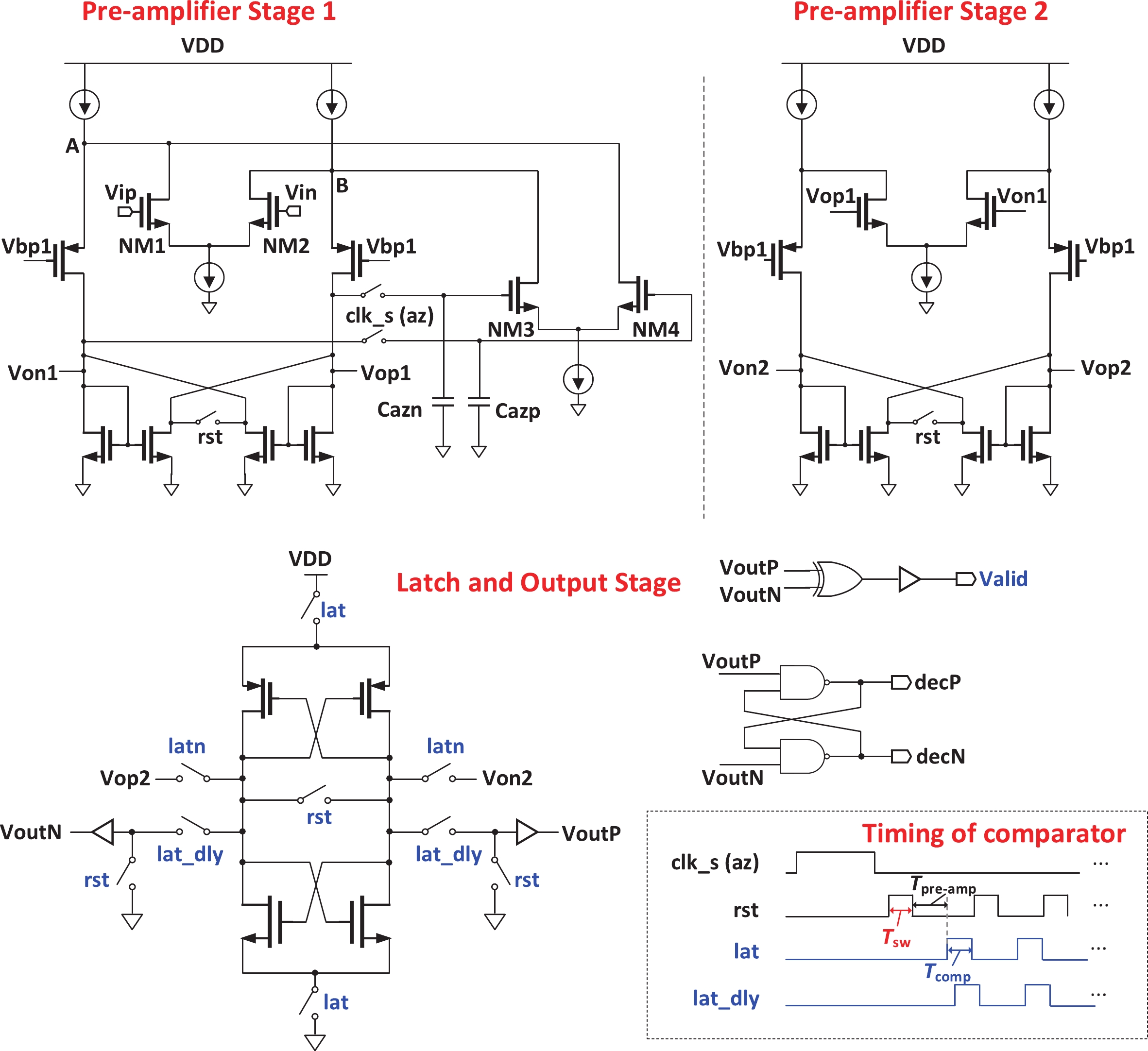
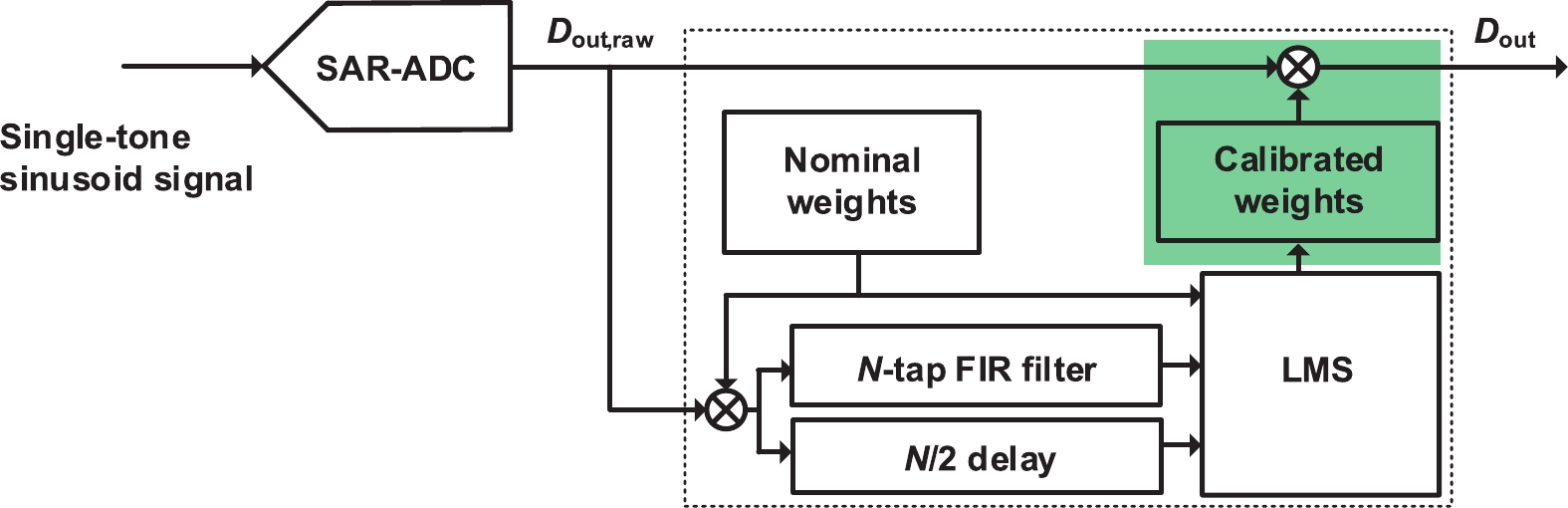
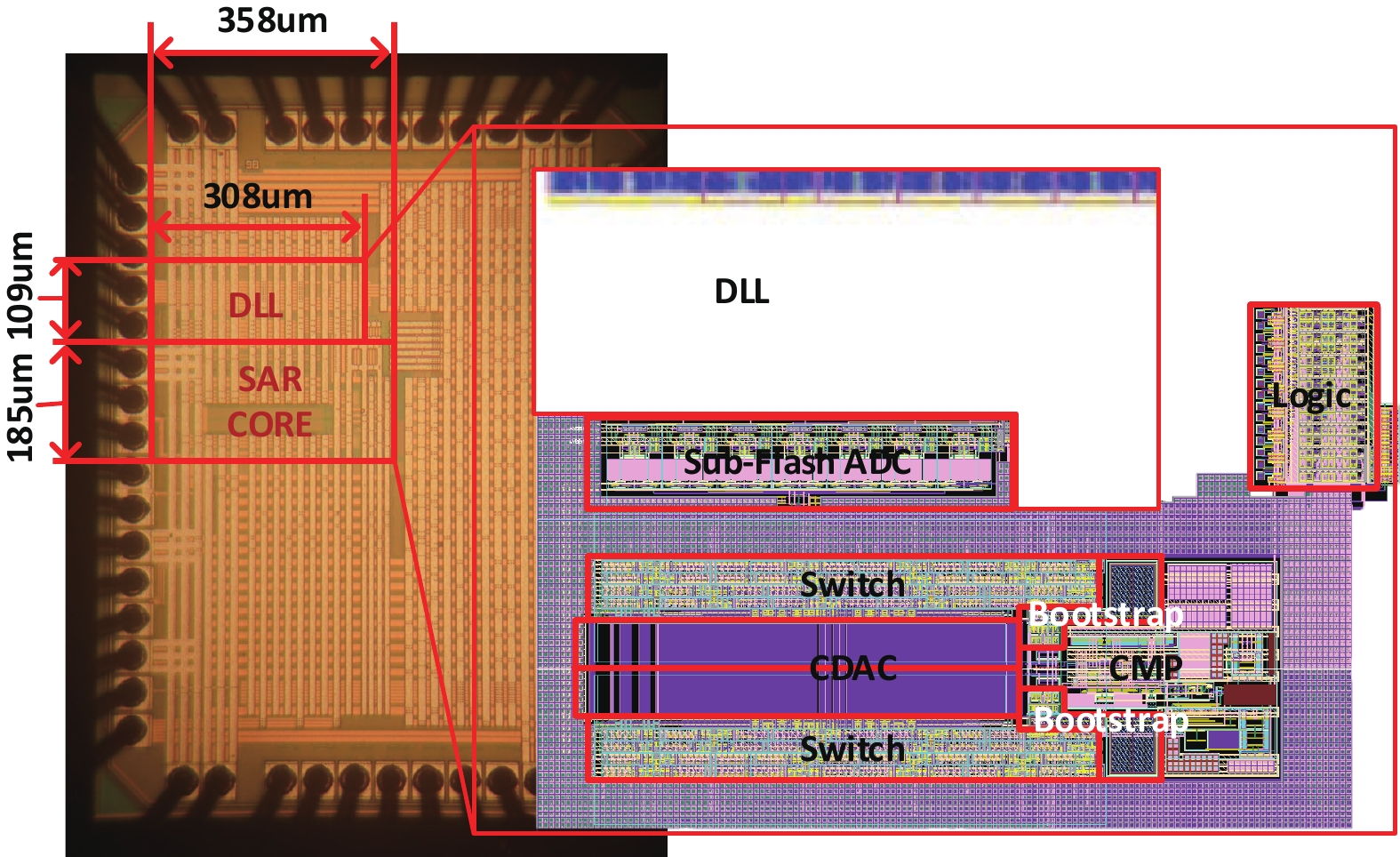
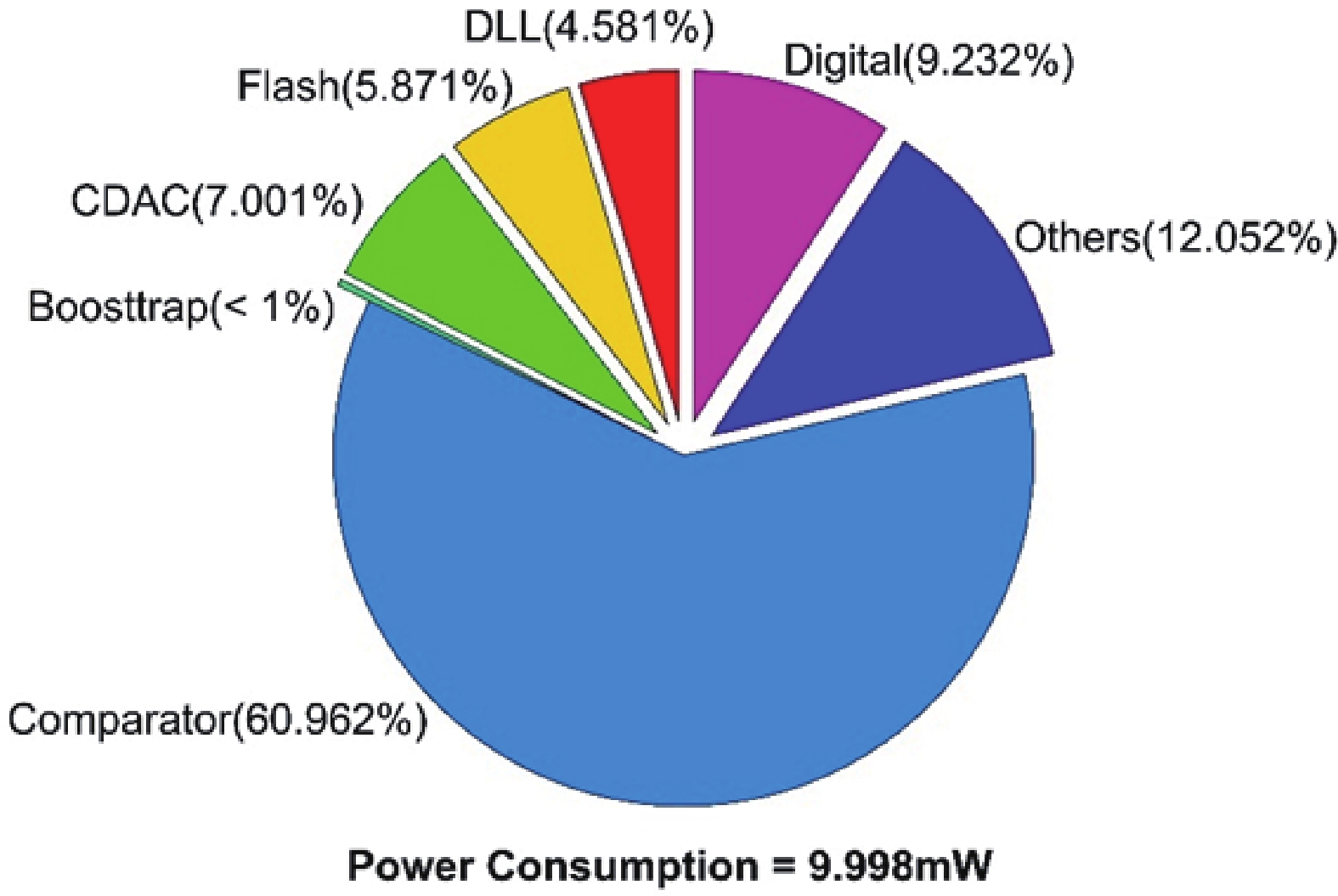
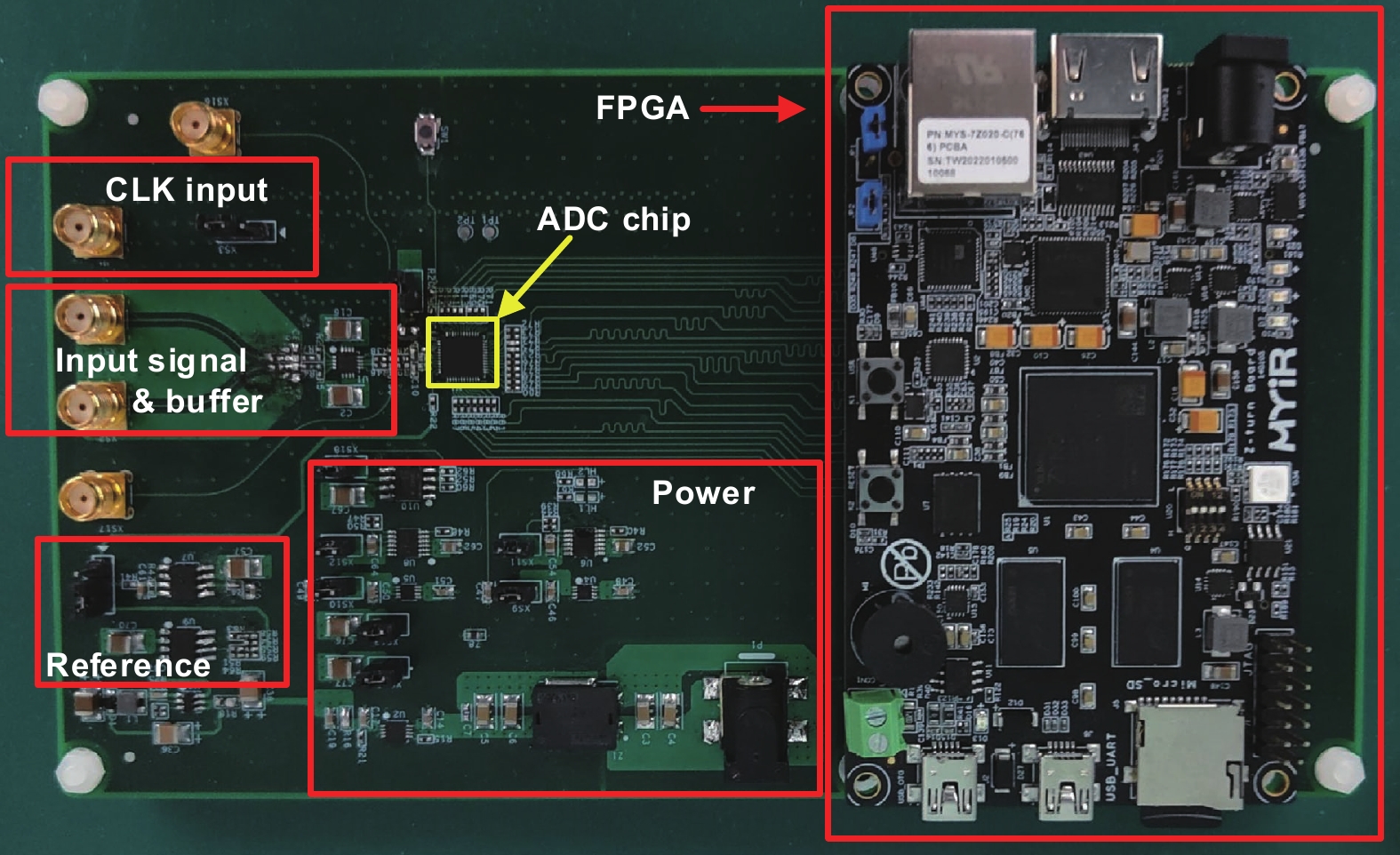
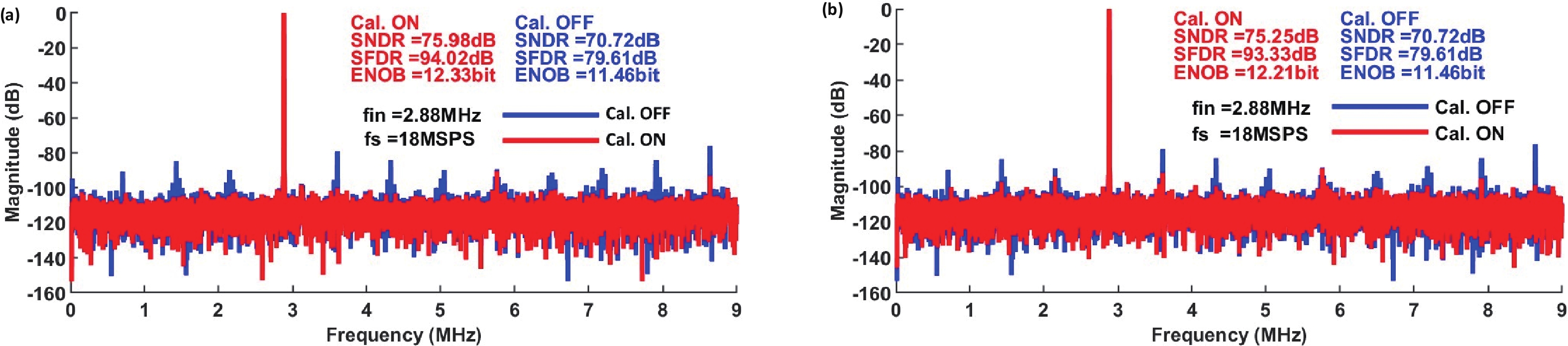
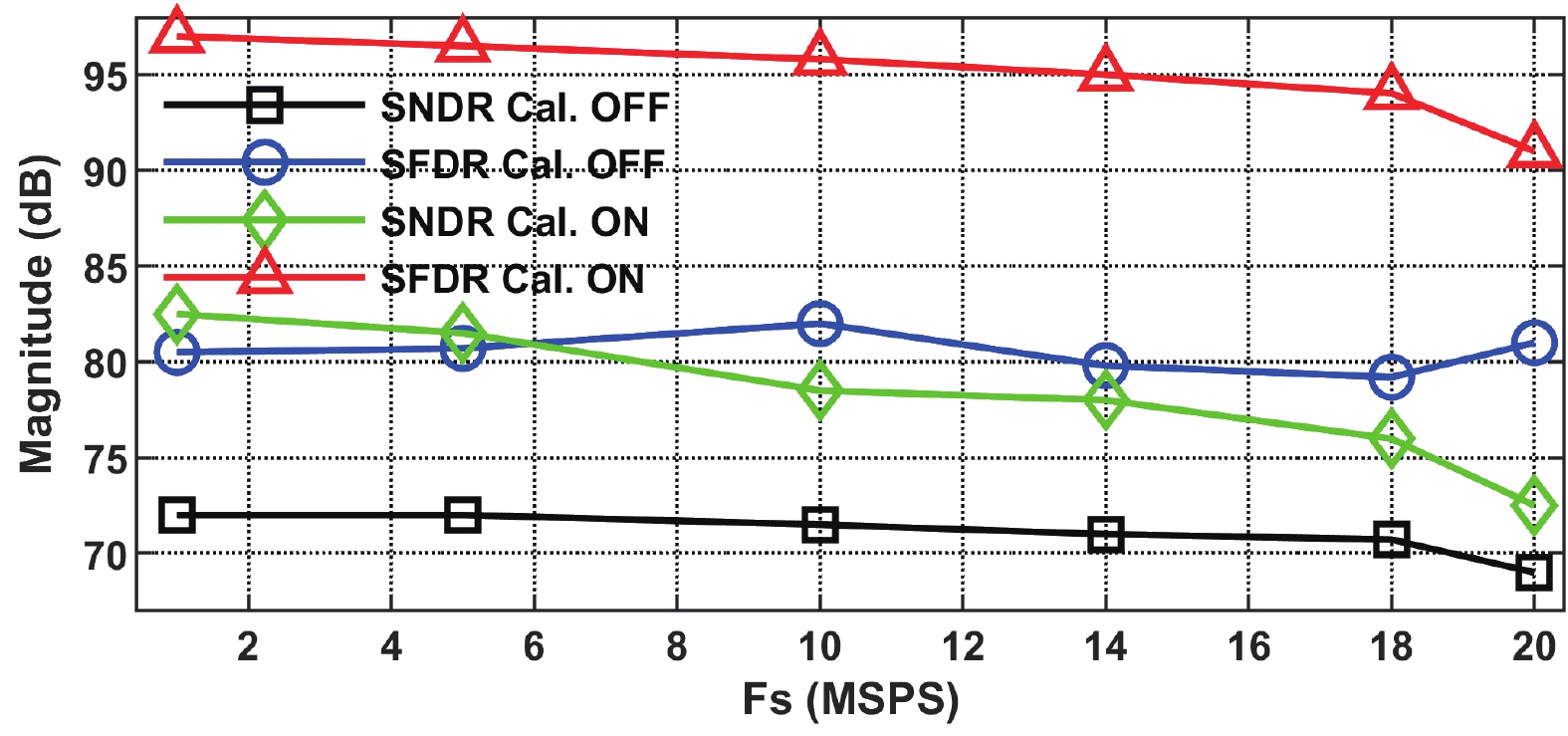
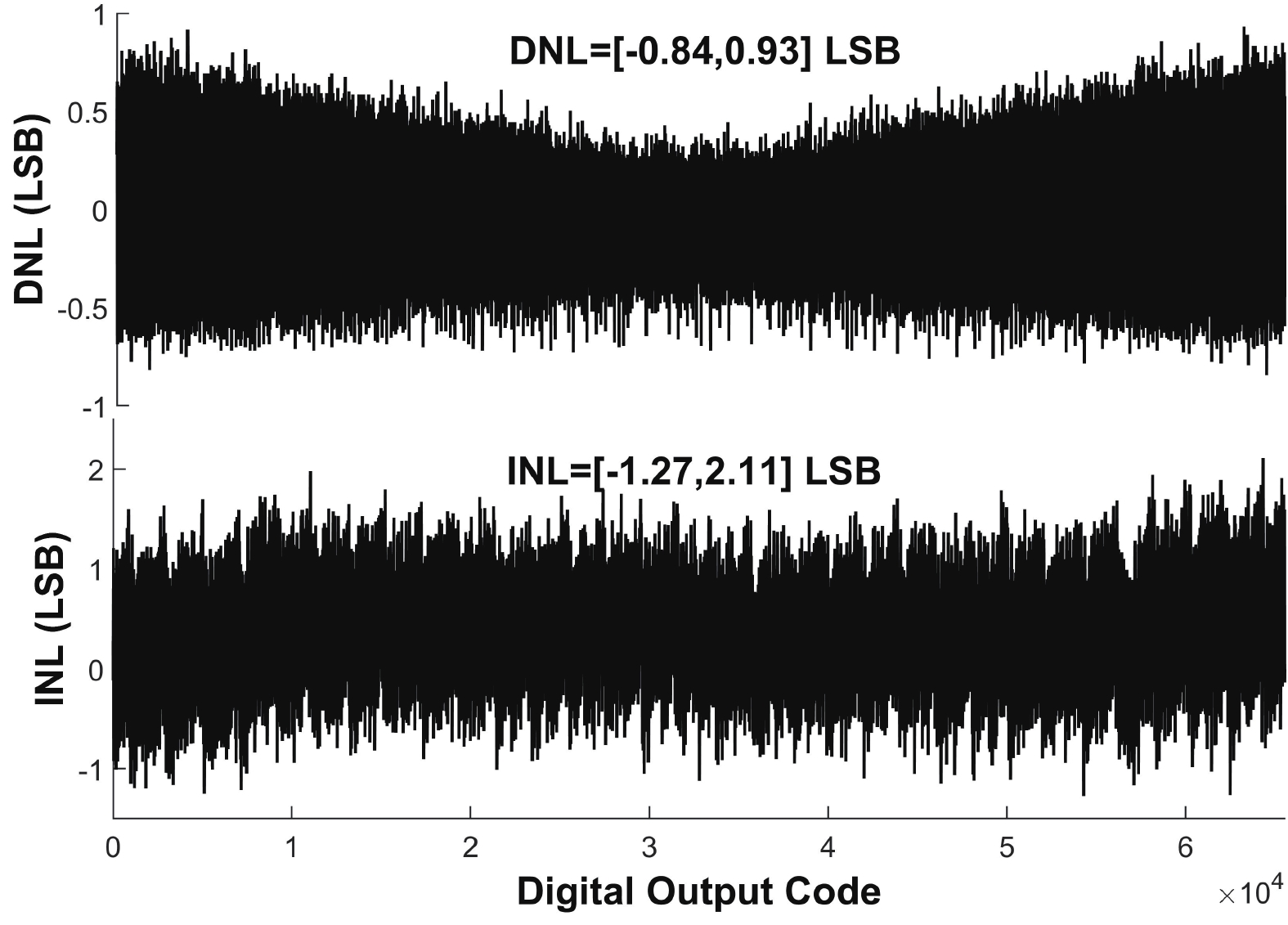
This paper presents a 16-bit, 18-MSPS (million samples per second) flash-assisted successive-approximation-register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) utilizing hybrid synchronous and asynchronous (HYSAS) timing control logic based on an on-chip delay-locked loop (DLL). The HYSAS scheme can provide a longer settling time for the capacitive digital-to-analog converter (CDAC) than the synchronous and asynchronous SAR ADC. Therefore, the issue of incomplete settling or ringing in the DAC voltage for cases of either on-chip or off-chip reference voltage can be solved to a large extent. In addition, the foreground calibration of the CDAC’s mismatch is performed with a finite-impulse-response bandpass filter (FIR-BPF) based least-mean-square (LMS) algorithm in an off-chip FPGA (field programmable gate array). Fabricated in 40-nm CMOS process, the prototype ADC achieves 94.02-dB spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR), and 75.98-dB signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio (SNDR) for a 2.88-MHz input under 18-MSPS sampling rate.-
Keywords:
- SAR ADC,
- control logic,
- reference ringing,
- DAC incomplete settling
-
References
[1] Harpe P. Successive approximation analog-to-digital converters: Improving power efficiency and conversion speed. IEEE Solid State Circuits Mag, 2016, 8, 64 doi: 10.1109/MSSC.2016.2573978[2] Liu J X, Tang X Y, Shen L X, et al. Error suppression techniques for energy-efficient high-resolution SAR ADCs. J Semicond, 2020, 41, 111403 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/11/111403[3] Luo H R, Zhao X L, Jiao Z H, et al. A 16-bit, ±10-V input range SAR ADC with a 5-V supply voltage and mixed-signal nonlinearity calibration. Chin J Electronics, 2022, 31, 690 doi: 10.1049/cje.2021.00.057[4] Pan X X, Zhou X, Chang S, et al. A 12-bit 30-MS/s VCO-based SAR ADC with NOC-assisted multiple adaptive bypass windows. J Semicond, 2020, 41, 112401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/11/112401[5] Zhang B C, Yao B B, Liu L Y, et al. High power-efficient asynchronous SAR ADC for IoT devices. J Semicond, 2017, 38, 105001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/10/105001[6] He X J, Gu X, Li W T, et al. An 11-bit 200 MS/s subrange SAR ADC with low-cost integrated reference buffer. J Semicond, 2017, 38, 105007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/10/105007[7] Guo X F, Ye F, Ren J Y. A 9 b/12 b 50 MS/s experimental ADC with continuous approximation architecture in 65 nm CMOS. J Semicond, 2016, 37, 105003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/10/105003[8] Jiao Z H, Chen Y, Su X B, et al. A configurable noise-shaping band-pass SAR ADC with two-stage clock-controlled amplifier. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2020, 67, 3728 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3012998[9] Doris K, Janssen E, Nani C, et al. A 480 mW 2.6 GS/s 10b time-interleaved ADC with 48.5 dB SNDR up to nyquist in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2011, 46, 2821 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2164961[10] Zhang H, Hassan A, Chen P, et al. Estimation of broadband time-interleaved ADC’s impairments and performance using only single-tone measurements. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 50403 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3173651[11] Li D Q, Zhu Z M, Liu J X, et al. A 7-bit 900-MS/s 2-Then-3-bit/cycle SAR ADC with background offset calibration. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55, 3051 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3011753[12] Zhang H S, Zhang H, Song Y, et al. A 10-bit 200-ks/s 1.76-μw SAR ADC with hybrid cap-mos dac for energy-limited applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2019, 66, 1716 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2899162[13] Ali A M A, Dinc H, Bhoraskar P, et al. A 14 bit 1 GS/s RF sampling pipelined ADC with background calibration. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49, 2857 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2361339[14] Miki T, Morie T, Matsukawa K, et al. A 4.2 mW 50 ms/s 13 bit CMOS SAR ADC with SNR and SFDR enhancement techniques. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50, 1372 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2417803[15] Kramer M J, Janssen E, Doris K, et al. A 14 b 35 MS/s SAR ADC achieving 75 dB SNDR and 99 dB SFDR with loop-embedded input buffer in 40 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50, 2891 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2463110[16] Shen J H, Shikata A, Fernando L D, et al. A 16-bit 16-MS/s SAR ADC with on-chip calibration in 55-nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53, 1149 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2784761[17] Liu J X, Tang X Y, Zhao W D, et al. A 13-bit 0.005-mm2 40-MS/s SAR ADC with kT/C noise cancellation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55, 3260 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3016656[18] Zhang X, Cao X D, Zhang X L. A 16-bit 1 MSPS SAR ADC with foreground calibration and residual voltage shift strategy. J Semicond, 2020, 41, 122401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/12/122401[19] Cao C, Zhu Z M. High-resolution 1 MS/s sub-2 radix split-capacitor SAR ADC. J Semicond, 2017, 38, 105008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/10/105008[20] Li C, Chan C H, Zhu Y, et al. Analysis of reference error in high-speed SAR ADCs with capacitive DAC. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2019, 66, 82 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2861835[21] Tang X Y, Shen L X, Kasap B, et al. An energy-efficient comparator with dynamic floating inverter amplifier. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55, 1011 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2960485[22] Zhang H R, Li N N, Wang J F, et al. A 1.25-MHz-BW, 83-dB SNDR pipelined noise-shaping SAR ADC with mash 2-2 structure and kt/C noise cancellation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs, 2023, 70, 3872 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2023.3289860[23] Jiao Z H, Luo H R, Zhang J, et al. An 84dB-SNDR 1-0 quasi-MASH NS SAR with LSB repeating and 12-bit bridge-crossing segmented CDAC. 2023 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC). San Antonio, TX, USA, IEEE, 2023, 1 doi: 10.1109/CICC57935.2023.10121259[24] Zhang H R, Wang X F, Li N N, et al. A 2.5-mhz bw, 75-dB SNDR noise-shaping SAR ADC with a 1st-order hybrid EF-CIFF structure assisted by unity-gain buffer. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2022, 30, 1928 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2022.3213365[25] Bankman D, Yu A, Zheng K, et al. Understanding metastability in SAR ADCs: Part I: Synchronous. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag, 2019, 11, 86 doi: 10.1109/MSSC.2019.2910647[26] Yu A, Bankman D, Zheng K, et al. Understanding metastability in SAR ADCs: Part ii: Asynchronous. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag, 2019, 11, 16 doi: 10.1109/MSSC.2019.2922890[27] Waters A, Muhlestein J, Moon U K. Analysis of metastability errors in asynchronous SAR ADCs. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (ICECS). Cairo, Egypt, IEEE, 2015, 547 doi: 10.1109/ICECS.2015.7440375[28] Zhu Y, Chan C H, Chio U F, et al. A 10-bit 100-MS/s reference-free SAR ADC in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45, 1111 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2048498[29] Zhang W P, Tong X. Noise modeling and analysis of SAR ADCs. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2015, 23, 2922 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2014.2379613[30] Obata K, Matsukawa K, Miki T, et al. A 97.99 dB SNDR, 2 kHz BW, 37.1 µW noise-shaping SAR ADC with dynamic element matching and modulation dither effect. 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits (VLSI-Circuits). Honolulu, HI, USA, IEEE, 2016, 1 doi: 10.1109/VLSIC.2016.7573463[31] Kim T, Chae Y. A 2Mhz bw buffer-embedded noise-shaping SAR ADC achieving 73.8dB SNDR and 87.3dB SFDR. 2019 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC). Austin, TX, USA, IEEE, 2019, 1 doi: 10.1109/CICC.2019.8780230[32] Shu Y S, Kuo L T, Lo T Y. An oversampling SAR ADC with DAC mismatch error shaping achieving 105 dB SFDR and 101 dB SNDR over 1 kHz BW in 55 nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2016, 51, 2928 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2592623[33] McNeill J A, Chan K Y, Coln M C W, et al. All-digital background calibration of a successive approximation ADC using the “split ADC” architecture. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2011, 58, 2355 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2011.2123590[34] Lan Z C, Dong L, Jing X X, et al. A 12-bit 100MS/s SAR ADC with digital error correction and high-speed LMS-based background calibration. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). Daegu, Korea, IEEE, 2021, 1 doi: 10.1109/ISCAS51556.2021.9401172[35] Chen S W M, Brodersen R W. A 6-bit 600-MS/s 5.3-mW asynchronous ADC in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2006, 41, 2669 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.884231[36] Liang Y H, Li C Y, Liu S B, et al. A 14-b 20-MS/s 78.8 dB-SNDR energy-efficient SAR ADC with background mismatch calibration and noise-reduction techniques for portable medical ultrasound systems. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2022, 16, 200 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2022.3147954[37] Analog Devices. AD9269-20 datasheet. (2010-02-01)[2024-03-01]. https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ad9269.pdf -
Proportional views





 Junyao Ji got his B.S. degree in microelectronic science and engineering from Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an China, in 2023. His research interests include analog/mixed-signal IC design such as ADC, amplifiers, bandgap references, and so on.
Junyao Ji got his B.S. degree in microelectronic science and engineering from Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an China, in 2023. His research interests include analog/mixed-signal IC design such as ADC, amplifiers, bandgap references, and so on. Xinao Ji got his B.S. from Xi'an Jiaotong University in 2023. Now he is a Master student at Xi'an Jiaotong University under the supervision of Prof. Hong Zhang. His research focuses on mixed signal systems and computing in memory.
Xinao Ji got his B.S. from Xi'an Jiaotong University in 2023. Now he is a Master student at Xi'an Jiaotong University under the supervision of Prof. Hong Zhang. His research focuses on mixed signal systems and computing in memory. Hong Zhang received the Ph. D. degree in electronic engineering from Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an China, in 2008. Since 2008, he has been with the Department of Microelectronics at Xi’an Jiaotong University, where he is currently a Professor. From June to September 2009, he was a visiting scholar at KU Leuven and IMEC, Belgium. From Aug. 2016 to Aug. 2017, he was a visiting professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto. His research interests include analog/mixed-signal IC design such as ADC, low-power and low-voltage references, bio-medical ICs, and so on.
Hong Zhang received the Ph. D. degree in electronic engineering from Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an China, in 2008. Since 2008, he has been with the Department of Microelectronics at Xi’an Jiaotong University, where he is currently a Professor. From June to September 2009, he was a visiting scholar at KU Leuven and IMEC, Belgium. From Aug. 2016 to Aug. 2017, he was a visiting professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto. His research interests include analog/mixed-signal IC design such as ADC, low-power and low-voltage references, bio-medical ICs, and so on.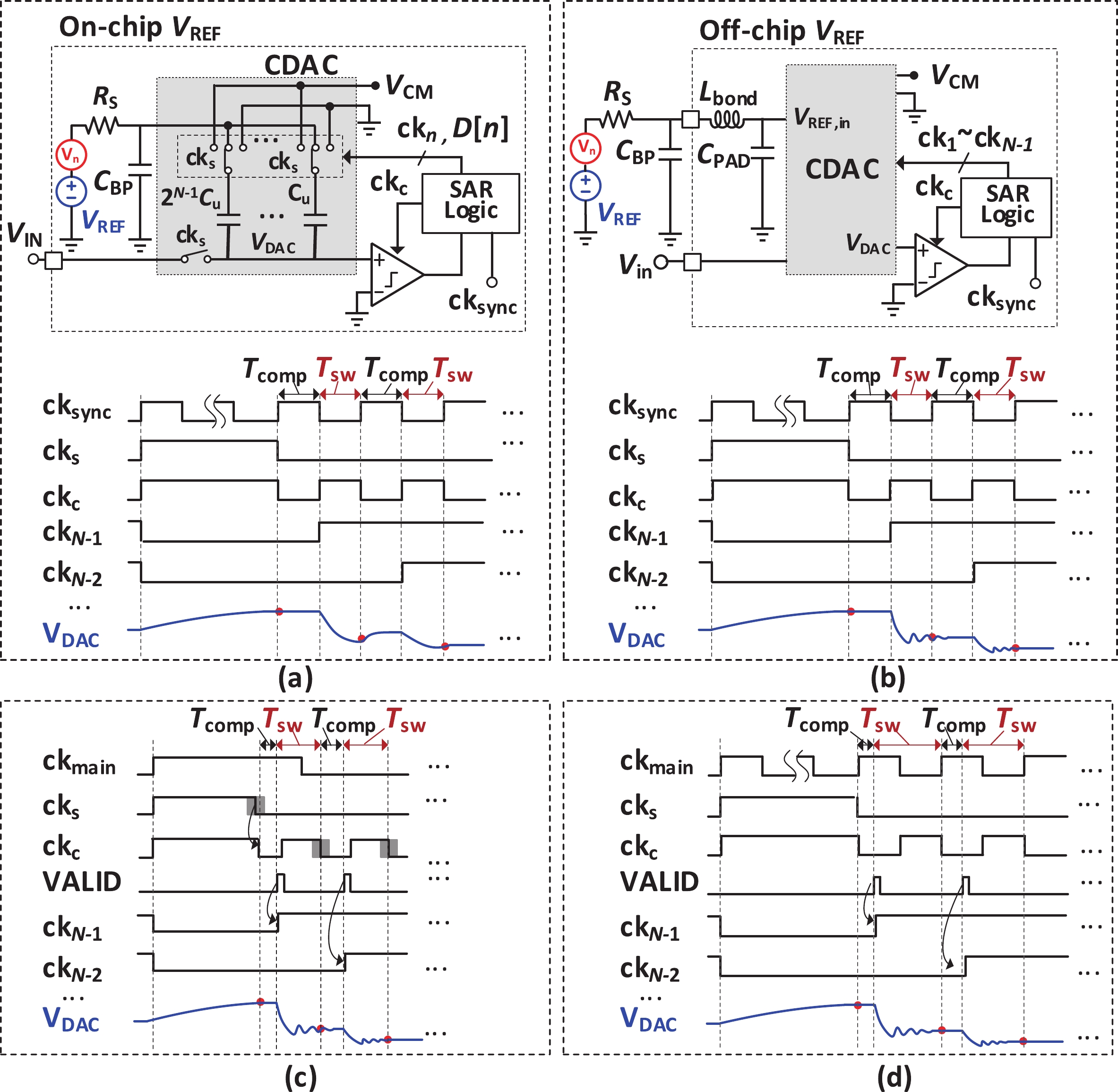
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: