| Citation: |
Chenzhe Hu, Yuyu Bu, Xianying Dai, Fengqiu Jiang, Yue Hao. Calculation of the carrier dynamics and impedance spectroscopy model in quantum well infrared photodetectors[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, 46(3): 032403. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24090033
****
C Z Hu, Y Y Bu, X Y Dai, F Q Jiang, and Y Hao, Calculation of the carrier dynamics and impedance spectroscopy model in quantum well infrared photodetectors[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, 46(3), 032403 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24090033
|
Calculation of the carrier dynamics and impedance spectroscopy model in quantum well infrared photodetectors
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24090033
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.24090033
More Information-
Abstract
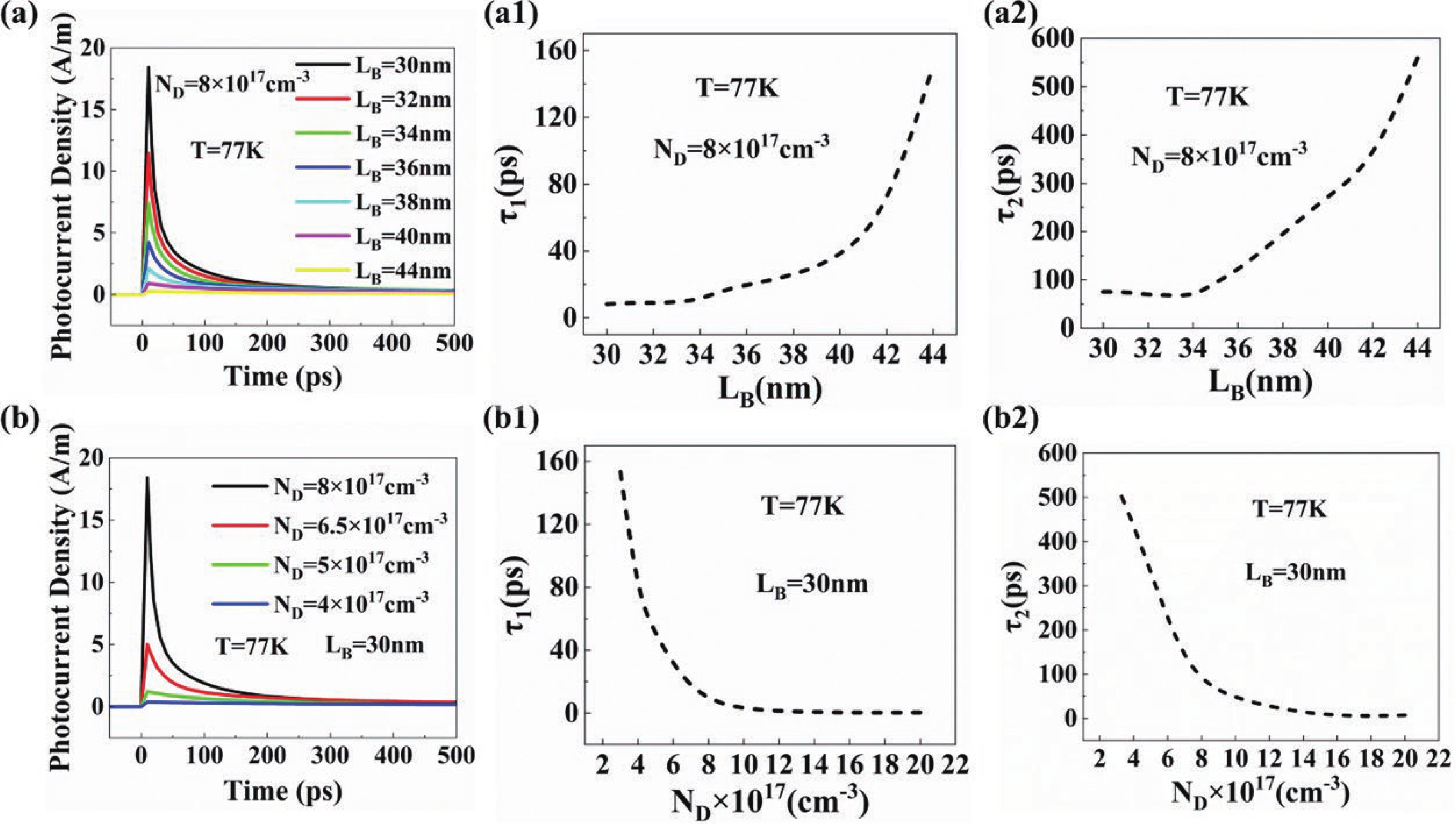
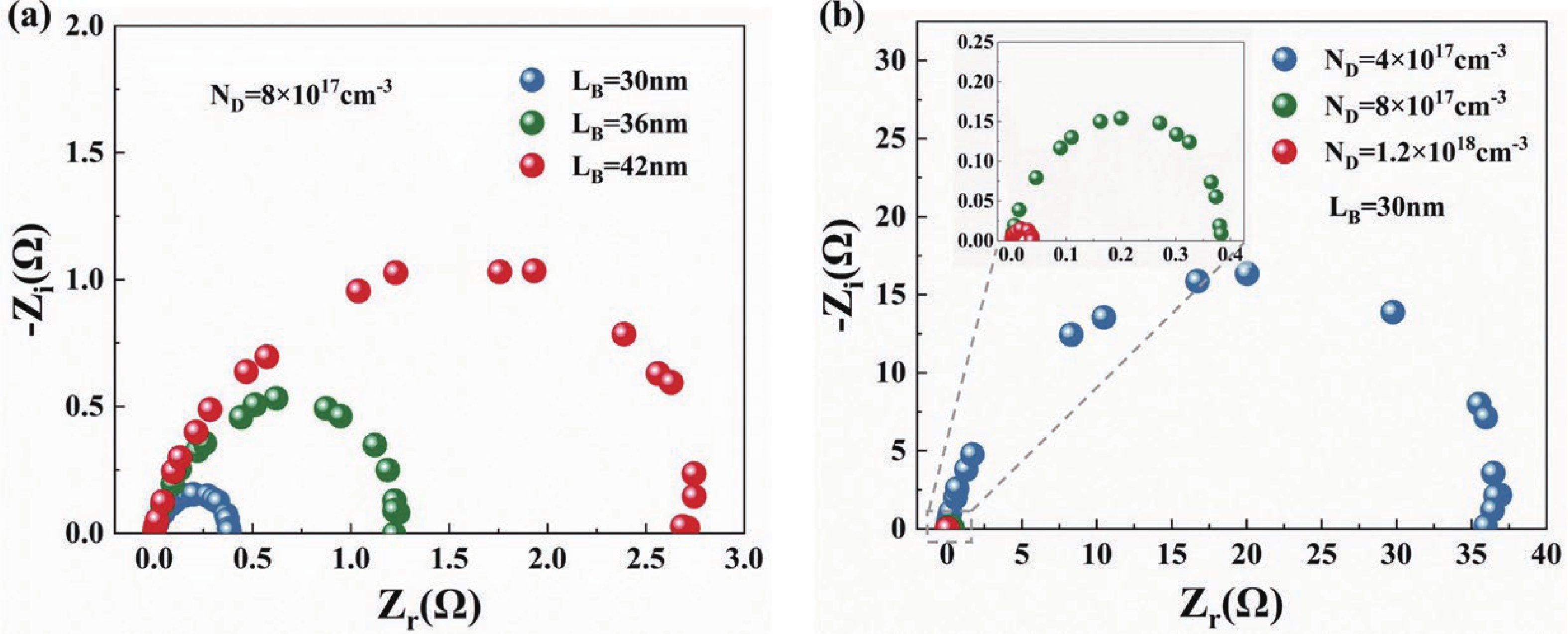
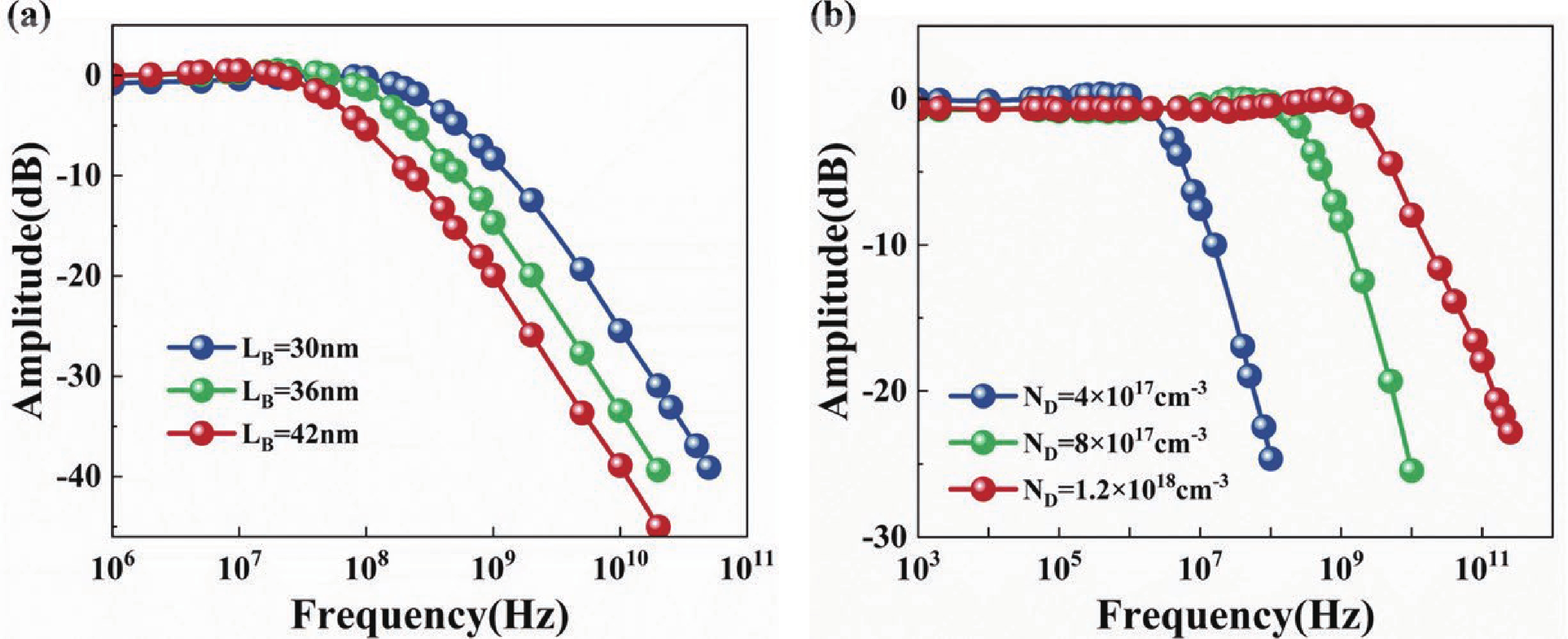
Quantum well infrared photodetectors (QWIPs) based on intersubband transitions hold significant potential for high bandwidth operation. In this work, we establish a carrier transport optimization model incorporating electron injection at the emitter to investigate the carrier dynamics time and impedance spectroscopy in GaAs/AlGaAs QWIPs. Our findings provide novel evidence that the escape time of electrons is the key limiting factor for the 3-dB bandwidth of QWIPs. Moreover, to characterize the impact of carrier dynamics time and non-equilibrium space charge region on impedance, we developed an equivalent circuit model where depletion region resistance and capacitance are employed to describe non-equilibrium space charge region. Using this model, we discovered that under illumination, both net charge accumulation caused by variations in carrier dynamics times within quantum wells and changes in width of non-equilibrium space charge region exert different dominant influences on depletion region capacitance at various doping concentrations. -
References
[1] Liu H C, Jenkins G E, Brown E R, et al. Optical heterodyne detection and microwave rectification up to 26 GHz using quantum well infrared photodetectors. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 1995, 16, 253 doi: 10.1109/55.790726[2] Liu H C, Li J M, Brown E R, et al. Quantum well intersubband heterodyne infrared detection up to 82 GHz. Appl Phys Lett, 1995, 67, 1594 doi: 10.1063/1.114950[3] Palaferri D, Todorov Y, Bigioli A, et al. Room-temperature nine-µm-wavelength photodetectors and GHz-frequency heterodyne receivers. Nature, 2018, 556, 85 doi: 10.1038/nature25790[4] Hakl M, Lin Q Y, Lepillet S, et al. Ultrafast quantum-well photodetectors operating at 10 μm with a flat frequency response up to 70 GHz at room temperature. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8, 464 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01299[5] Weidmann D, Reburn W J, Smith K M. Ground-based prototype quantum cascade laser heterodyne radiometer for atmospheric studies. Rev Sci Instrum, 2007, 78, 073107 doi: 10.1063/1.2753141[6] Pang X D, Ozolins O, Schatz R, et al. Gigabit free-space multi-level signal transmission with a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser operating at room temperature. Opt Lett, 2017, 42, 3646 doi: 10.1364/OL.42.003646[7] Martini R, Paiella R, Gmachl C, et al. High-speed digital data transmission using mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers. Electron Lett, 2001, 37, 1290 doi: 10.1049/el:20010884[8] Chaisakul P, Marris-Morini D, Isella G, et al. Ge/SiGe multiple quantum well photodiode with 30 GHz bandwidth. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98, 131112 doi: 10.1063/1.3574539[9] Chow Y C, Lee C, Wong M S, et al. Dependence of carrier escape lifetimes on quantum barrier thickness in InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well photodetectors. Opt Express, 2020, 28, 23796 doi: 10.1364/OE.399924[10] Guériaux V, Nedelcu A, Bois P. Double barrier strained quantum well infrared photodetectors for the 3–5μm atmospheric window. J Appl Phys, 2009, 105, 114515 doi: 10.1063/1.3143102[11] Kane M J, Millidge S, Emeny M T, et al. Electron mobilities and photoelectron lifetimes in AlGaAs/GaAs and InGaAs/GaAs quantum-well infrared detectors. J Appl Phys, 1993, 73, 7966 doi: 10.1063/1.353905[12] Duboz J Y, Costard E, Nagle J, et al. Electron capture time measurements in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum-well infrared photodetectors: Photoresponse saturation by a free-electron laser. J Appl Phys, 1995, 78, 1224 doi: 10.1063/1.360362[13] Liu H C, Li J M, Buchanan M, et al. High-frequency quantum-well infrared photodetectors measured by microwave-rectification technique. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 1996, 32, 1024 doi: 10.1109/3.502380[14] Ehret S, Schneider H, Fleissner J, et al. Ultrafast intersubband photocurrent response in quantum-well infrared photodetectors. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 71, 641 doi: 10.1063/1.119815[15] Morris D, Deveaud B, Regreny A, et al. Electron and hole capture in multiple-quantum-well structures. Phys Rev B Condens Matter, 1993, 47, 6819 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.47.6819[16] Schmidt S R, Seilmeier A, Liu H C. Intersubband carrier dynamics in a biased GaAs/AlGaAs quantum-well infrared photodetector. J Appl Phys, 2002, 91, 5545 doi: 10.1063/1.1464214[17] Billaha M A, Das M K. Transient response analysis of quantum well infrared photodetector. Opt Quantum Electron, 2021, 53, 451 doi: 10.1007/s11082-021-03113-5[18] Ershov M, Ryzhii V, Hamaguchi C. Contact and distributed effects in quantum well infrared photodetectors. Appl Phys Lett, 1995, 67, 3147 doi: 10.1063/1.114862[19] Thibaudeau L, Bois P, Duboz J Y. A self-consistent model for quantum well infrared photodetectors. J Appl Phys, 1996, 79, 446 doi: 10.1063/1.362712[20] Ehret S, Schneider H, Schönbein C, et al. Analysis of the transport mechanism in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum-well infrared photodetection structures using time resolved photocurrent measurements. Appl Phys Lett, 1996, 69, 931 doi: 10.1063/1.116947[21] Chang B Y. Conversion of a constant phase element to an equivalent capacitor. J Electrochem Sci Technol, 2020, 11, 318 doi: 10.33961/jecst.2020.00815[22] Takagi K, Nagase T, Kobayashi T, et al. Determination of deep trapping lifetime in organic semiconductors using impedance spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett, 2016, 108, 053305 doi: 10.1063/1.4941235[23] Gabbitas A, Pattnaik D P, Zhou Z, et al. Resistive switching study on diffusive memristors using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2023, 56, 305102 doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/acd06c[24] Davydov V N, Morgunov A N. Determining the equivalent circuit elements of heterostructures with multiple quantum wells. Russ Phys J, 2016, 58, 1619 doi: 10.1007/s11182-016-0692-0[25] Perera A G U, Silvestrov V G, Matsik S G, et al. Nonuniform vertical charge transport and relaxation in quantum well infrared detectors. J Appl Phys, 1998, 83, 991 doi: 10.1063/1.366787[26] Davydov V N, Novikov D A. Equivalent circuit of a heterostructure with multiple quantum wells. Russ Phys J, 2015, 58, 987 doi: 10.1007/s11182-015-0599-1[27] Wang G, Tokumitsu T, Hanawa I, et al. A time-delay equivalent-circuit model of ultrafast p-i-n photodiodes. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2003, 51, 1227 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2003.809642[28] Lee J M, Cho S H, Choi W Y. An equivalent circuit model for a Ge waveguide photodetector on Si. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2016, 28, 2435 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2598369[29] Baraff G A. Semiclassical description of electron transport in semiconductor quantum-well devices. Phys Rev B, 1997, 55, 10745 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.55.10745[30] Xia C S, Hu W D, Wang C, et al. Simulation of InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well light-emitting diodes with quantum dot model for electrical and optical effects. Opt Quantum Electron, 2006, 38, 1077 doi: 10.1007/s11082-006-9029-5[31] Turchinovich D, D’Angelo F, Bonn M. Femtosecond-timescale buildup of electron mobility in GaAs observed via ultrabroadband transient terahertz spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett, 2017, 110, 121102 doi: 10.1063/1.4978648[32] Lutgen S, Kaindl R A, Woerner M, et al. Nonequilibrium dynamics in a quasi-two-dimensional electron plasma after ultrafast intersubband excitation. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 77, 3657 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3657[33] Liu H Y, Meng Z M, Dai Q F, et al. Ultrafast carrier dynamics in undoped and p-doped InAs/ GaAs quantum dots characterized by pump-probe reflection measurements. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103, 083121 doi: 10.1063/1.2913316[34] Ershov M. Transient photoconductivity in quantum well infrared photodetectors. Appl Phys Lett, 1996, 69, 3480 doi: 10.1063/1.117258[35] Liu H C. Photoconductive gain mechanism of quantum-well intersubband infrared detectors. Appl Phys Lett, 1992, 60, 1507 doi: 10.1063/1.107286[36] Li J C, He S, Ma M M, et al. An extensive large signal equivalent circuit model of GaAs-PIN photodiode. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2022, 43, 1195 doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3184299 -
Proportional views




 Chenzhe Hu received his bachelor’s degree from Xi’an University of Post & Telecommunications. Now he is a master student at Faculty of Integrated Circuit Xidian University under the supervision of Prof. Xianying Dai. His research focuses on the development and application of semiconductor optoelectronic devices.
Chenzhe Hu received his bachelor’s degree from Xi’an University of Post & Telecommunications. Now he is a master student at Faculty of Integrated Circuit Xidian University under the supervision of Prof. Xianying Dai. His research focuses on the development and application of semiconductor optoelectronic devices. Yuyu Bu received his PhD degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Tokushima University, Japan, in 2017. Then, he returned to Xidian University, School of Microelectronics, where he was appointed as an associate professor in 2017. His research focus on the sustainable solar energy conversion, semiconductor electrochemistry and photoelectrochemistry, semiconductor-based detectors and sensors.
Yuyu Bu received his PhD degree in Electrical and Electronic Engineering from Tokushima University, Japan, in 2017. Then, he returned to Xidian University, School of Microelectronics, where he was appointed as an associate professor in 2017. His research focus on the sustainable solar energy conversion, semiconductor electrochemistry and photoelectrochemistry, semiconductor-based detectors and sensors. Xianying Dai obtained a doctoral degree from Xi'an University of Electronic Science and Technology in 2012. He is currently a professor, doctoral and master's supervisor at the School of Microelectronics, Xidian University, and a senior member of the China Electronics Society. His research focuses on silicon-based strain theory and technology, semiconductor material growth kinetics and defect behavior, and semiconductor photoelectrochemical biosensors.
Xianying Dai obtained a doctoral degree from Xi'an University of Electronic Science and Technology in 2012. He is currently a professor, doctoral and master's supervisor at the School of Microelectronics, Xidian University, and a senior member of the China Electronics Society. His research focuses on silicon-based strain theory and technology, semiconductor material growth kinetics and defect behavior, and semiconductor photoelectrochemical biosensors.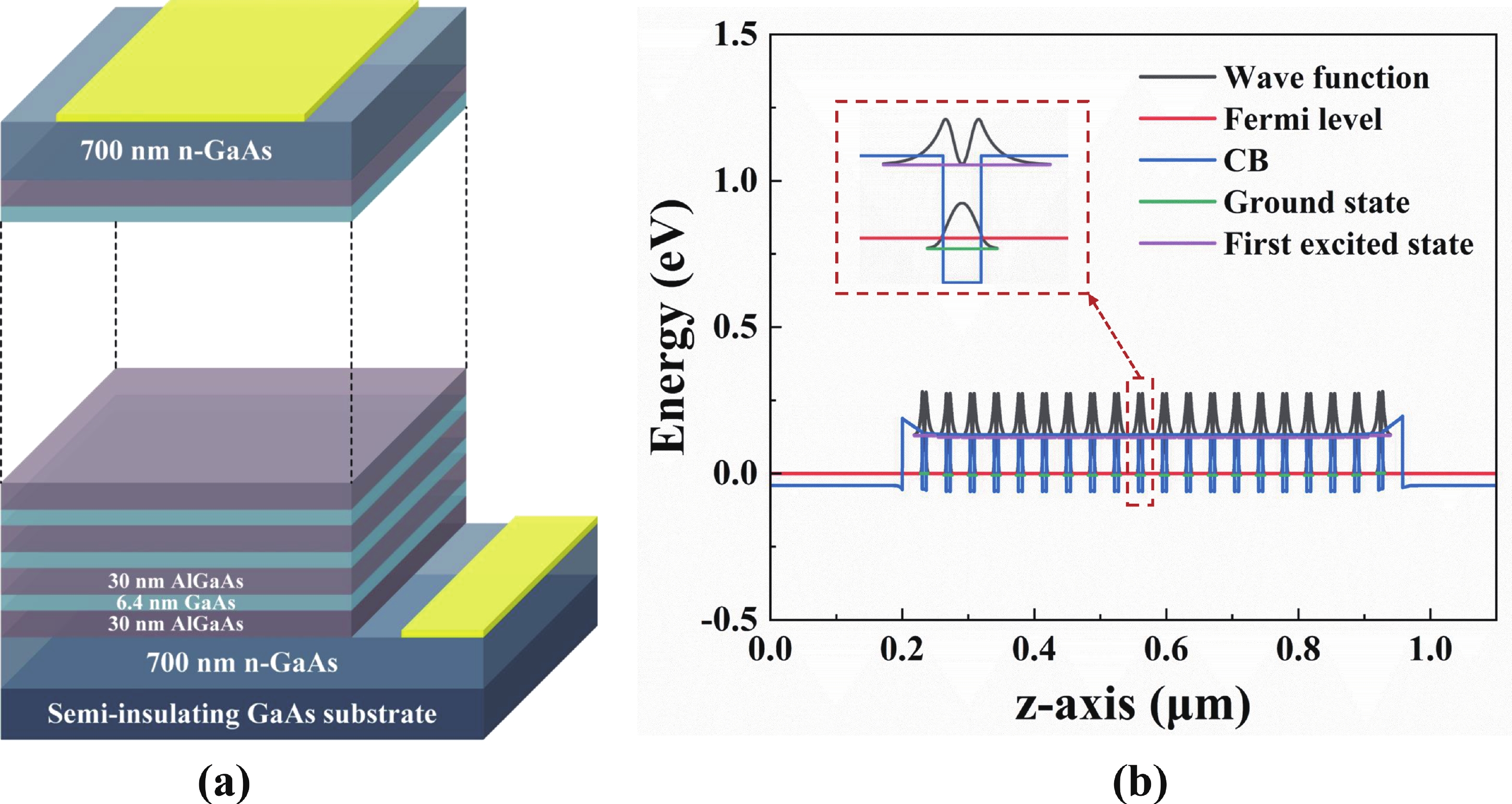
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: