| Citation: |
Xinyu Shen, Zhao Zhang, Jie Yang, Jian Liu, Nanjian Wu, Mohamad Sawan, Liyuan Liu. A 0.0012-mm2 0.66-pJ/bit BPSK demodulator incorporating a loop-filter-less PLL achieving the maximum data rate of fcarrier/2[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, 46(3): 032201. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24100022
****
X Y Shen, Z Zhang, J Yang, J Liu, N J Wu, M Sawan, and L Y Liu, A 0.0012-mm2 0.66-pJ/bit BPSK demodulator incorporating a loop-filter-less PLL achieving the maximum data rate of fcarrier/2[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, 46(3), 032201 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24100022
|
A 0.0012-mm2 0.66-pJ/bit BPSK demodulator incorporating a loop-filter-less PLL achieving the maximum data rate of fcarrier/2
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24100022
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.24100022
More Information-
Abstract
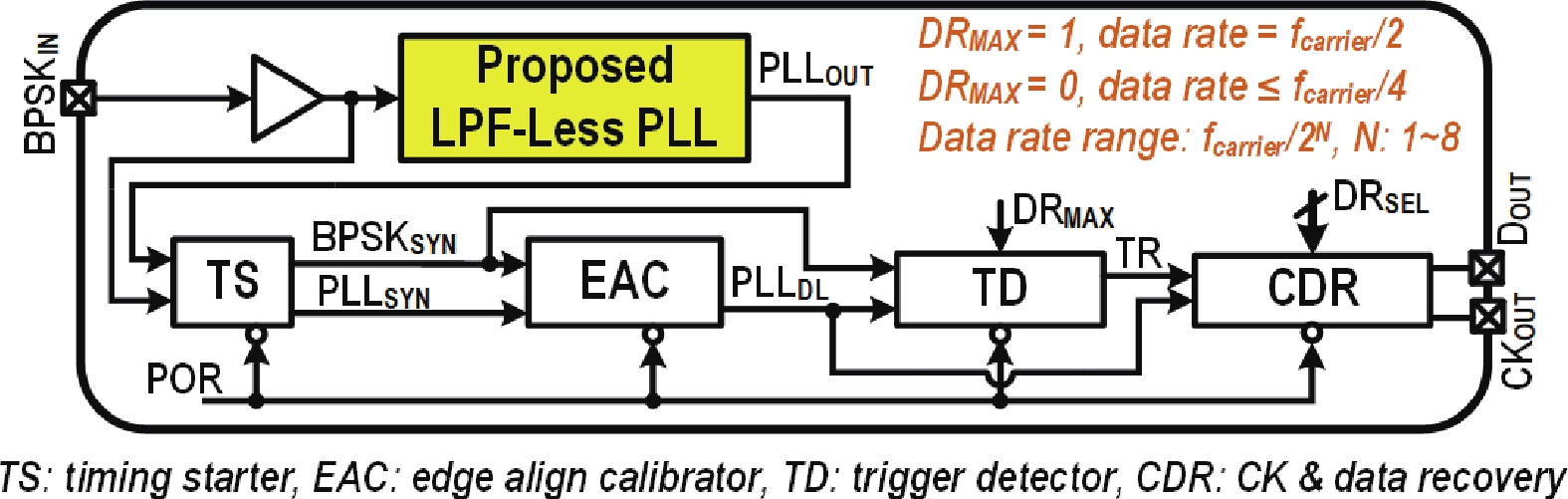
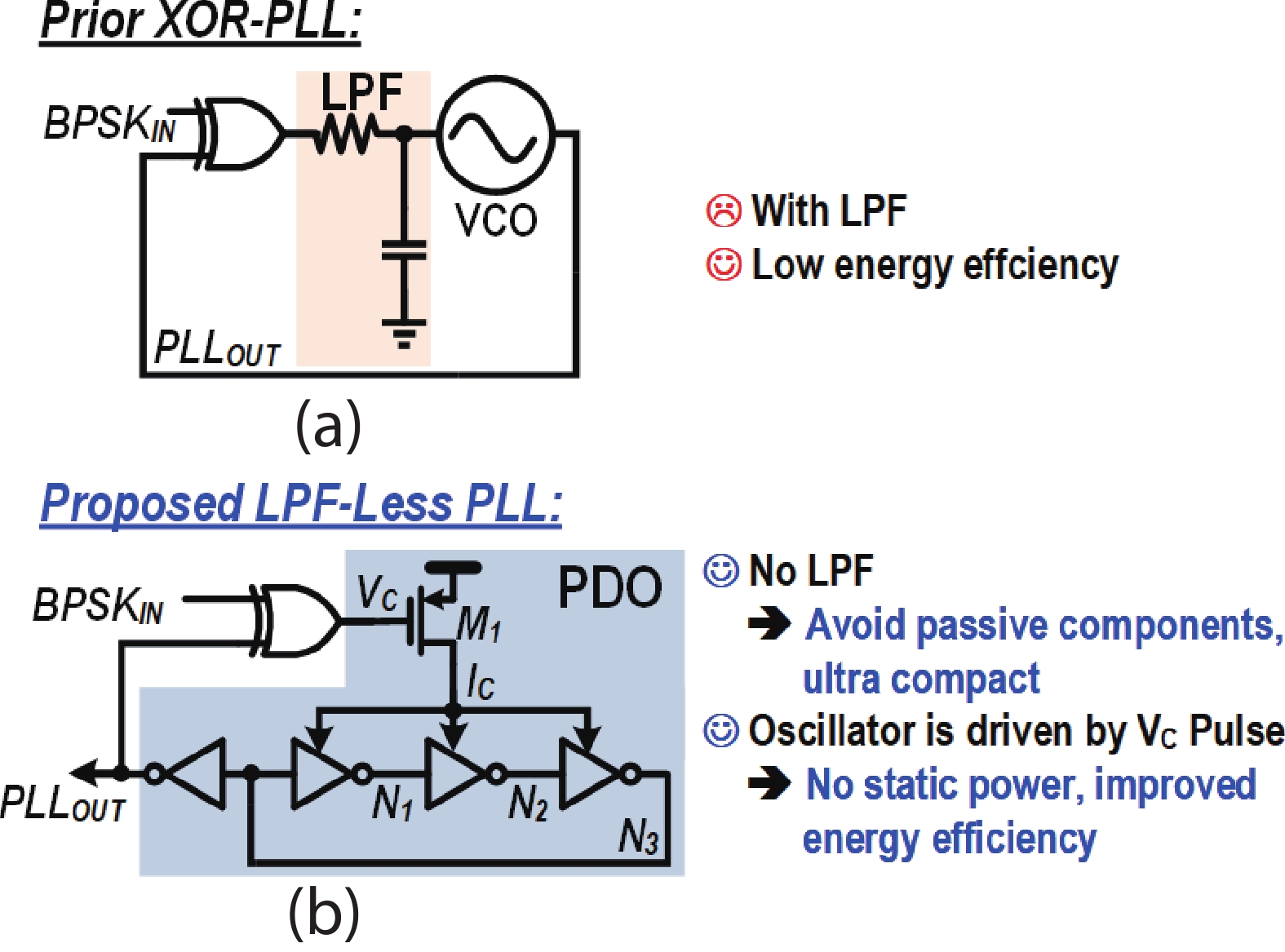
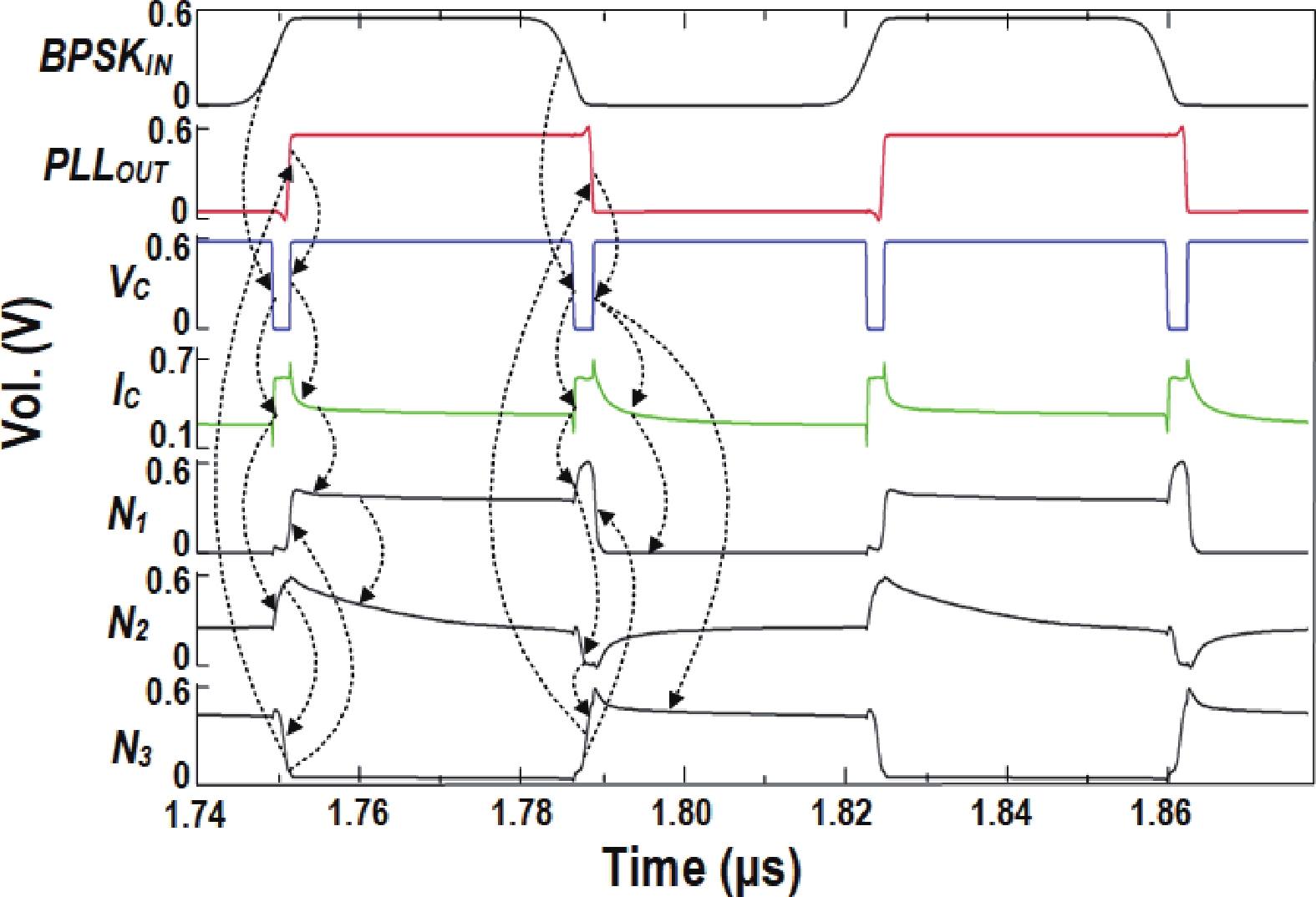
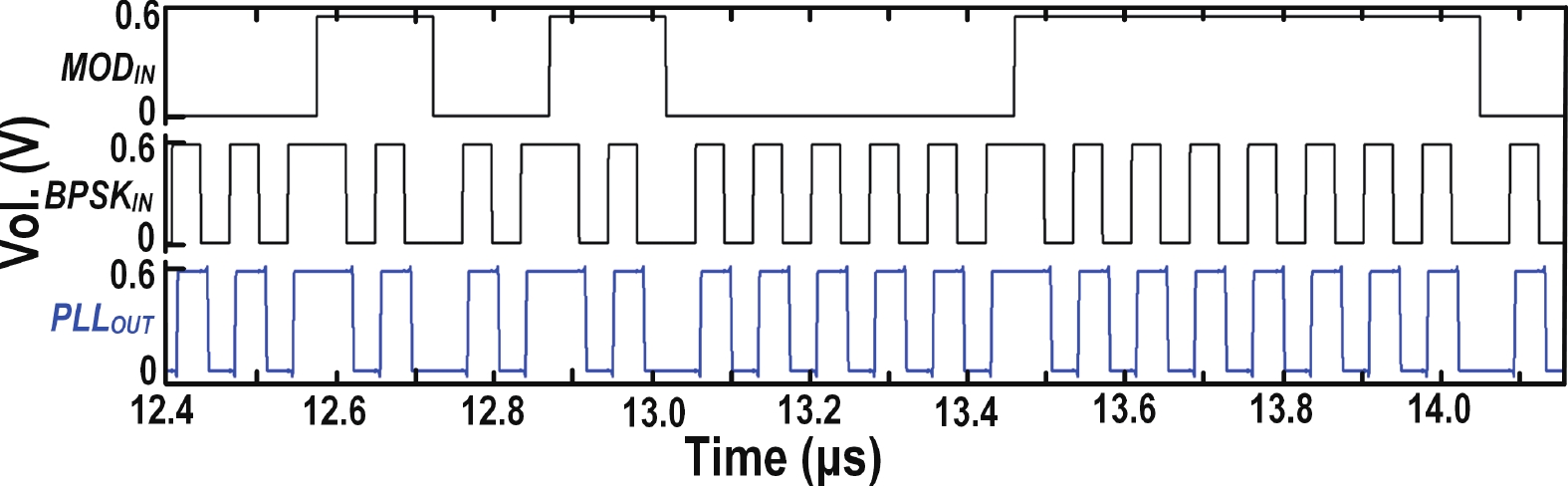
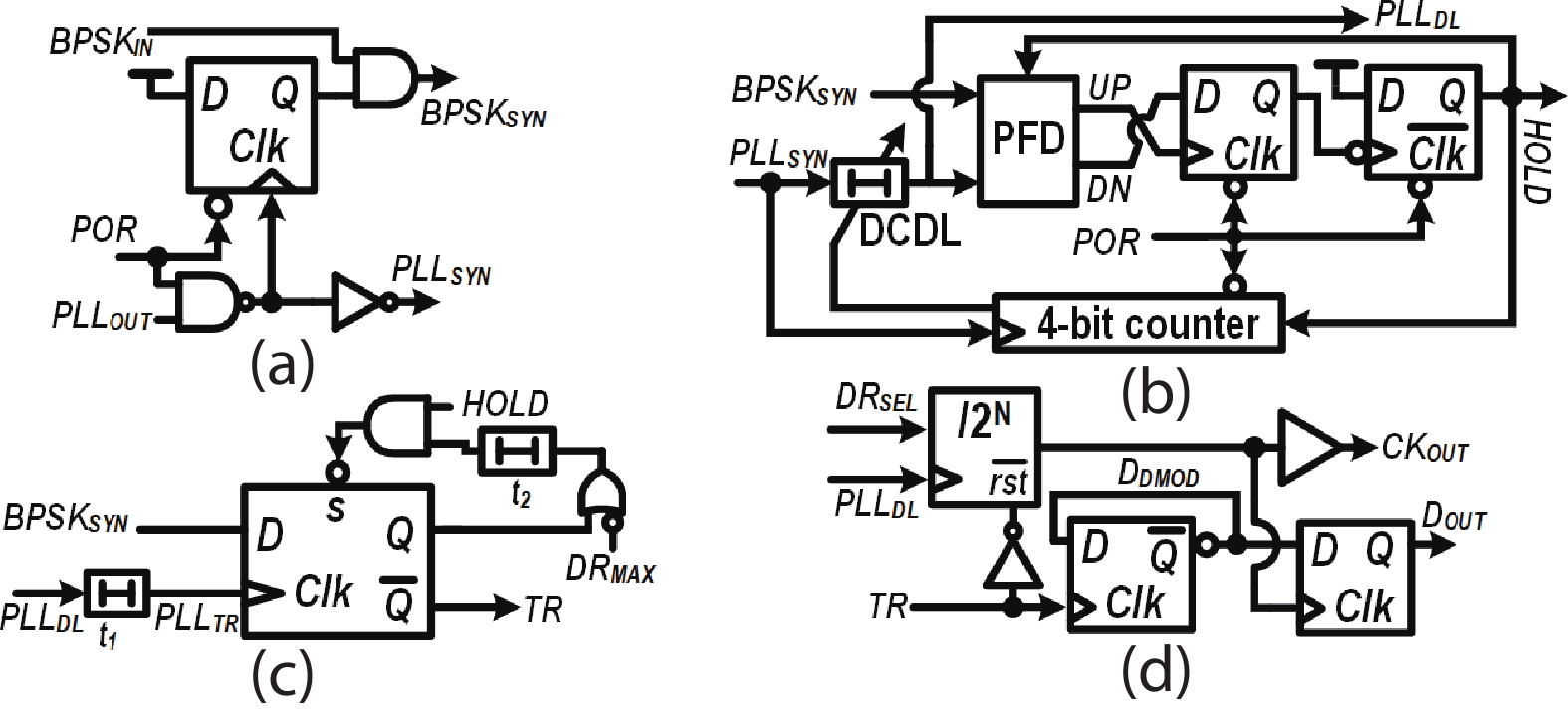
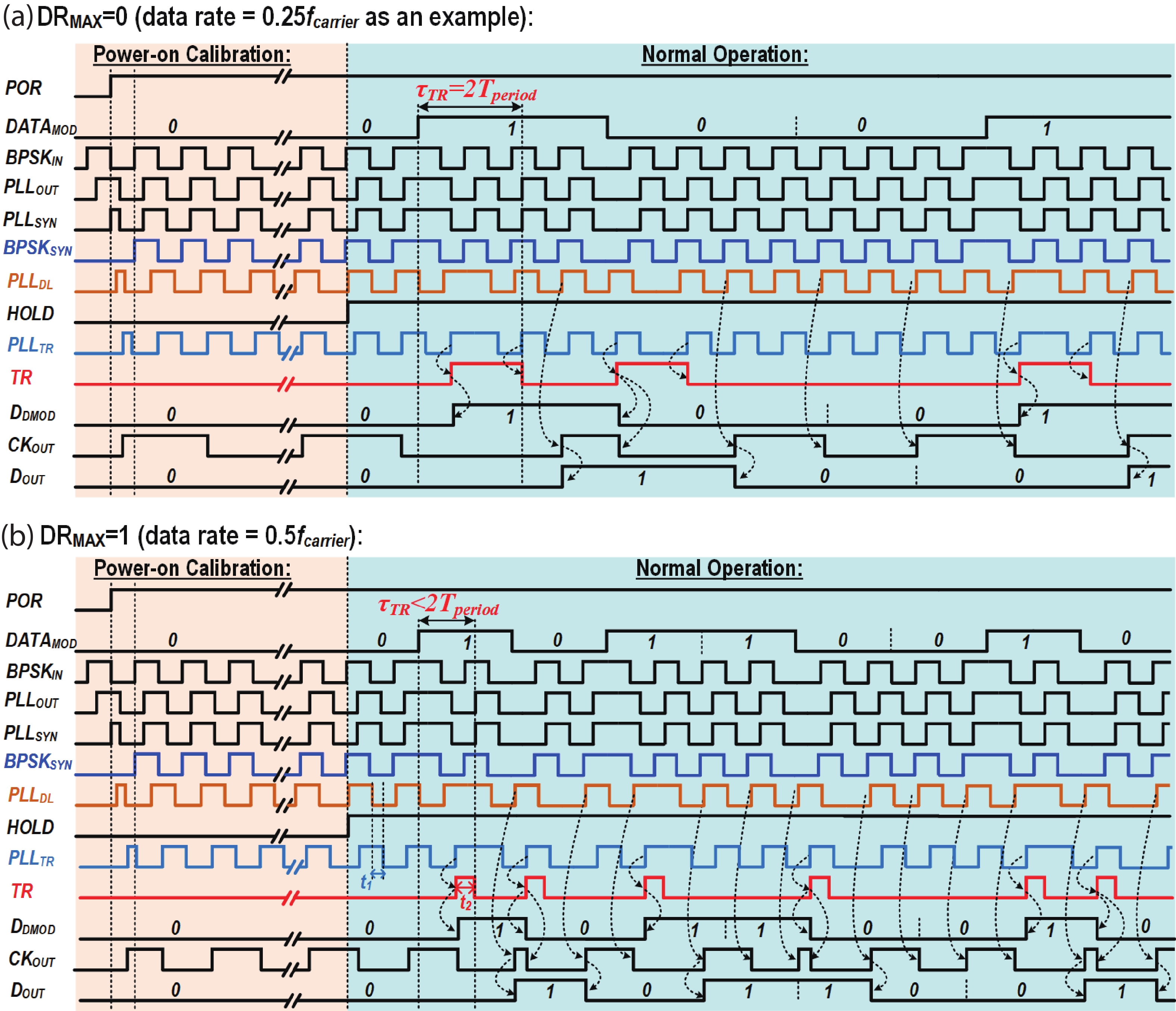
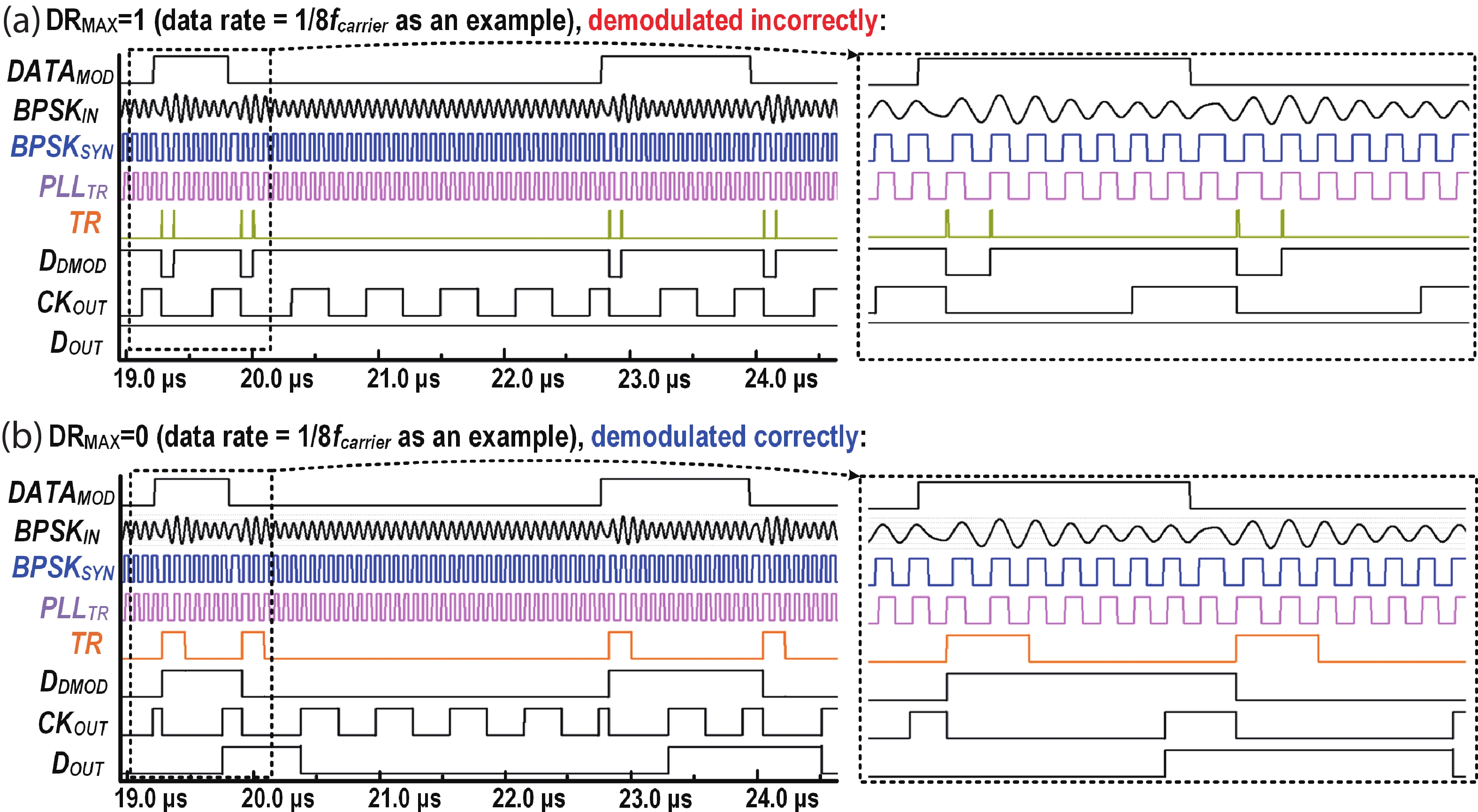
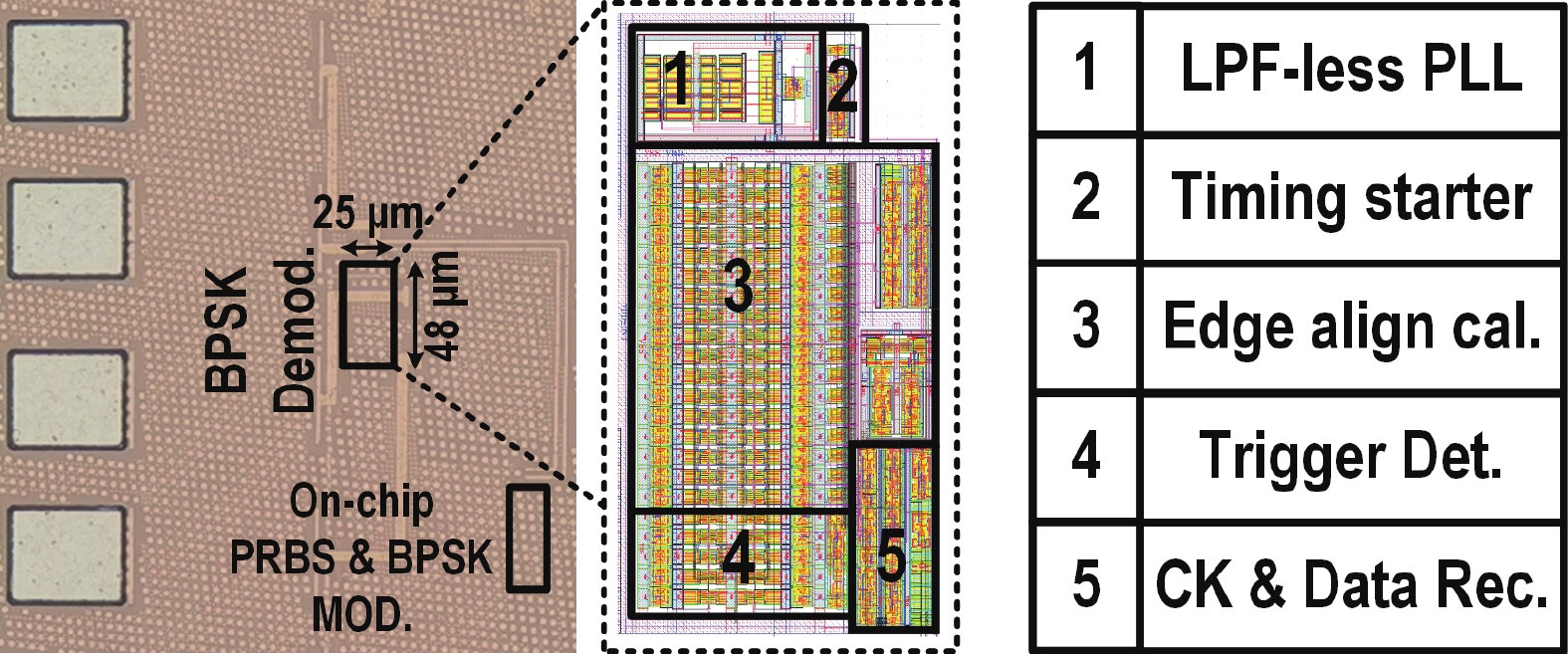
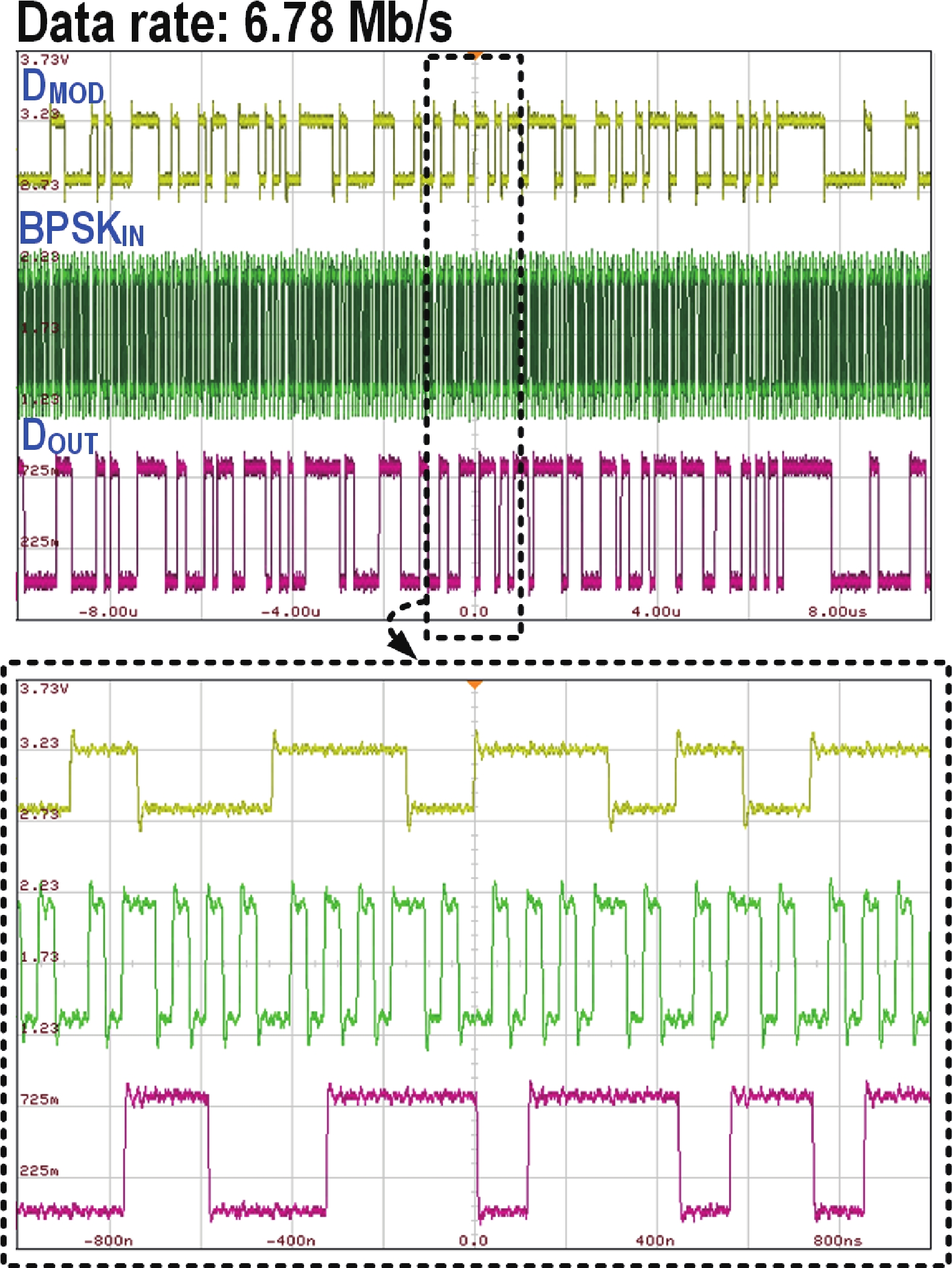
This paper presents a compact ultra-low-power phase-locked loop (PLL) based binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) demodulator. The loop-filter-less (LPF-less) PLL is proposed to make phase of PLL output carrier signal track the phase of BPSK signal in real time. Thus, the maximum date rate can be significantly extended to the half of the carrier frequency (fcarrier) with a very compact size compared to prior PLL-based BPSK demodulators. Furthermore, eliminating all the static power in our LPF-less PLL, the energy efficiency is obviously improved. Fabricated in a 40-nm CMOS process, our prototype occupies 0.0012-mm2 core active area, and achieves the maximum data rate of 6.78 Mb/s (fcarrier/2) at fcarrier of 13.56 MHz. The power consumption and energy efficiency is 4.47 μW and 0.66 pJ/bit at 6.78-Mb/s data rate, respectively.-
Keywords:
- BPSK,
- PLL,
- loop filter,
- compact,
- low-power,
- demodulator,
- wireless power transmission (WPT)
-
References
[1] Wang S H, Huang Y K, Chen C Y, et al. Design of a bone-guided cochlear implant microsystem with monopolar biphasic multiple stimulations and evoked compound action potential acquisition and its in vivo verification. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2021, 56(10), 3062 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3087629[2] Qian X H, Lee Y C, Chang J H, et al. Design and in vivo verification of a CMOS bone-guided cochlear implant microsystem. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2019, 66(11), 3156 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2901374[3] Jia Y Y, Guler U, Lai Y P, et al. 26.8 A trimodal wireless implantable neural interface system-on-chip. 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2020, 414 doi: 10.1109/ISSCC19947.2020.9063065[4] Park Y, Koh S T, Lee J, et al. 33.7 A frequency-splitting-based wireless power and data transfer IC for neural prostheses with simultaneous 115mW power and 2.5Mb/s forward data delivery. 2021 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2021, 472 doi: 10.1109/ISSCC42613.2021.9365781[5] Hu Y M, Sawan M. A fully integrated low-power BPSK demodulator for implantable medical devices. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2005, 52(12), 2552 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2005.858163[6] Cheng C H, Tsai P Y, Yang T Y, et al. A fully integrated 16-channel closed-loop neural-prosthetic CMOS SoC with wireless power and bidirectional data telemetry for real-time efficient human epileptic seizure control. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2018, 53(11), 3314 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2867293[7] Li Y X, Shen X Y, Zhang Z Y, et al. A 0.004-mm2 0.7-V 31.654-μW BPSK demodulator incorporating dual-path loop self-biased PLL. 2022 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), 2022, 569 doi: 10.1109/APCCAS55924.2022.10090331[8] Pan L, Chen M Y, Chen Y F, et al. An energy-autonomous power-and-data telemetry circuit with digital-assisted-PLL-based BPSK demodulator for implantable flexible electronics applications. IEEE Open J Circuits Syst, 2021, 2, 721 doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2021.3119931[9] Cho H, Lee H, Bae J, et al. A 5.2 mW IEEE 802.15. 6 HBC standard compatible transceiver with power efficient delay-locked-loop based BPSK demodulator. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2015, 50(11), 2549 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2475179[10] Lo C Y, Hong H C. A 0.9 pJ/b, reference clock free, delay-based, all-digital coherent BPSK demodulator. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett, 2993, 3, 498 doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2020.3032993[11] Wilkerson B P, Kang J K. A low power BPSK demodulator for wireless implantable biomedical devices. 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2013, 626 doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2013.6571920[12] Zhang Z, Zhu G, Yue C P. A 0.25–0.4-V, sub-0.11-mW/GHz, 0.15–1.6-GHz PLL using an offset dual-path architecture with dynamic charge pumps. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2021, 56(6), 1871 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3028376[13] Kong L, Razavi B. A 2.4 GHz 4 mW integer-N inductorless RF synthesizer. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2016, 51(3), 626 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2511157[14] Zhang Z, Yang J C, Liu L Y, et al. A 0.9–2.25-GHz sub-0.2-mW/GHz compact low-voltage low-power hybrid digital PLL with loop bandwidth-tracking technique. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2018, 26(5), 933 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2018.2797280[15] Molex, Inc. , Lisle, IL, USA). Product Specification 1462360001-PS. [Online].[16] Karimi M, Maghami M H, Faizollah M, et al. A noncoherent low-power high-data-rate BPSK demodulator and clock recovery circuit for implantable biomedical devices. 2014 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) Proceedings, 2014, 372 doi: 10.1109/BioCAS.2014.6981740 -
Proportional views




 Xinyu Shen is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. His current research interests include low-jitter analog and wideband frequency synthesizers.
Xinyu Shen is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree with the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. His current research interests include low-jitter analog and wideband frequency synthesizers. Zhao Zhang is now a a Full Professor with the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. His research interests include the design of wireline transceivers, low-jitter and low-power PLLs, and ultra-low voltage ICs for bio/energy-harvesting applications.
Zhao Zhang is now a a Full Professor with the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. His research interests include the design of wireline transceivers, low-jitter and low-power PLLs, and ultra-low voltage ICs for bio/energy-harvesting applications. Jie Yang is a Research Professor at Westlake University. He earned his B.S. in Electronic Science and Technology from Tianjin University (2010) and his Ph.D. in Microelectronics from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2015). From 2015 to 2019, he was a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Calgary. His research focuses on brain-computer interfaces, energy-efficient neuromorphic computing chips, and neural decoding.
Jie Yang is a Research Professor at Westlake University. He earned his B.S. in Electronic Science and Technology from Tianjin University (2010) and his Ph.D. in Microelectronics from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2015). From 2015 to 2019, he was a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Calgary. His research focuses on brain-computer interfaces, energy-efficient neuromorphic computing chips, and neural decoding. Jian Liu is a Full Professor in microelectronics and solid-state electronics with the State Key Laboratory of Super-lattices and Microstructures, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, since 2005. His research interests include semiconductor optoelectronic detectors, terahertz imagers, and metamaterials.
Jian Liu is a Full Professor in microelectronics and solid-state electronics with the State Key Laboratory of Super-lattices and Microstructures, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, since 2005. His research interests include semiconductor optoelectronic detectors, terahertz imagers, and metamaterials. Nanjian Wu has been a Professor with the State Key Laboratory of Super-lattices and Microstructures, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, since 2000. His research includes the field of mixed-signal VLSI and vision chip design.
Nanjian Wu has been a Professor with the State Key Laboratory of Super-lattices and Microstructures, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, since 2000. His research includes the field of mixed-signal VLSI and vision chip design. Mohamad Sawan is Chair Professor at Westlake University. He has published over 800 peer-reviewed papers, holds 12 patents, and received numerous awards, including the Queen Elizabeth Ⅱ Golden Jubilee Medal and the Barbara Turnbull Award. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Sciences of Canada (FRSC), a Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Engineering (FCAE), a Fellow of the Engineering Institutes of Canada (FEIC), a Life Fellow of the IEEE (LFIEEE), and an "Officer" of the National Order of Quebec. His research interests include biomedical engineering, particularly in the field of implantable bionics.
Mohamad Sawan is Chair Professor at Westlake University. He has published over 800 peer-reviewed papers, holds 12 patents, and received numerous awards, including the Queen Elizabeth Ⅱ Golden Jubilee Medal and the Barbara Turnbull Award. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Sciences of Canada (FRSC), a Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Engineering (FCAE), a Fellow of the Engineering Institutes of Canada (FEIC), a Life Fellow of the IEEE (LFIEEE), and an "Officer" of the National Order of Quebec. His research interests include biomedical engineering, particularly in the field of implantable bionics. Liyuan Liu joined the State Key Laboratory of Super-lattices and Microstructures, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, as an Associate Professor in 2012, where he became a Professor in 2018. His research interests include mixed-signal IC design, CMOS image sensors design, terahertz image sensors design, and monolithic vision chip design.
Liyuan Liu joined the State Key Laboratory of Super-lattices and Microstructures, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, as an Associate Professor in 2012, where he became a Professor in 2018. His research interests include mixed-signal IC design, CMOS image sensors design, terahertz image sensors design, and monolithic vision chip design.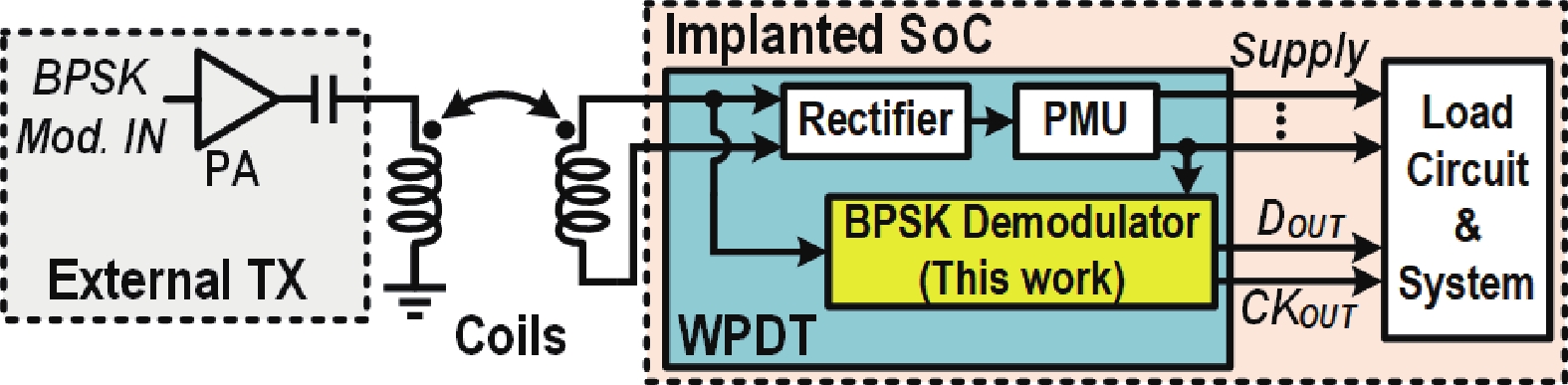
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: