| Citation: |
Chen Jiang, Yumei Huang, Zhiliang Hong. A multi-path gated ring oscillator based time-to-digital converter in 65 nm CMOS technology[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(3): 035004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/035004
****
C Jiang, Y M Huang, Z L Hong. A multi-path gated ring oscillator based time-to-digital converter in 65 nm CMOS technology[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(3): 035004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/035004.
|
A multi-path gated ring oscillator based time-to-digital converter in 65 nm CMOS technology
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/3/035004
More Information
-
Abstract
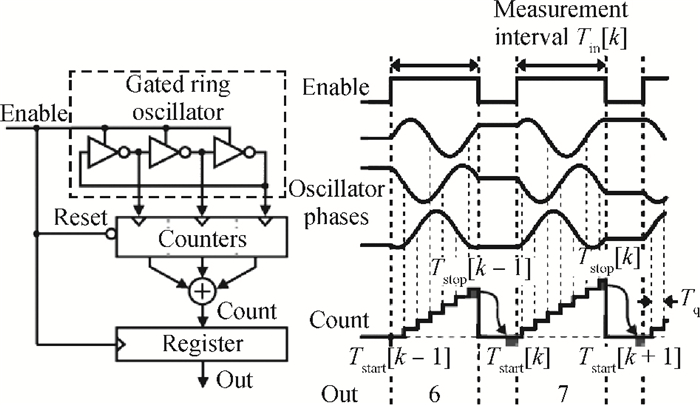
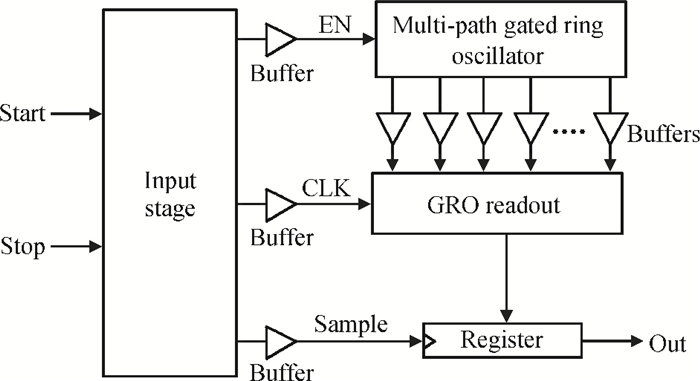
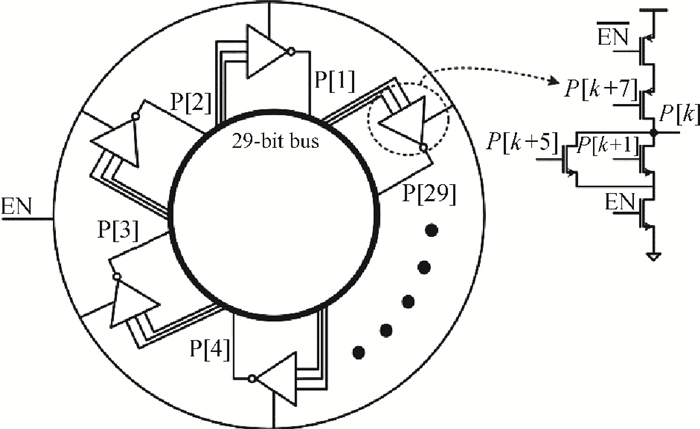
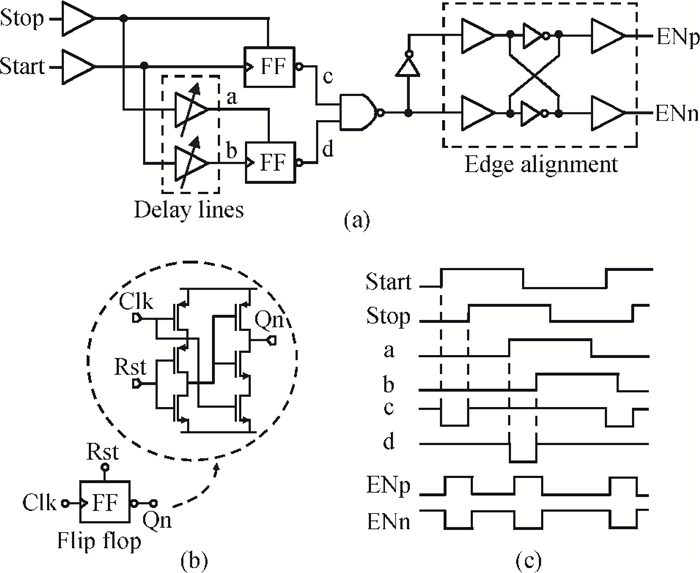
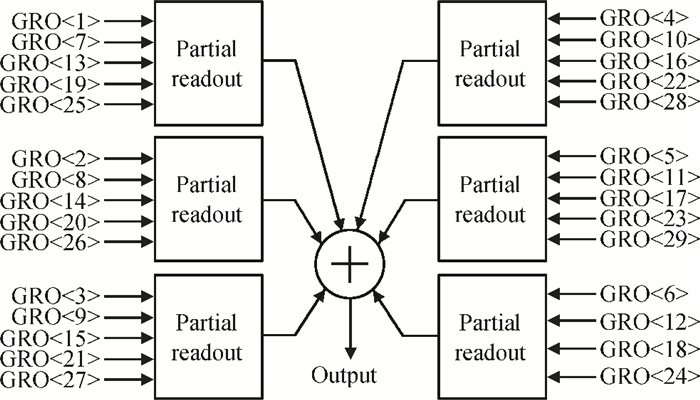
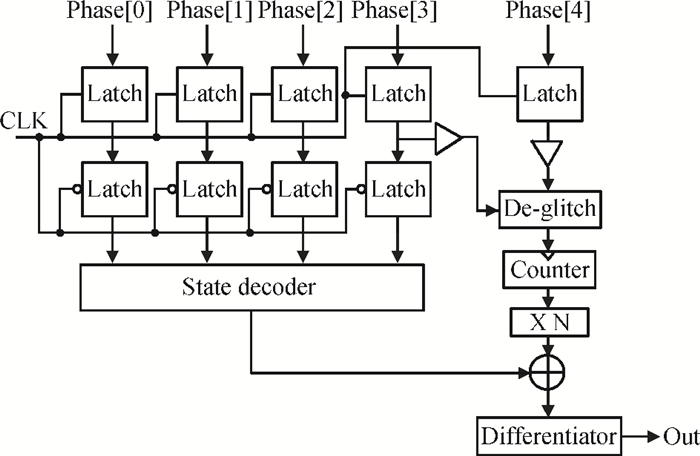
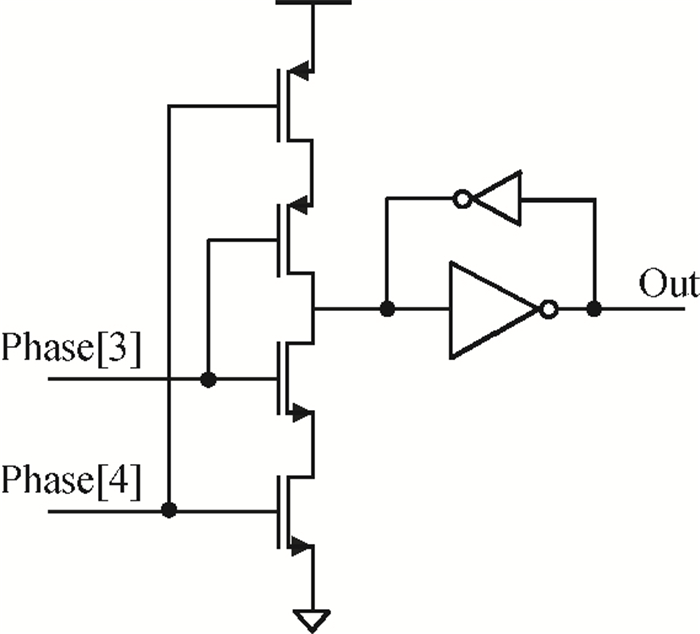
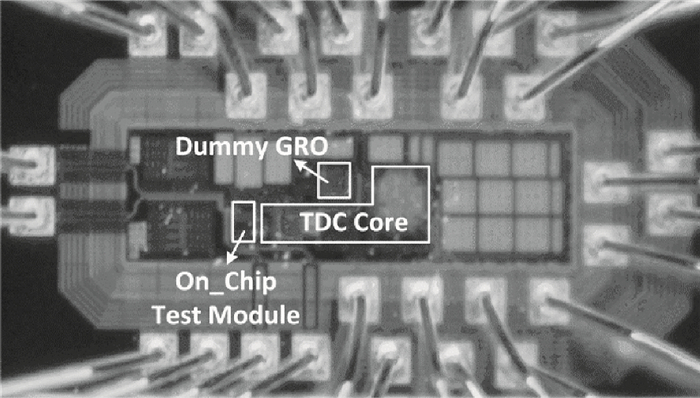
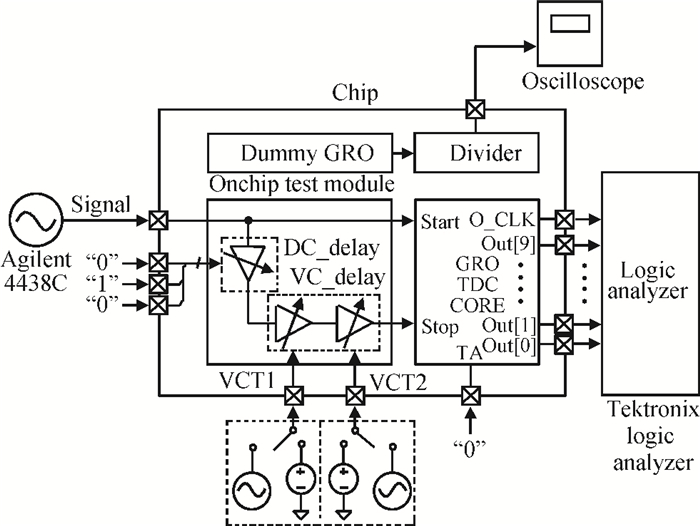
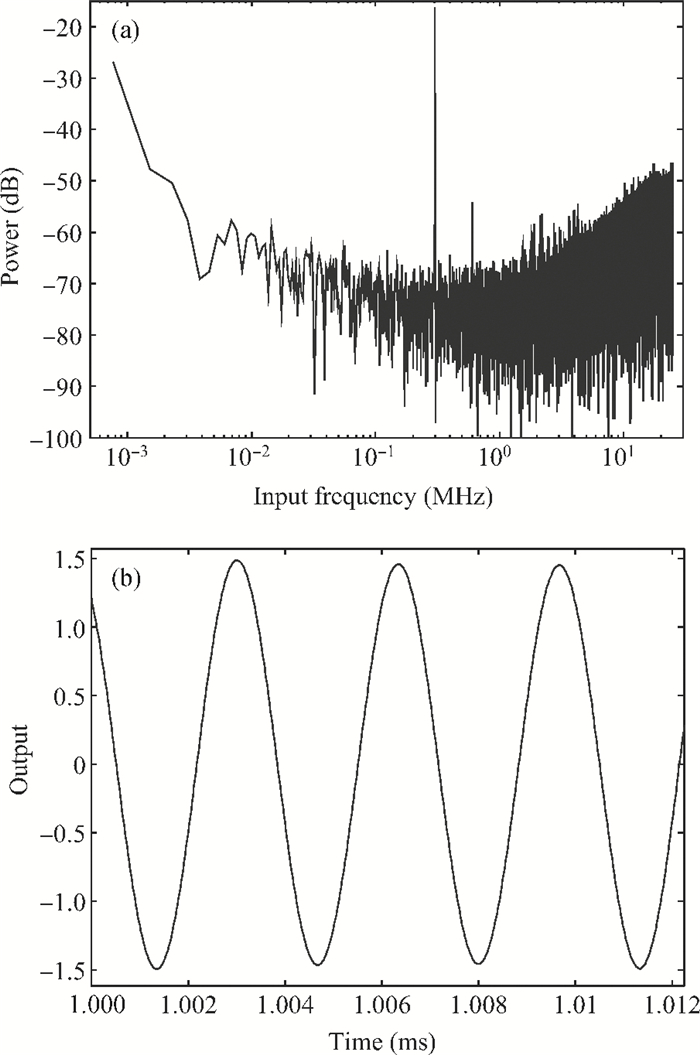
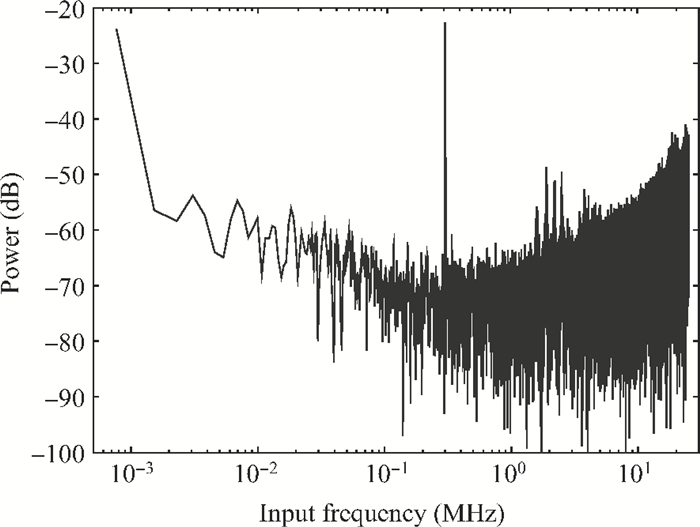
A gated ring oscillator (GRO) based time-to-digital converter (TDC) is presented. To enhance the resolution of the TDC, a multi-path structure for the GRO is used to achieve a higher oscillation frequency and an input stage is also presented to equivalently amplify the input time difference with a gain of 2. The GRO based TDC circuit is fabricated in TSMC 65 nm CMOS technology and the core area is about 0.02 mm2. According to the measurement results, the effective resolution of this circuit is better than 4.22 ps under a 50 MHz clock frequency. With a 1 ns input range, the maximum clock frequency of this circuit is larger than 200 MHz. Under a 1 V power supply, with a 200-800 ps input time difference, the measured power consumption is 1.24 to 1.72 mW at 50 MHz clock frequency and 1.73 to 2.20 mW at 200 MHz clock frequency. -
References
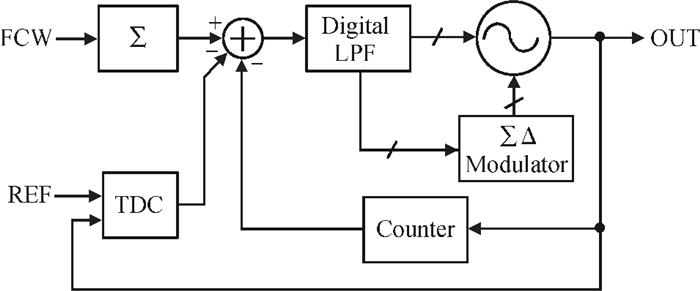
[1] Staszewski R B, Wallberg J L, Rezeq S, et al. All-digital PLL and transmitter for mobile phones. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(12):2469 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.857417[2] Jiang C, Liu J, Huang Y, et al. A low-noise, 8.95-11 GHz all-digital frequency synthesizer with a metastability-free time-to-digital converter and a sleepy counter in 65 nm CMOS. Proceeding of the 38th European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2012:3[3] Dudek P, Szczepanski S, Hatfield J V. A high-resolution CMOS time-to-digital converter utilizing a vernier delay line. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2000, 35(2):240 doi: 10.1109/4.823449[4] Chen P, Liu S, Wu J. A CMOS pulse-shrinking delay element for time interval measurement. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, 2000, 47(9):954 doi: 10.1109/82.868466[5] Straayer M Z, Perrott M H. A multi-path gated ring oscillator TDC with first-order noise shaping. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(4):1089 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2014709[6] Minjae L, Abidi A A. A 9 b, 1.25 ps resolution coarse-fine time-to-digital converter in 90 nm CMOS that amplifies a time residue. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(4):769 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.917405[7] Nissinen I, Mantyniemi A, Kostamovaara J. A CMOS time-to-digital converter based on a ring oscillator for a laser radar. Proceedings of the 29th European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2003:469 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1257174/?tp=&arnumber=1257174&contentType=Conference%20Publications&searchField%3DSearch_All%26queryText%3DA%20CMOS%20time-to%20digital%20converter%20based%20on%20a%20ring%20oscillator%20for%20a%20laser%20radar[8] Lee S, Kim B, Lee K. A novel high-speed ring oscillator for multiphase clock generation using negative skewed delay scheme. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1997, 32(2):289 doi: 10.1109/4.551926[9] Staszewski R B, Vemulapalli S, Vallur P, et al. 1.3 V 20 ps time-to-digital converter for frequency synthesis in 90-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅱ, 2006, 53(3):220 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2005.858754 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: