| Citation: |
Lian Ning, Lijun Guo, Mei Kong, Tuoyuan Chen. Waveguide-type optical passive ring resonator gyro using frequency modulation spectroscopy technique[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(12): 124008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/124008
****
L Ning, L J Guo, M Kong, T Y Chen. Waveguide-type optical passive ring resonator gyro using frequency modulation spectroscopy technique[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(12): 124008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/124008.
|
Waveguide-type optical passive ring resonator gyro using frequency modulation spectroscopy technique
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/124008
More Information
-
Abstract
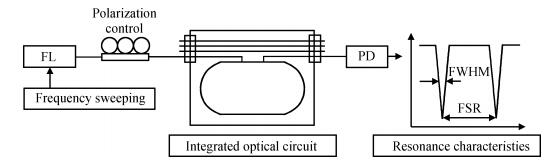
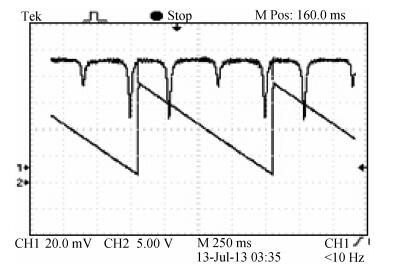
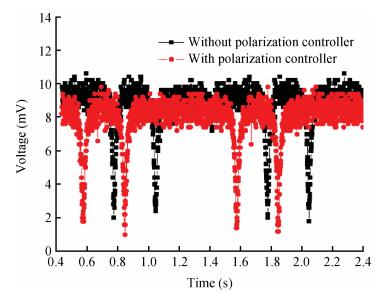
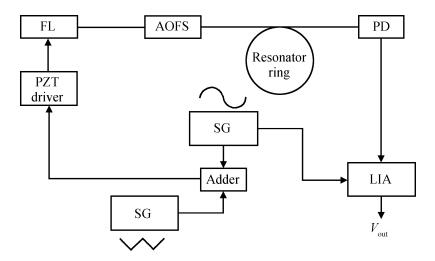
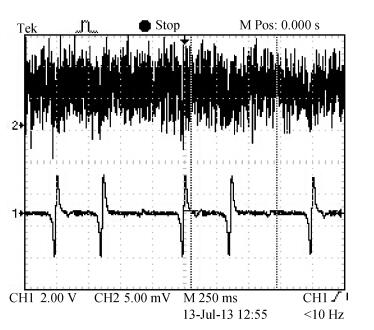
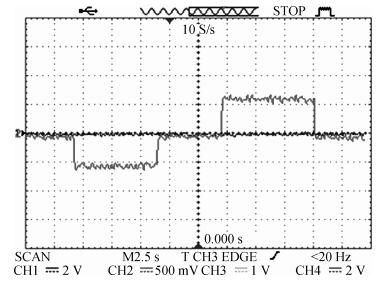
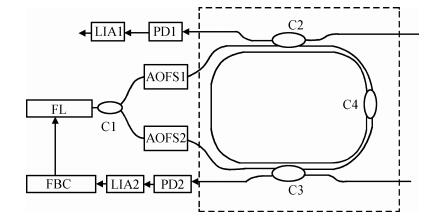
This paper reports the experimental results of silica on a silicon ring resonator in a resonator micro optic gyroscope based on the frequency modulation spectroscopy technique by our research group. The ring resonator is composed of a 4 cm diameter silica waveguide. By testing at λ=1550 nm, the FSR, FWHM and the depth of resonance are 3122 MHz, 103.07 MHz and 0.8 respectively. By using a polarization controller, the resonance curve under the TM mode can be inhibited. The depth of resonance increased from 0.8 to 0.8913, namely the finesse increase from 30.33 to 33.05. In the experiments, there is an acoustic-optical frequency shifter (AOFS) in each light loop. We lock the lasing frequency at the resonance frequency of the silica waveguide ring resonator for the counterclockwise lightwave; the frequency difference between the driving frequencies of the two AOFS is equivalent to the Sagnac frequency difference caused by gyro rotation. Thus, the gyro output is observed. The slope of the linear fit is about 0.330 mV/(°/s) based on the -900 to 900 kHz equivalent frequency and the gyro dynamic range is ±2.0×103 rad/s.-
Keywords:
- ring resonator,
- micro optic gyroscope,
- resonance frequency
-
References
[1] Chen W Y, Grover R, Ibrahim T A, et al. High-finesse laterally coupled single-mode benzocyclobutene microring resonators. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2004, 16:470 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2003.823131[2] Haavisto J, Pajer G A. Resonance effects in low-loss ring waveguides. Opt Lett, 1980, 5:510 doi: 10.1364/OL.5.000510[3] Connors J, Mahapatra A. High finesse ring resonators made by silver ion exchange in glass. Lightwave Technol, 1987, 5:1686 doi: 10.1109/JLT.1987.1075482[4] Walker R G, Wilkinson C D W. Integrated optical ring resonators made by silver ion-exchange in glass. Opt, 1983, 22:1029[5] Naumaan A, Boyd J. Ring resonator fabricated in phosphosilicate glass films deposited by chemical vapor deposition. Lightwave Technol, 1986, 4:1294 doi: 10.1109/JLT.1986.1074887[6] Bismuth J, Gidon P, Revol F, et al. Low-loss ring resonators fabricated from silicon based integrated optics technologies. Lett, 1991, 27:722[7] Ciminelli, Caterina, Dell'Olio F, et al. Armenise photonic technologies for angular velocity sensing. Opt, 2010, 2:370[8] Yu H Y, Zhang C X, Feng L S, et al. SiO2 waveguide resonator used in an integrated optical gyroscope. Chin Phys Lett, 2009, 26:054210 doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/26/5/054210[9] Guo L J, Shi B R, Zhao M, et al. A single-mode single-polarization monolithically silica waveguide ring resonator used in microoptic gyro. J Mod Opt, 2010, 57:303 doi: 10.1080/09500340903576425[10] Zhang B, Pan Z W, Ding H G, et al. Research on surface acoustic wave acousto-optic frequency shifter for a micro optic gyro. J Tsinghua University (Sci Technol), 1999, 39:65[11] Suzuki K, Takiguchi K, Hotate K. Monolithically integrated resonator microoptic gyro on silica planar lightwave circuit. J Lightwave Technol, 2000, 18:66 doi: 10.1109/50.818908[12] Armenise M N, Ciminelli C, Dell'Oli F. Advances in gyroscope technologies, Springer Verlag, 2011[13] Guo L J, Shi B R, Zhao M. A single-mode single-polarization monolithically silica waveguide ring resonator used in microoptic gyro. J Mod Optic, 2010, 57:303 doi: 10.1080/09500340903576425[14] Pinnoji P D, Nayak J. Design and analysis of a dual-axis resonator fiber optic gyroscope employing a single source. Appl Opt, 2013, 52:5350 doi: 10.1364/AO.52.005350[15] Barbour N M. Inertial navigation sensors. RTO EN SET, 2011, 116:1[16] Vlasov Y, Green W. High-throughput silicon nanophotonic wavelength insensitive switch for on-chip optical networks. Nat Photon, 2008, 4:242[17] Carroll R, Coccoli C D, Cardarelli D. The passive resonator fiber optic gyro and comparison to the interferometer fiber gyro. SPIE, 1986, 719:169[18] Imai T, Nishide K I, Ochi H. Passive ring resonator fiber optic gyro using modulatable highly coherent laser diode module. SPIE, 1992, 1585:153[19] Ma H L, Zhang X L, Jin Z H. Waveguide-type optical passive ring resonator gyro using phase modulation spectroscopy technique. OE Lett, 2006, 45:1[20] Zhang X L, Zhou K J. Open-loop experiments of resonator micro-optic gyro. Optoelectron Lett, 2009, 5:970[21] Zhang X L, Ma H L, Zhou K J. Experiments by PM spectroscopy in resonator fiber optic gyro. Opt Fiber Technol, 2007, 13:135 doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2006.10.004[22] Zhang X L, Ma H L. An open-loop test of a resonator fiber optic gyro. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2006, 27:688[23] Comtois J H, Michalicek M A, Barron C C. Characterization of electrothermal actuators and arrays fabricated in a four-level, planarized surface-micromachined polycrystalline silicon process. Proceedings of the 43 International Instrumentation Symposium, 1997, 2:169[24] Ezekiel S, Balsamo R. Passive ring resonator laser gyroscope. Appl Phys Lett, 1977, 30:478 doi: 10.1063/1.89455[25] Zhang X L, Zhou K J. Open-loop experiments of resonator micro-optic gyro. Optoelectron Lett, 2009, 5(2):97 doi: 10.1007/s11801-009-8144-5 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: