| Citation: |
Yongye Liang, Kyungsoo Jang, S. Velumani, Cam Phu Thi Nguyen, Junsin Yi. Effects of interface trap density on the electrical performance of amorphous InSnZnO thin-film transistor[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(2): 024007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/024007
****
Y Y Liang, K Jang, S. Velumani, C P T Nguyen, J. Yi. Effects of interface trap density on the electrical performance of amorphous InSnZnO thin-film transistor[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(2): 024007. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/024007.
|
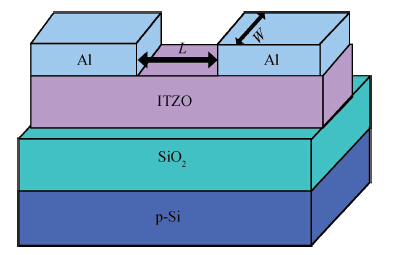
Effects of interface trap density on the electrical performance of amorphous InSnZnO thin-film transistor
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/2/024007
More Information
-
Abstract
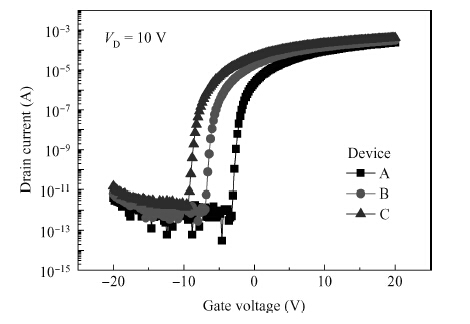
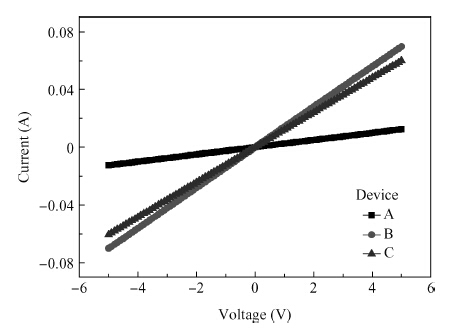
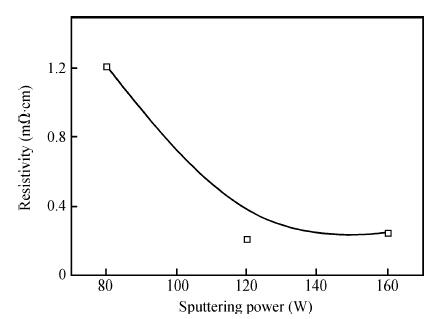
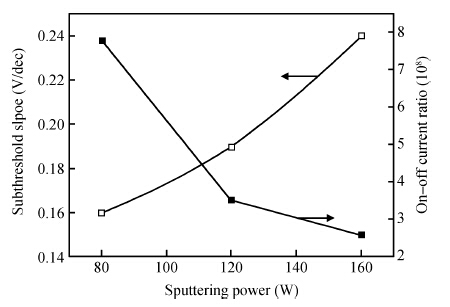
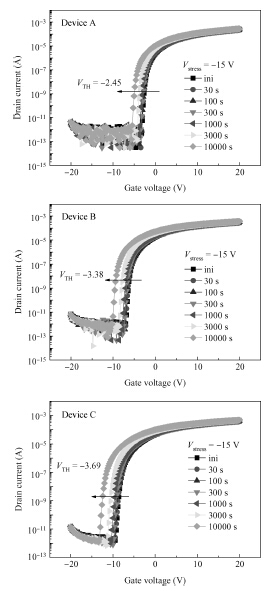
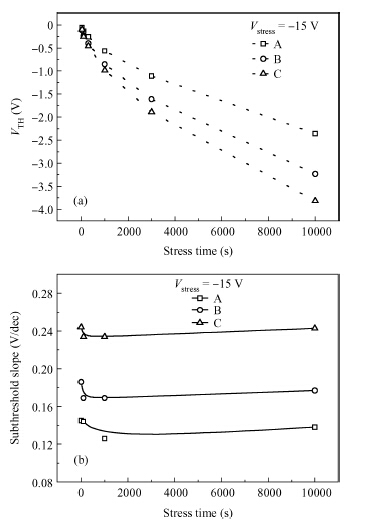
We reported the influence of interface trap density (Nt) on the electrical properties of amorphous InSnZnO based thin-film transistors, which were fabricated at different direct-current (DC) magnetron sputtering powers. The device with the smallest Nt of 5.68 × 1011 cm-2 and low resistivity of 1.21 × 10-3 Ω · cm exhibited a turn-on voltage (VON) of -3.60 V, a sub-threshold swing (S.S) of 0.16 V/dec and an on-off ratio (ION/IOFF) of ~ 8 × 108. With increasing Nt, the VON, S.S and ION/IOFF were suppressed to —9.40 V, 0.24 V/dec and 2.59 × 108, respectively. The VTH shift under negative gate bias stress has also been estimated to investigate the electrical stability of the devices. The result showed that the reduction in Nt contributes to an improvement in the electrical properties and stability. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: