| Citation: |
Pengjun Wang, Xuelong Zhang, Yuejun Zhang, Jianrui Li. Design of a reliable PUF circuit based on R-2R ladder digital-to-analog convertor[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(7): 075005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/7/075005
****
P J Wang, X L Zhang, Y J Zhang, J R Li. Design of a reliable PUF circuit based on R-2R ladder digital-to-analog convertor[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(7): 075005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/7/075005.
|
Design of a reliable PUF circuit based on R-2R ladder digital-to-analog convertor
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/7/075005
More Information
-
Abstract
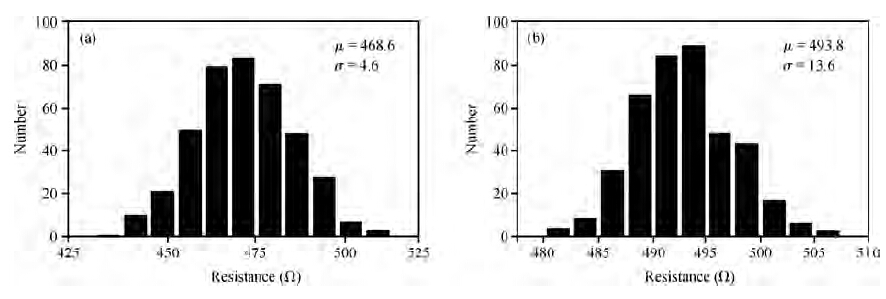
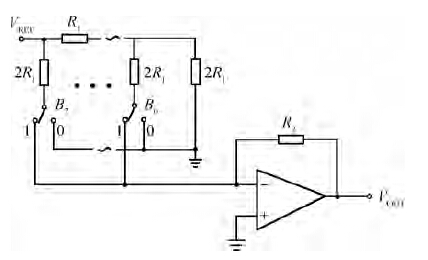
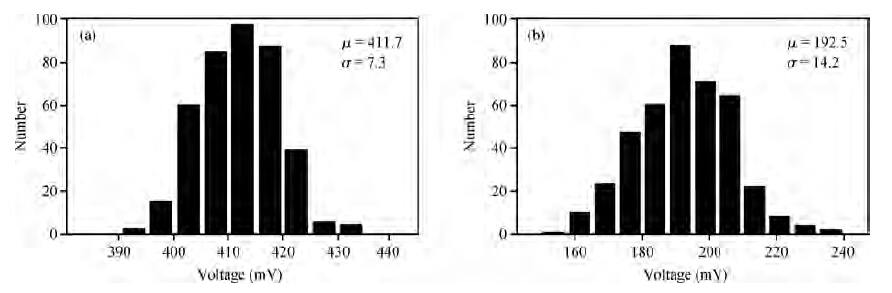
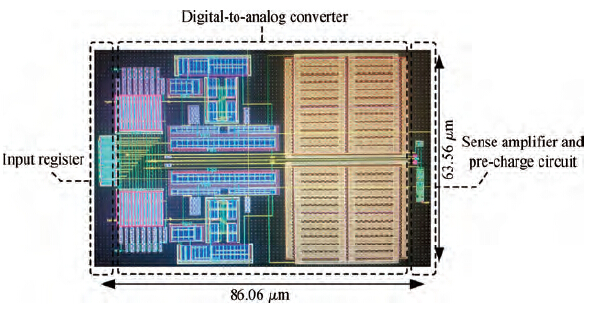
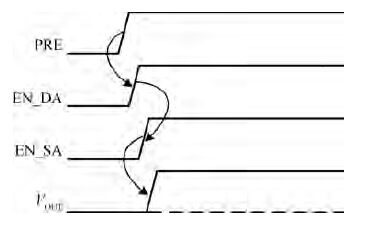
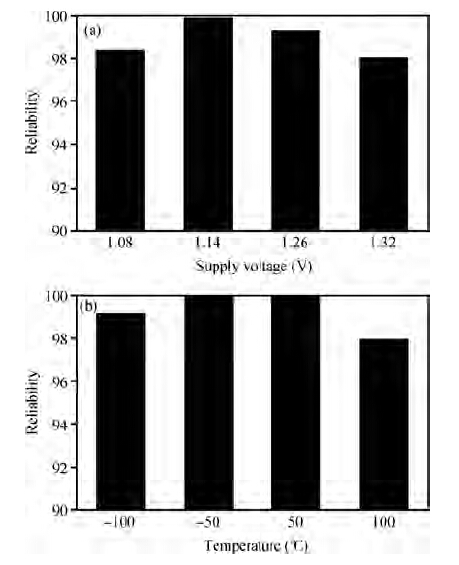
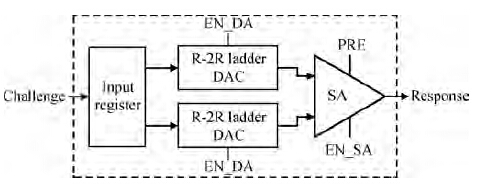
A novel physical unclonable functions (PUF) circuit is proposed, which relies on non-linear characteristic of analog voltage generated by R-2R ladder DAC. After amplifying the deviation signal, the robustness of the DAC-PUF circuit has increased significantly. The DAC-PUF circuit is designed in TSMC 65 nm CMOS technology and the layout occupies 86.06 × 63.56 μm2. Monte Carlo simulation results show that the reliability of the DAC-PUF circuit is above 98% over a comprehensive range of environmental variation, such as temperature and supply voltage. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: