| Citation: |
Miao Liu, Dong Wu, Zheyao Wang. A readout integrated circuit based on DBI-CTIA and cyclic ADC for MEMS-arraybased focal plane[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(11): 115002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/115002
****
M Liu, D Wu, Z Y Wang. A readout integrated circuit based on DBI-CTIA and cyclic ADC for MEMS-arraybased focal plane[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(11): 115002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/115002.
|
A readout integrated circuit based on DBI-CTIA and cyclic ADC for MEMS-arraybased focal plane
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/115002
More Information
-
Abstract
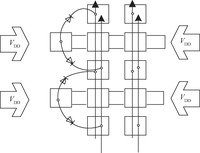
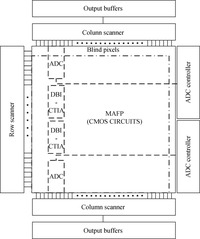
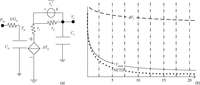
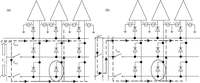
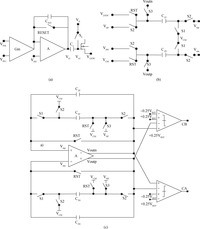
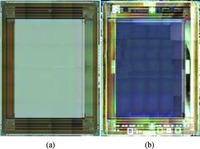
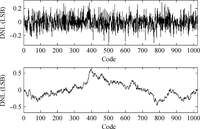
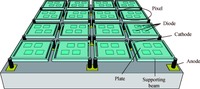
A readout integrated circuit (ROIC) for a MEMS (microelectromechanical system)-array-based focal plane (MAFP) intended for imaging applications is presented. The ROIC incorporates current sources for diode detectors, scanners, timing sequence controllers, differential buffered injection-capacitive trans-impedance amplifier (DBI-CTIA) and 10-bit cyclic ADCs, and is integrated with MAFP using 3-D integration technology. A small-signal equivalent model is built to include thermal detectors into circuit simulations. The biasing current is optimized in terms of signal-to-noise ratio and power consumption. Layout design is tailored to fulfill the requirements of 3-D integration and to adapt to the size of MAFP elements, with not all but only the 2 bottom metal layers to complete nearly all the interconnections in DBI-CTIA and ADC in a 40 μm wide column. Experimental chips are designed and fabricated in a 0.35 μm CMOS mixed signal process, and verified in a code density test of which the results indicate a (0.29/-0.31) LSB differential nonlinearity (DNL) and a (0.61/-0.45) LSB integral nonlinearity (INL). Spectrum analysis shows that the effective number of bits (ENOB) is 9.09. The ROIC consumes 248 mW of power at most if not to cut off quiescent current paths when not needed.-
Keywords:
- MAFP,
- ROIC,
- diode thermal detector,
- DBI-CTIA,
- cyclic ADC
-
References
[1] Rogalski A. Infrared detectors:an overview. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2002, 43(3):187 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2086316200&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[2] Schaufelbühl A, Schneeberger N, Münch U, et al. Uncooled lowcost thermal imager based on micromachined CMOS integrated sensor array. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2001, 10(4):503 doi: 10.1109/84.967372[3] Eminoglu S, Tanrikulu M Y, Tezcan D S, et al. Low-cost smallpixel uncooled infrared detector for large focal plane arrays using a standard CMOS process. AeroSense 2002 International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2002:111 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2090441290&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[4] Furuta M, Nishikawa Y, Inoue T, et al. A high-speed, highsensitivity digital CMOS image sensor with a global shutter and 12-bit column-parallel cyclic A/D converters. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(4):766 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.891655[5] Song Z, Du Y, Liu M, et al. Three-dimensional integration of suspended single-crystalline silicon MEMS arrays with CMOS. 201528th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) IEEE, 2015 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2025053642&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[6] Shen Ning, Tang Zhenan, Yu Jun, et al. A low-cost infrared absorbing structure for an uncooled infrared detector in a standard CMOS process. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(3):034014 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/3/034014[7] Gianchandani Y. Comprehensive microsystems. Netherlands:Elsevier, 2008:121[8] Ueno M, Kosasayama Y, Sugino T, et al. 640×480 pixel uncooled infrared FPA with SOI diode detectors. Defense and Security. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2005:566 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1990900364&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[9] Niklaus F, Vieider C, Jakobsen H. MEMS-based uncooled infrared bolometer arrays:a review. Photonics Asia 2007. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2007:68360D[10] Jun G, Zhongjian C, Wengao L, et al. Correlated double sample design for CMOS image readout IC. 7th International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuits Technology, 2004, 2:1437 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1572456703&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[11] Long Shanli, Liu Yan, He Kejun, et al. 116 dB dynamic range CMOS readout circuit for MEMS capacitive accelerometer. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(9):095004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/9/095004[12] Han Ye, Li Quanliang, Shi Cong, et al. A 10-bit column-parallel cyclic ADC for high-speed CMOS image sensors. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(8):085016 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/8/085016[13] Zhao Hongliang, Zhao Yiqiang, Geng Junfeng, et al. A lowpower 10-bit 250-KSPS cyclic ADC with offset and mismatch correction. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(2):025008 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/2/025008[14] Nie Kaiming, Yao Suying, Xu Jiangtao, et al. A 10-bit ratioindependent cyclic ADC with offset canceling for a CMOS image sensor. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(3):035005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/3/035005[15] Lewis S H, Gray P R. A pipelined 5-Msample/s 9-bit analog-todigital converter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1987, 22(6):954 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.1987.1052843[16] Abo A M, Gray P R. A 1.5-V, 10-bit, 14.3-MS/s CMOS pipeline analog-to-digital converter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1999, 34(5):599 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2099432139&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[17] Svard D, Jansson C, Alvandpour A. A readout circuit for an uncooled IR camera with mismatch and self-heating compensation. IEEE NORCHIP, 2012:1 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1978976569&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: