| Citation: |
Swagata Dey, Vedatrayee Chakraborty, Bratati Mukhopadhyay, Gopa Sen. Modeling of tunneling current density of GeC based double barrier multiple quantum well resonant tunneling diode[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(10): 104003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/10/104003
****
S Dey, V Chakraborty, B Mukhopadhyay, G Sen, Modeling of tunneling current density of GeC based double barrier multiple quantum well resonant tunneling diode[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(10): 104003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/10/104003.
|
Modeling of tunneling current density of GeC based double barrier multiple quantum well resonant tunneling diode
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/10/104003
More Information
-
Abstract
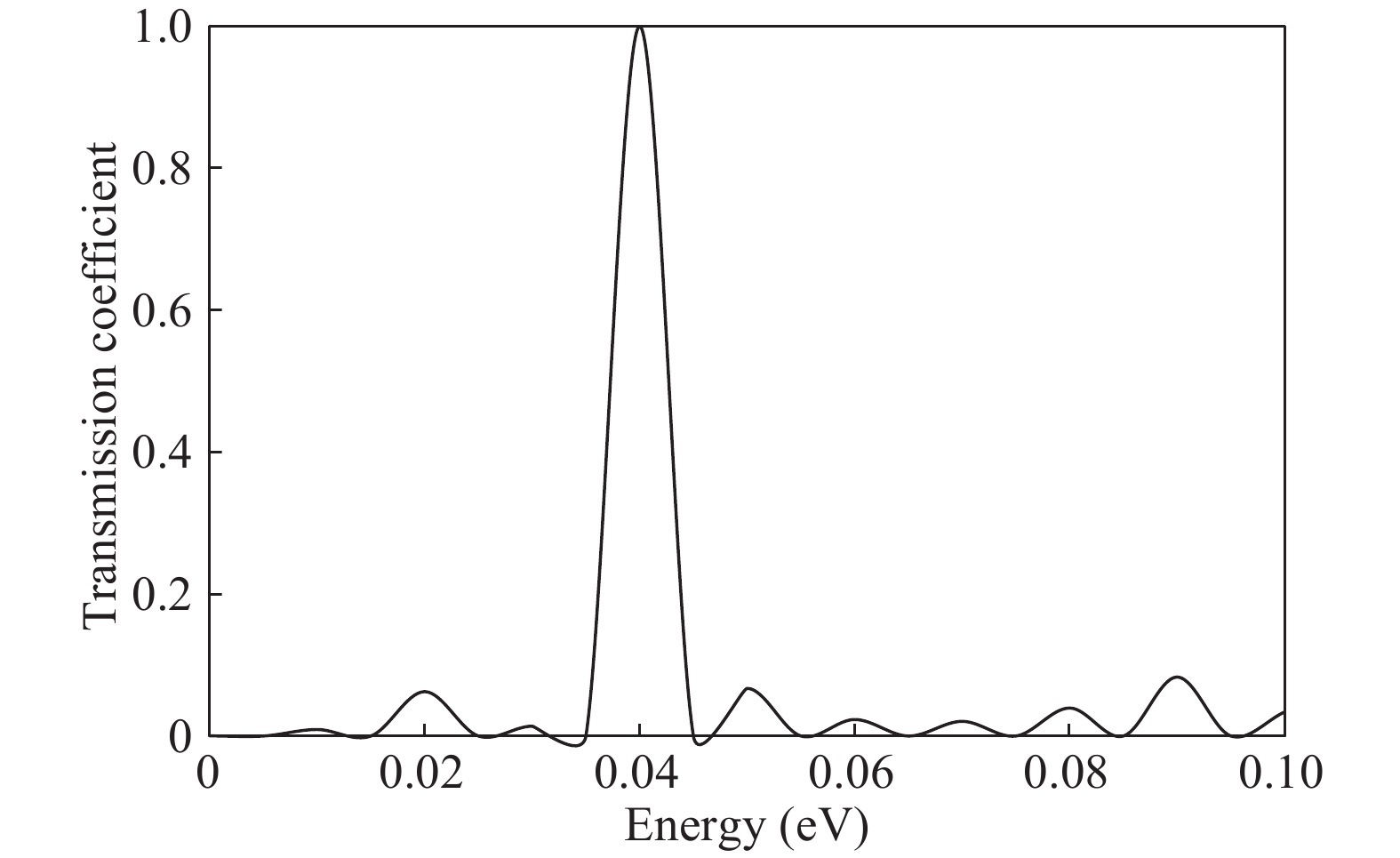
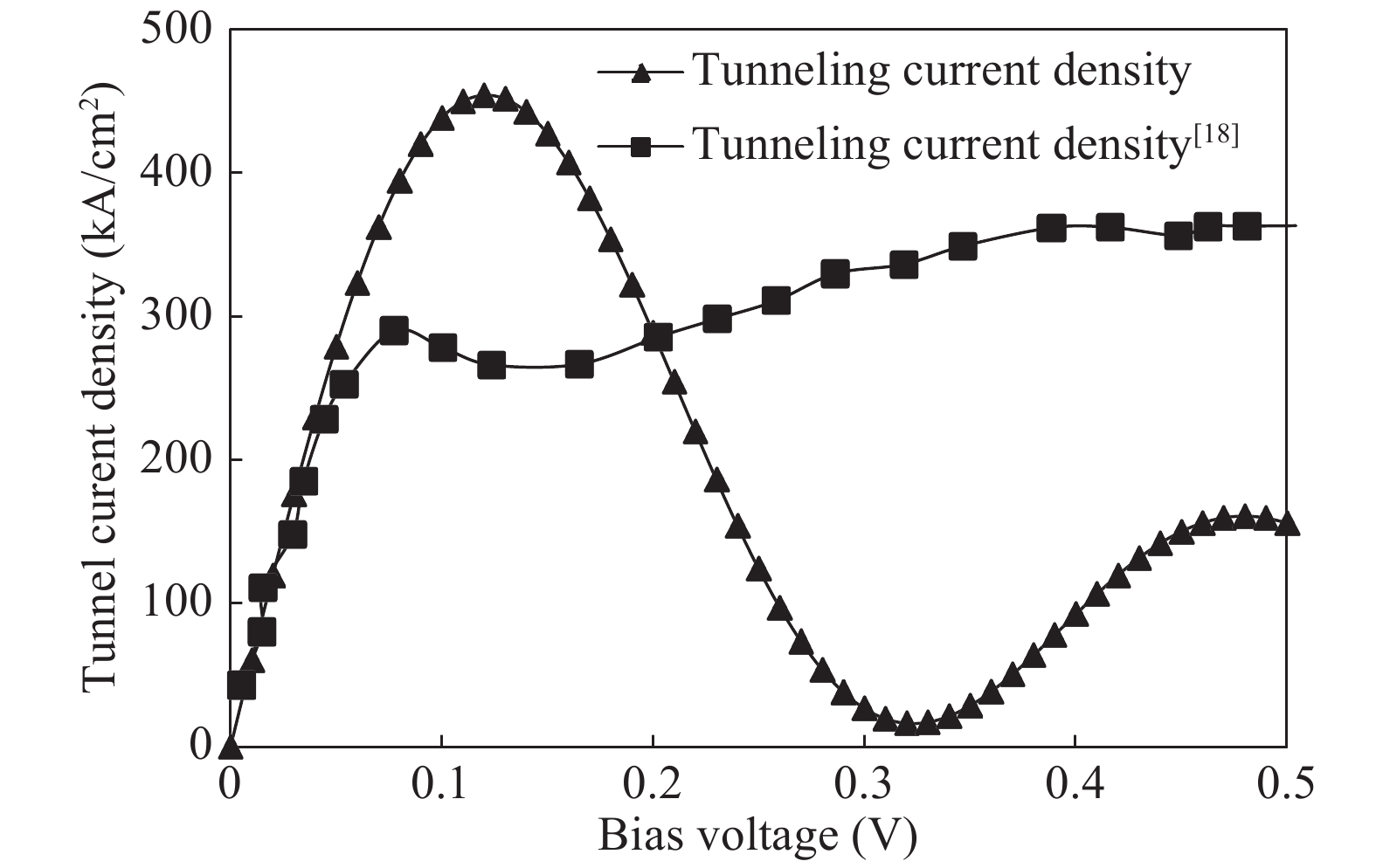
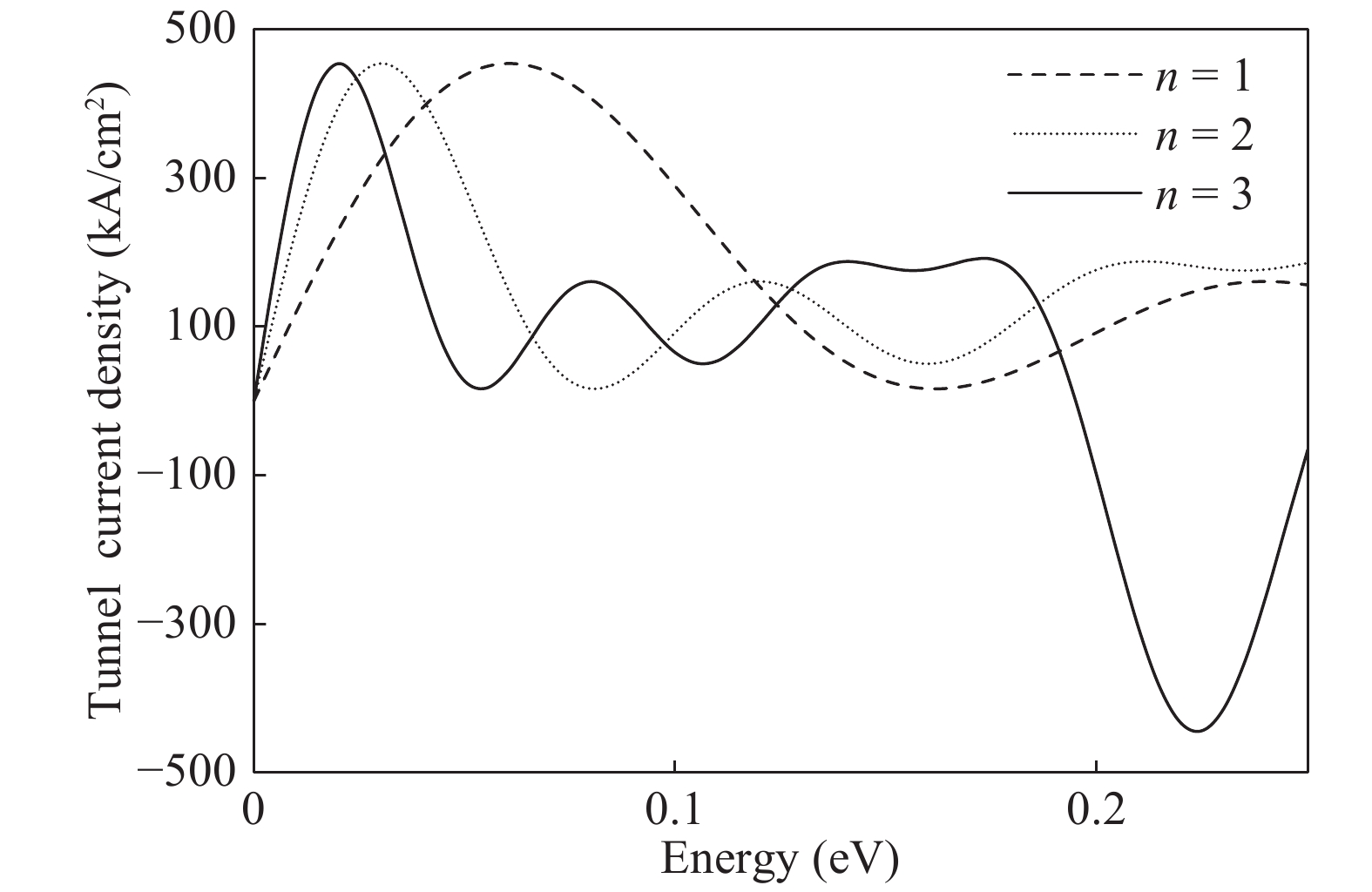
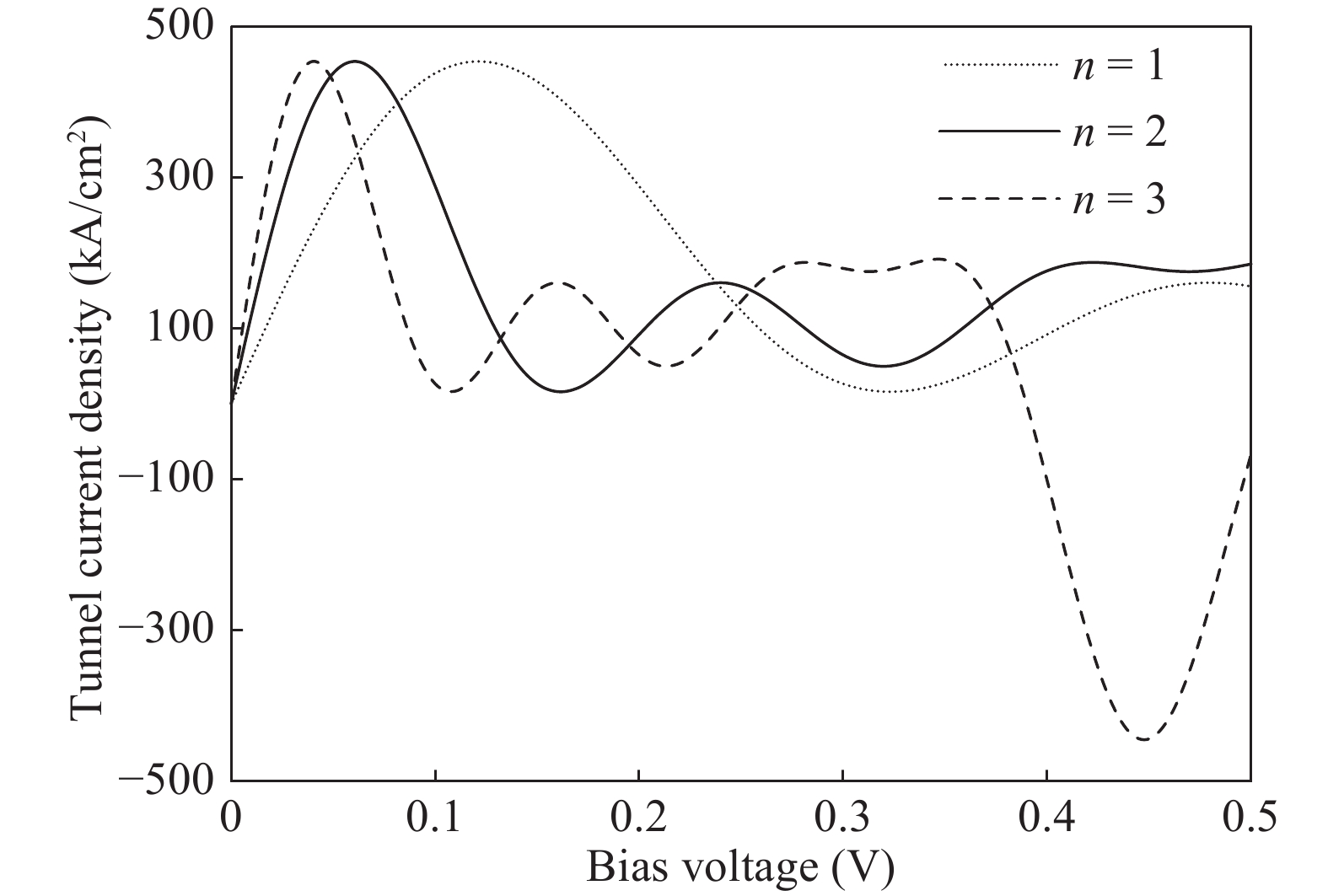
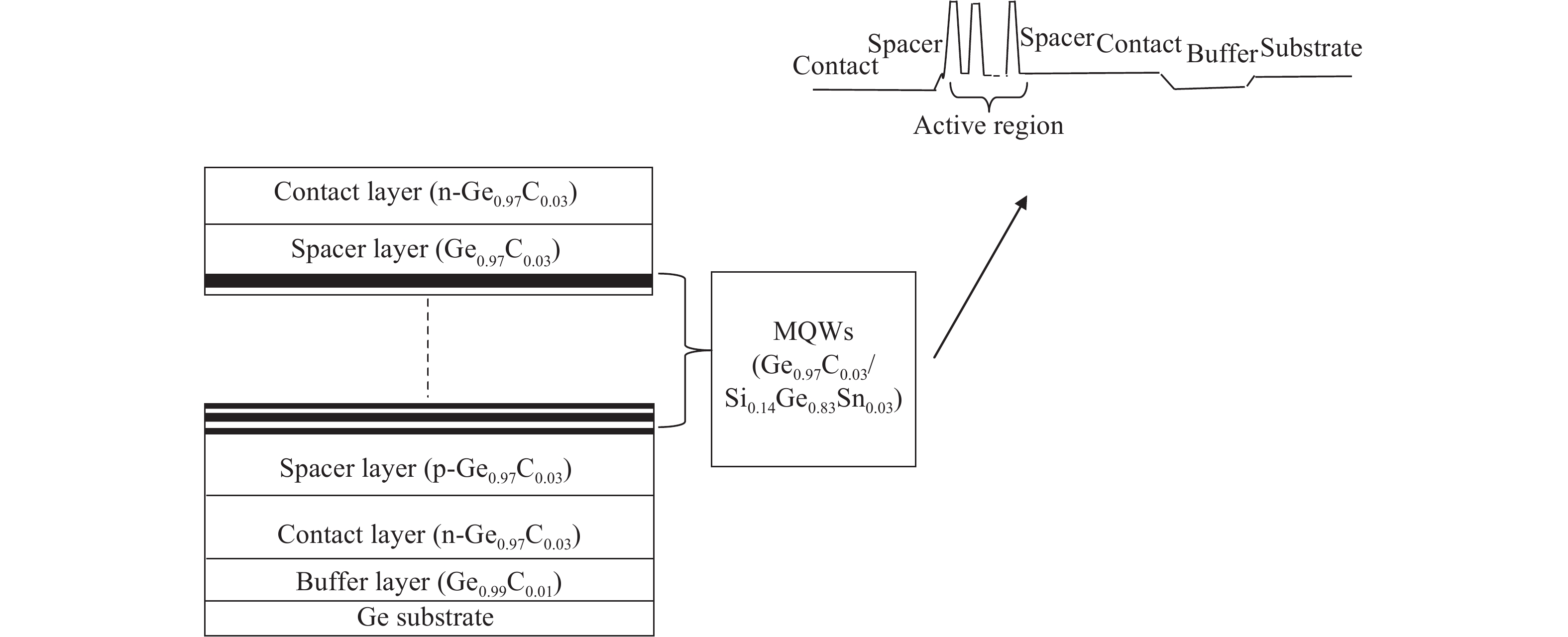
The double barrier quantum well (DBQW) resonant tunneling diode (RTD) structure made of SiGeSn/GeC/SiGeSn alloys grown on Ge substrate is analyzed. The tensile strained Ge1−zCz on Si1−x−yGexSny heterostructure provides a direct band gap type I configuration. The transmission coefficient and tunneling current density have been calculated considering single and multiple quantum wells. A comparative study of tunnelling current of the proposed structure is done with the existing RTD structure based on GeSn/SiGeSn DBH. A higher value of the current density for the proposed structure has been obtained.-
Keywords:
- DBQW,
- MQW,
- RTD,
- NDR,
- tunneling current density
-
References
[1] Deen M J, Basu P K. Silicon photonics: fundamentals and Devices. Chichester U K John Wiley, 2012.[2] Pavesi L, Lockwood D J. Silicon photonics. New York: Springer, 2004[3] Bauer M , Taraci J, Tolle J, et al. Ge–Sn semiconductors for band-gap and lattice engineering. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81: 2992 doi: 10.1063/1.1515133[4] Lee J W, Reed M A. Molecular beam epitaxial growth of AlGaAs/InGaAs resonant tunneling structures. J Vac Sci Technol B, 1987, 5(3): 771 doi: 10.1116/1.583745[5] Ghosh S, Basu P K. The calculated composition of Ge1−zCz/Ge1−x−zSixSny heterostructure grown on Si for direct gap emission from Ge1−zCz at 1.55 μm. Solid State Commun, 2010, 150: 844 doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2010.02.017[6] Menendez J, Kouvetakis J. Type-I Ge/GeSiSn strained layer heterostructures with a direct Ge band gap. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85: 1175 doi: 10.1063/1.1784032[7] Chakraborty V, Mukhopadhyay B. Group IV heterojunction laser structure based on S–Ge–Sn–C around 1550 nm: determination of gain coefficient. Proceedings in International Conference in Computers andDevices for Communication, 2015[8] Sun G, Soref R A, Cheng H H. Design of an electrically pumped SiGeSn/GeSn/SiGeSn double heterostructure mid infra red laser. J Appl Phys, 2010, 108: 033107 doi: 10.1063/1.3467766[9] Chang S W, Chuang S L. Theory of optical gain of Ge-SixGeySn1−x−y quantum-well lasers. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2007, 43(3): 249 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2006.890401[10] Zhu Y H, Xu Q, Fan W J, et al. Theoretical gain of strained GeSn/Ge1−x−ySixSny quantum well laser. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107: 073108 doi: 10.1063/1.3329424[11] Chang G E, Chang S W, Chuang S L. Strain-balanced GezSn1−z–SixGeySn1−x−y multiple quantum-well lasers. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2010, 46(12): 1813 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2010.2059000[12] Basu R, Chakraborty V, Mukhopadhyay B, et al. Predicted performance of Ge/GeSn hetero-photo transistors on Si substrate at 1.55 μm. Opt Quant Electron, 2013, 47(2): 387[13] Moontragoon P, Vukmirovi'C N, Ikoni'C Z, et al. SnGe asymmetric quantum well electro absorption modulators for long-wave silicon photonics. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2010, 16(1): 100 doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2009.2026691[14] Dey S, Mukhopadhyay B, Basu P K. Modeling of responsivity of GeSn/SiGeSn QWIP. Proceedings in International Conference in Computers andDevices for Communication, 2015[15] Esaki L, Tsu R. Superlattics and negative differential conductivity in semiconductors. IBM J Res Develop, 1970, 14: 61 doi: 10.1147/rd.141.0061[16] Tsu R, Esaki L. Tunneling in a finite superlattice. Appl Phys Lett, 1973, 22: 562 doi: 10.1063/1.1654509[17] Chang L L, Esaki L, Tsu R. Resonant tunnelling in semiconductor double barriers. Appl Phys Lett, 1974, 24: 593 doi: 10.1063/1.1655067[18] Wu K Y, Tsai B H, Chen J Z, et al. Sn-based group-IV structure for resonant tunneling diodes. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2013, 34(8): 951 doi: 10.1109/LED.2013.2266540[19] Mukherjee K, Das N R. Tunneling current calculations for nonuniform and asymmetric multiple quantum well structures. J Appl Phys, 2011, 109: 053708 doi: 10.1063/1.3553391[20] Handbook of mathematical functions. Edited by Abramowitz M A and Stegun I A. Dover, New York, 1965 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: