| Citation: |
D. K. Panda, G. Amarnath, T. R. Lenka. Small-signal model parameter extraction of E-mode N-polar GaN MOS-HEMT using optimization algorithms and its comparison[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2018, 39(7): 074001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/7/074001
****
D K Panda, G Amarnath, T R Lenka, Small-signal model parameter extraction of E-mode N-polar GaN MOS-HEMT using optimization algorithms and its comparison[J]. J. Semicond., 2018, 39(7): 074001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/7/074001.
|
Small-signal model parameter extraction of E-mode N-polar GaN MOS-HEMT using optimization algorithms and its comparison
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/39/7/074001
More Information
-
Abstract
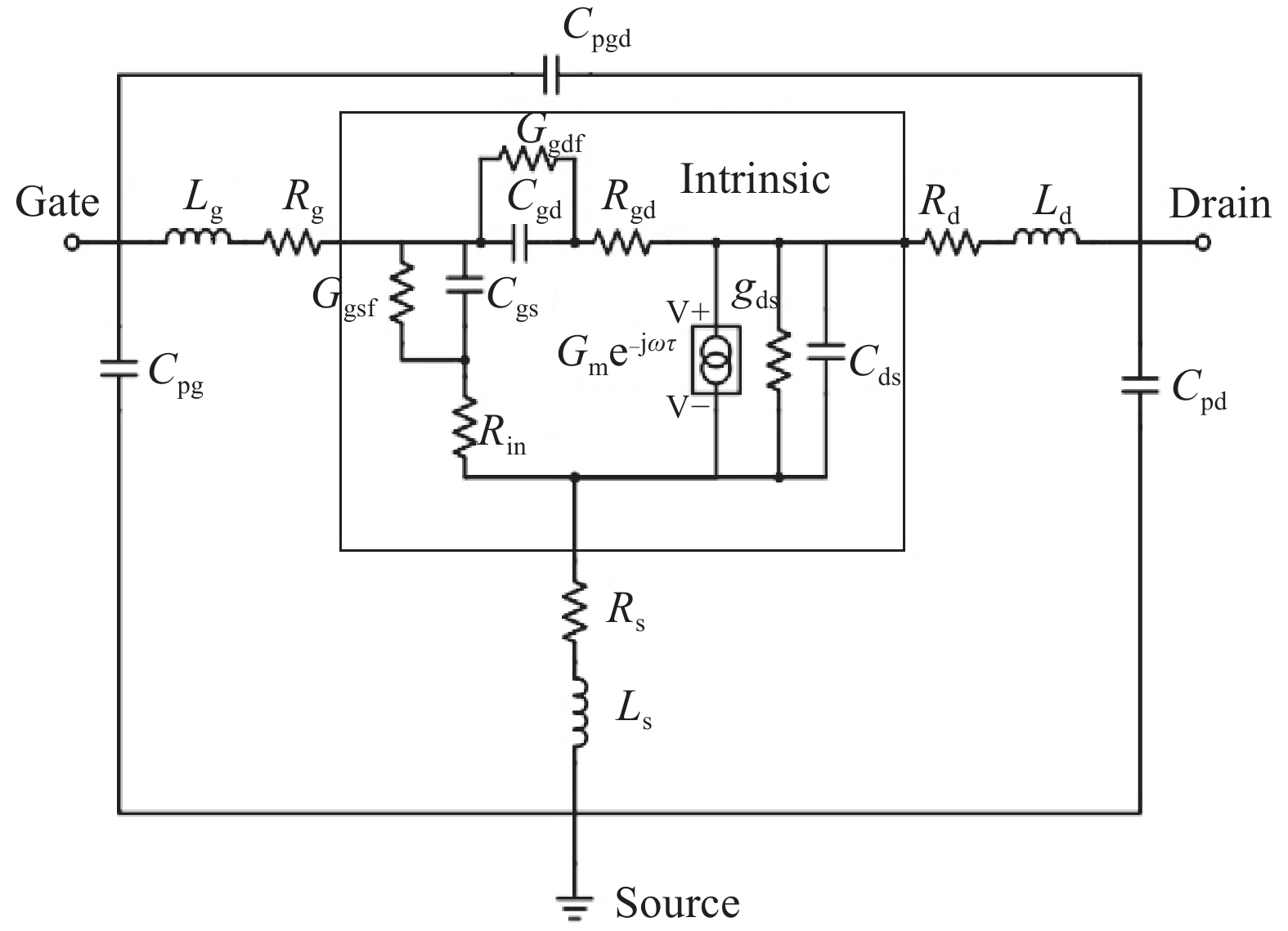
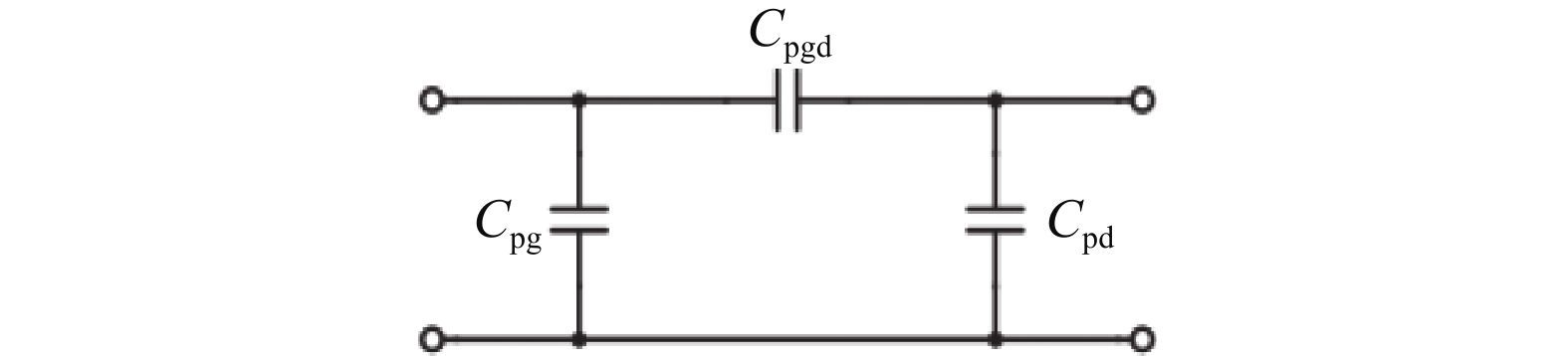
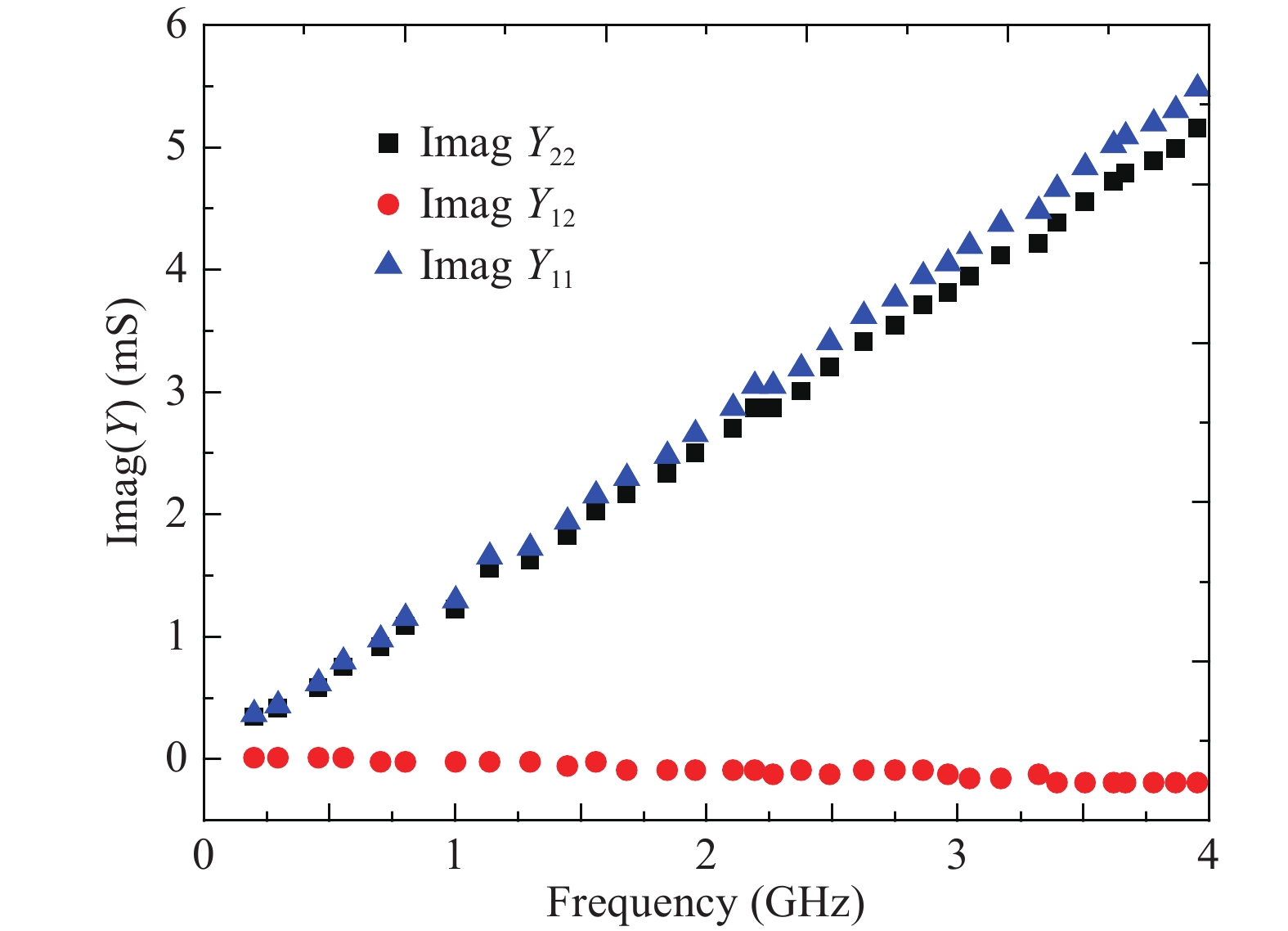
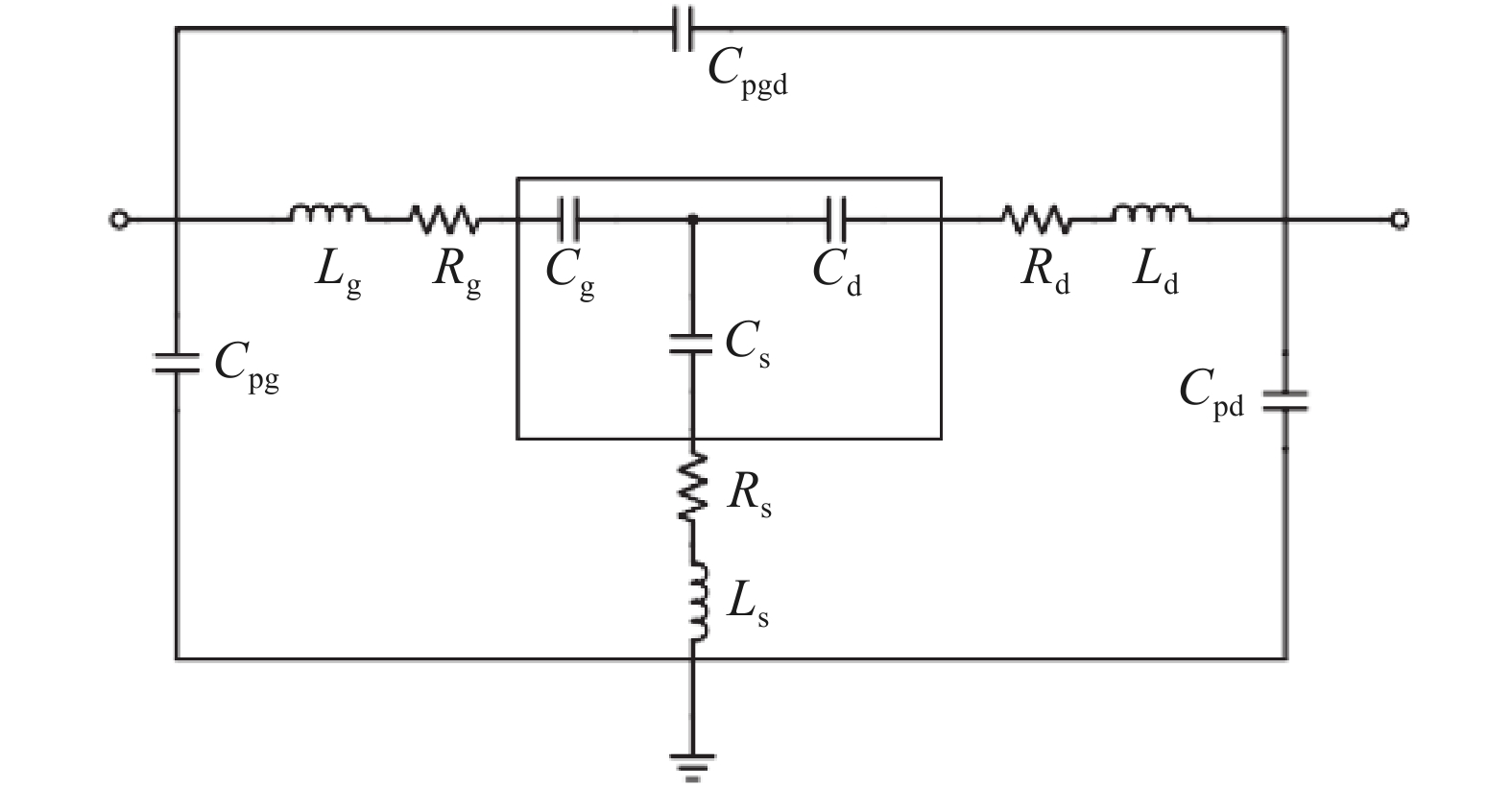
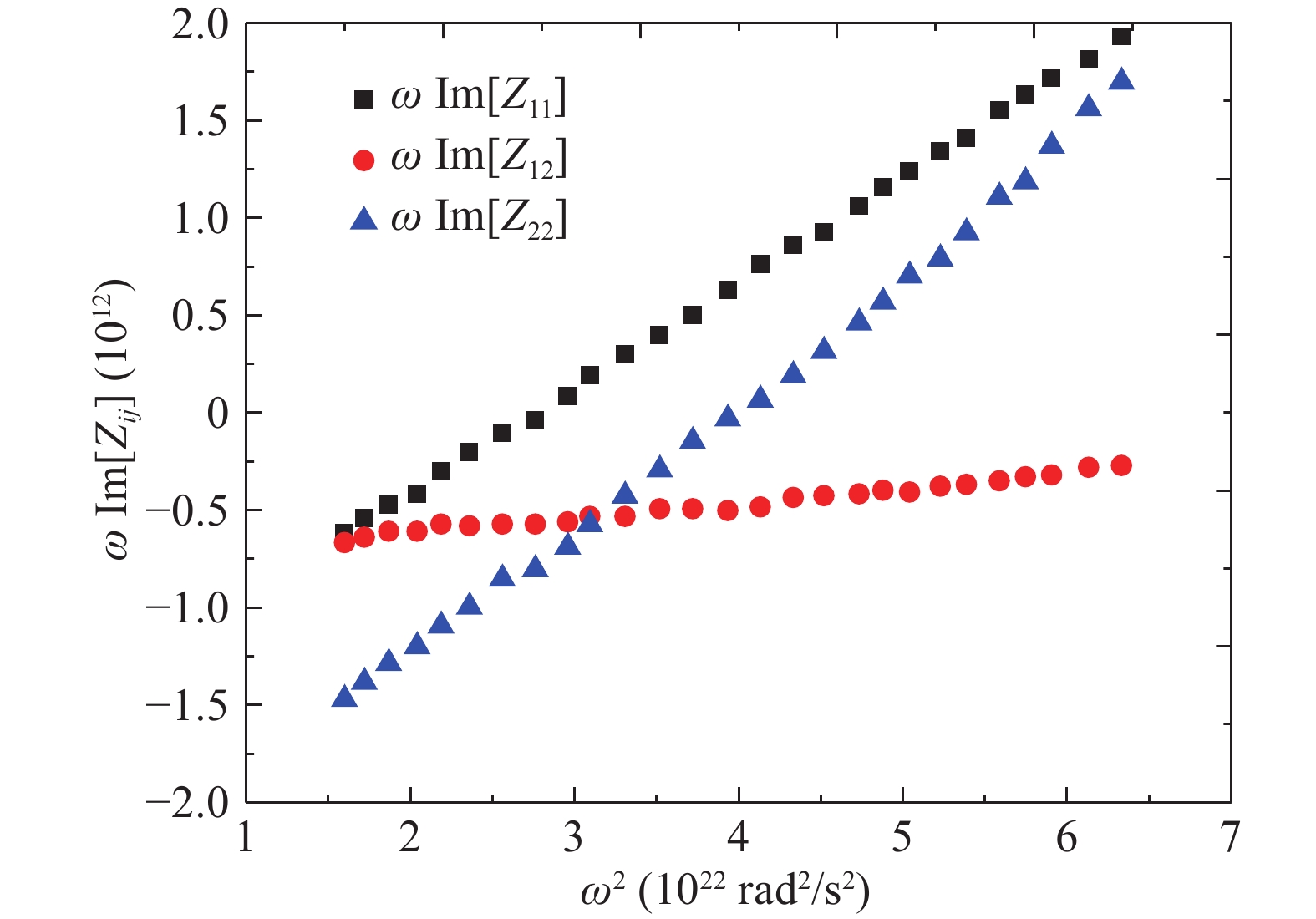
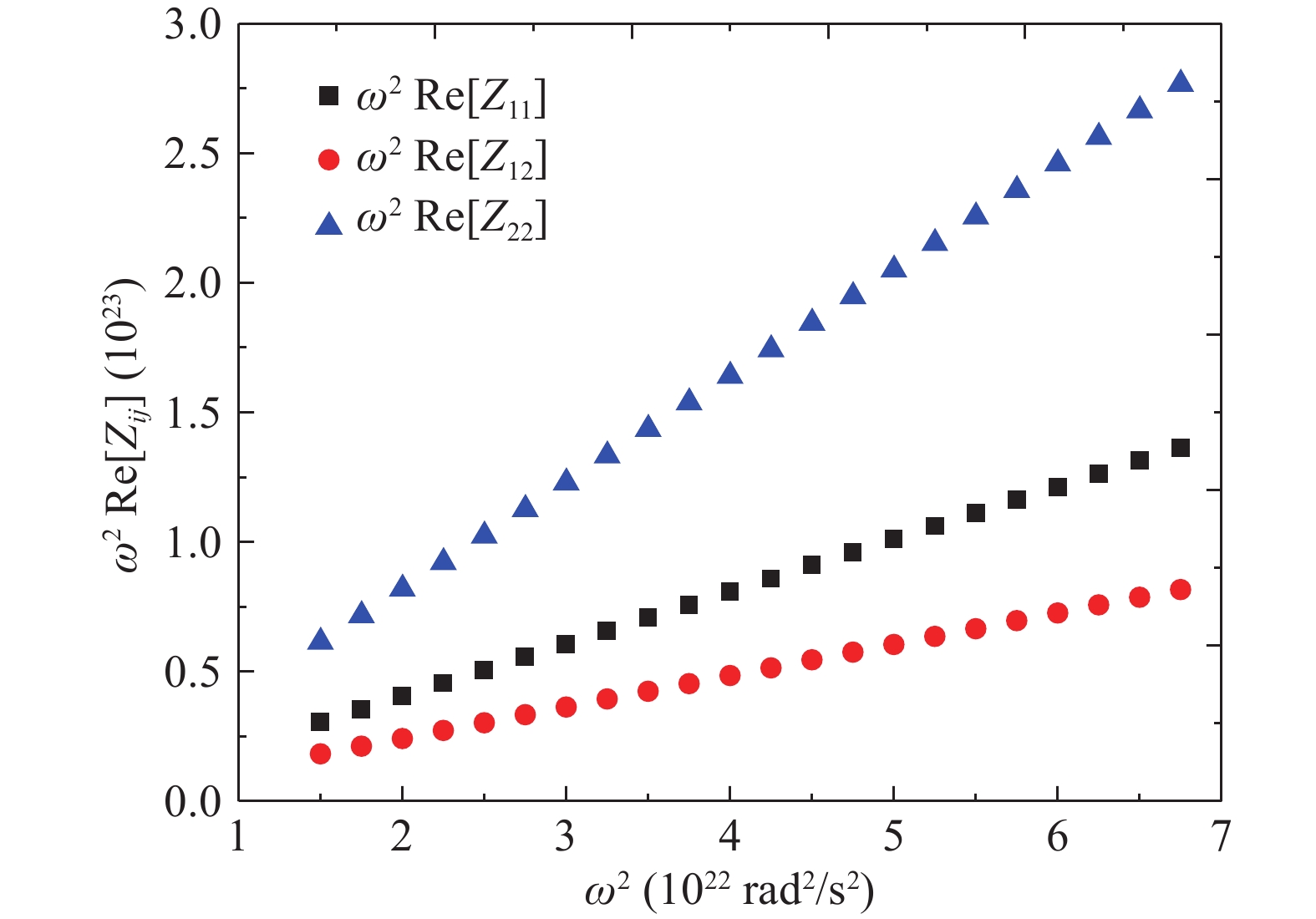
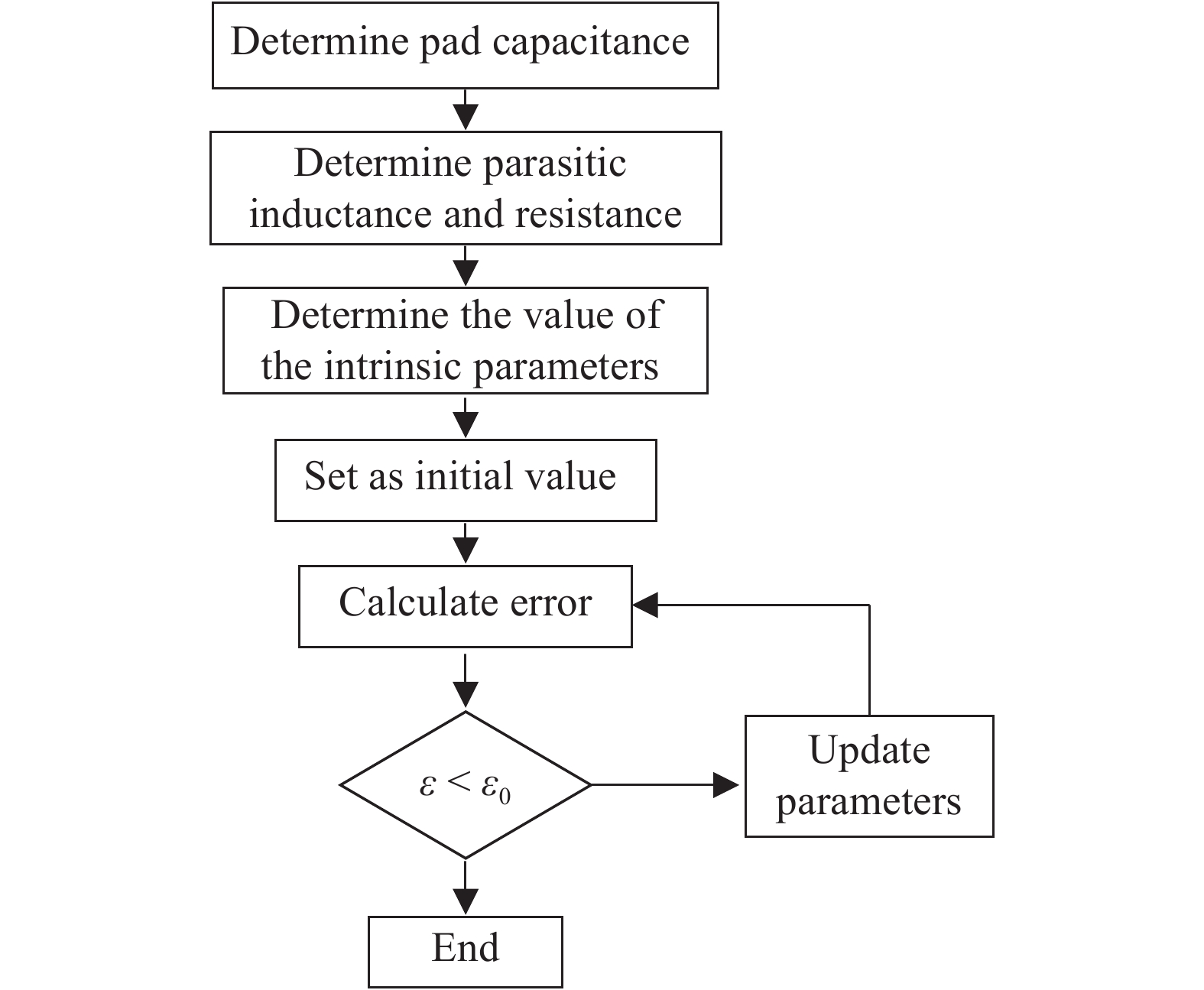
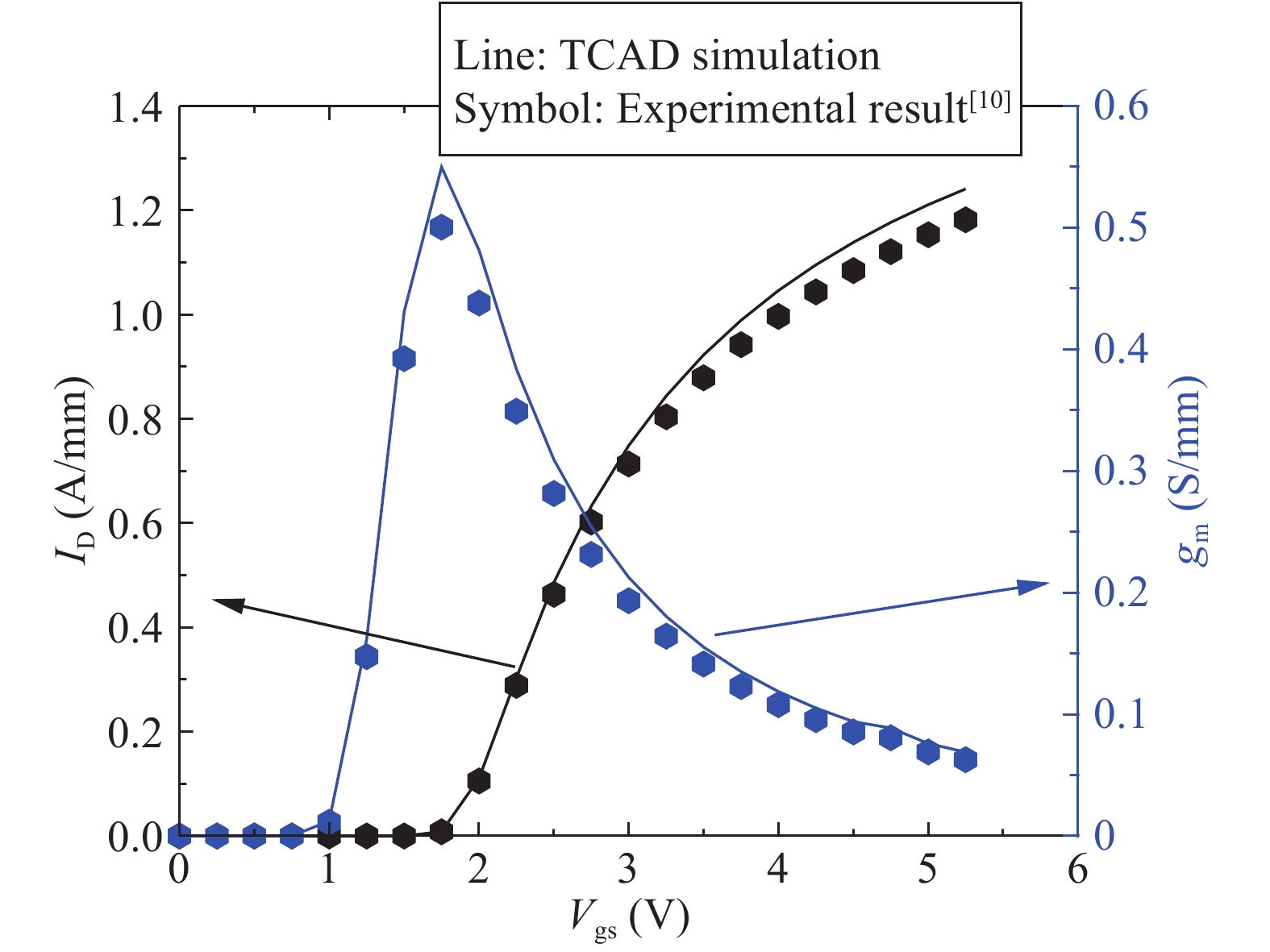
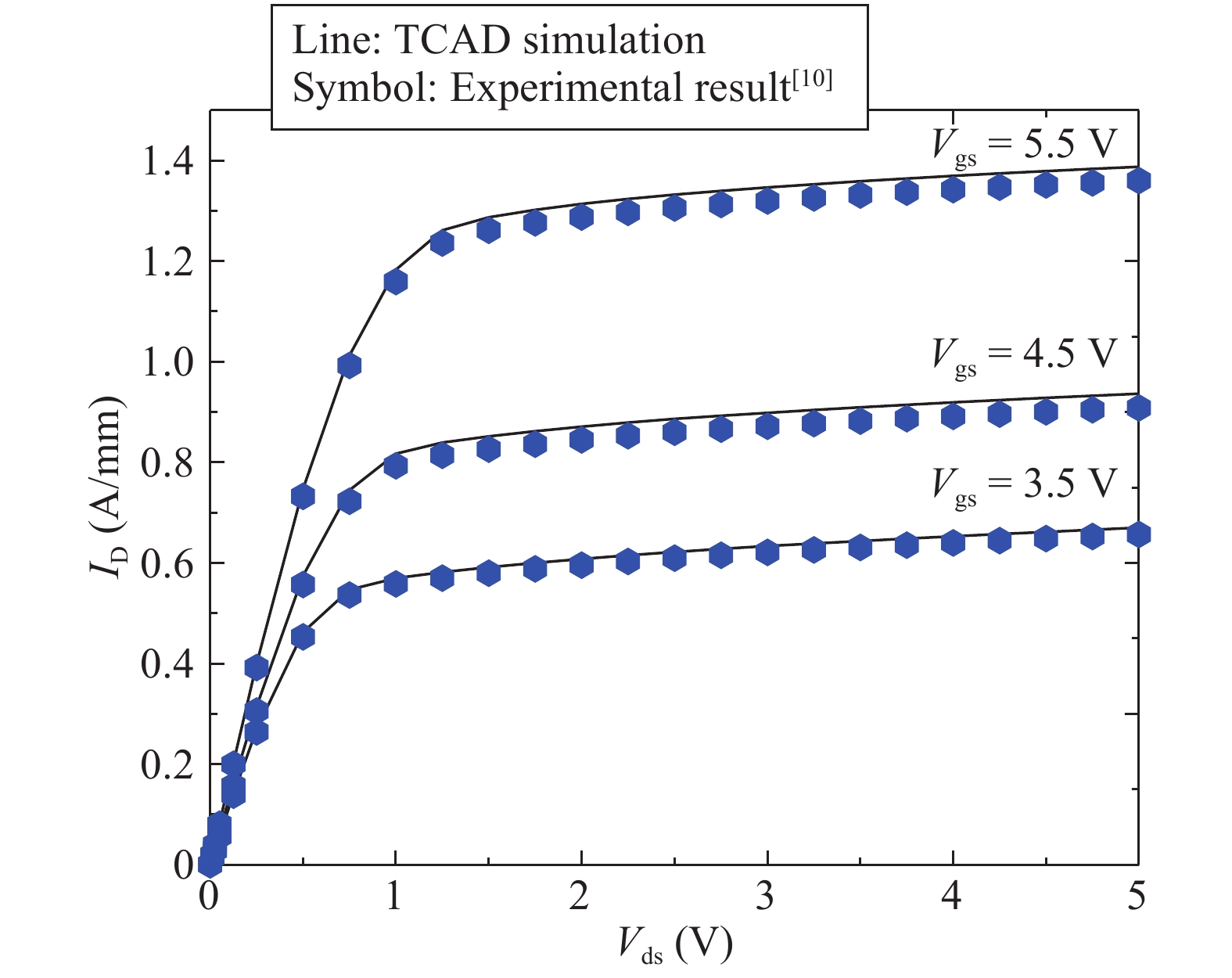
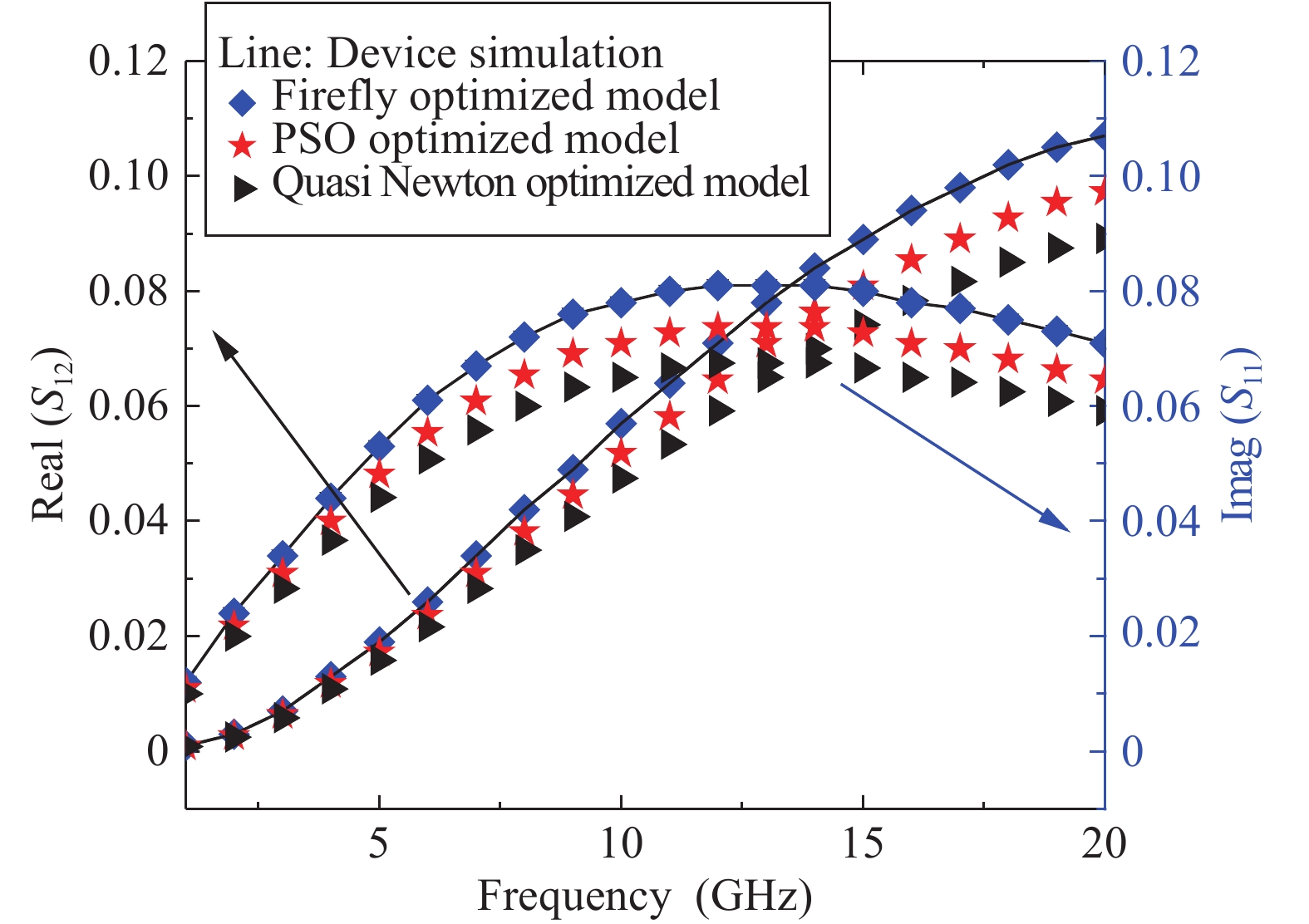
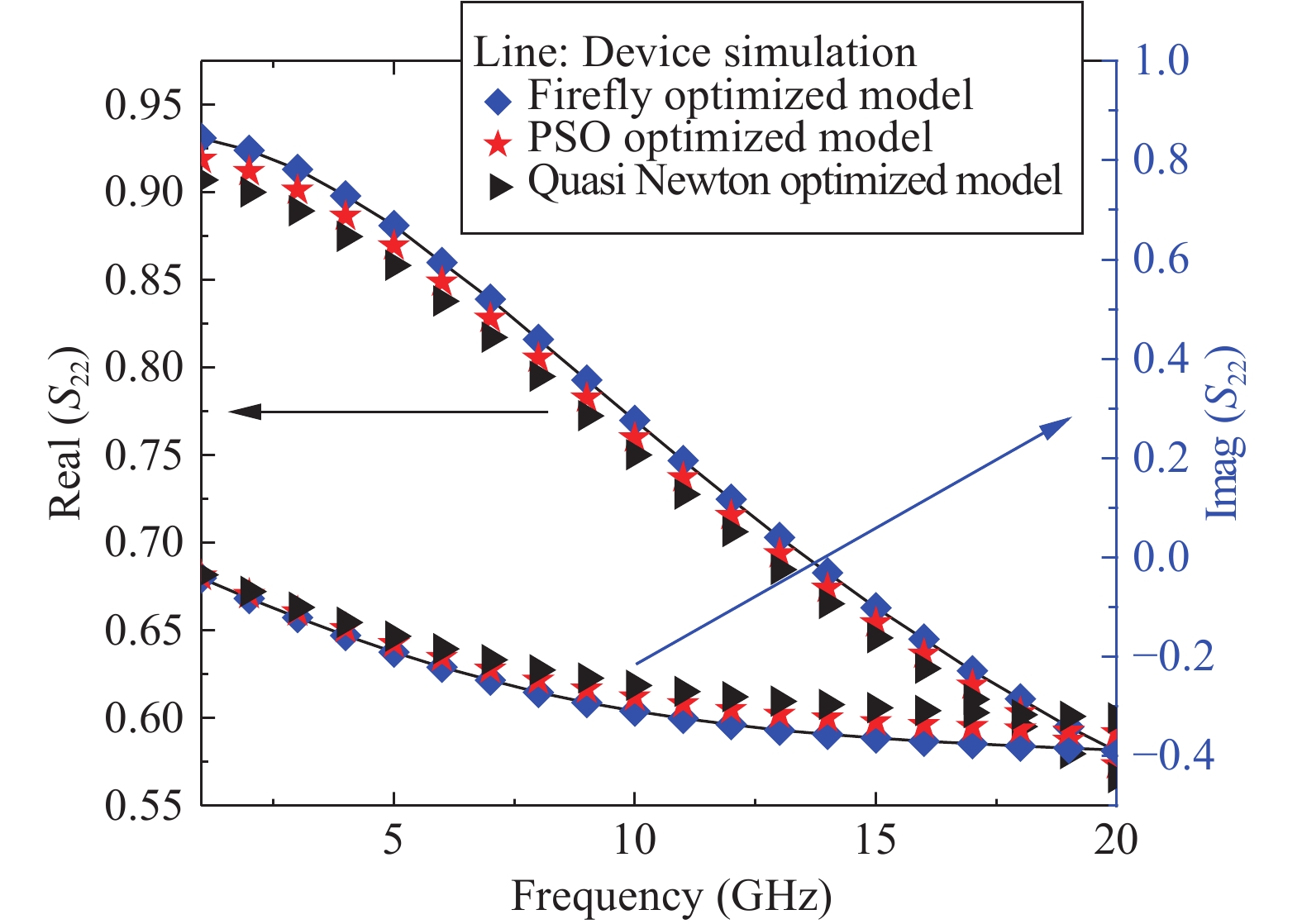
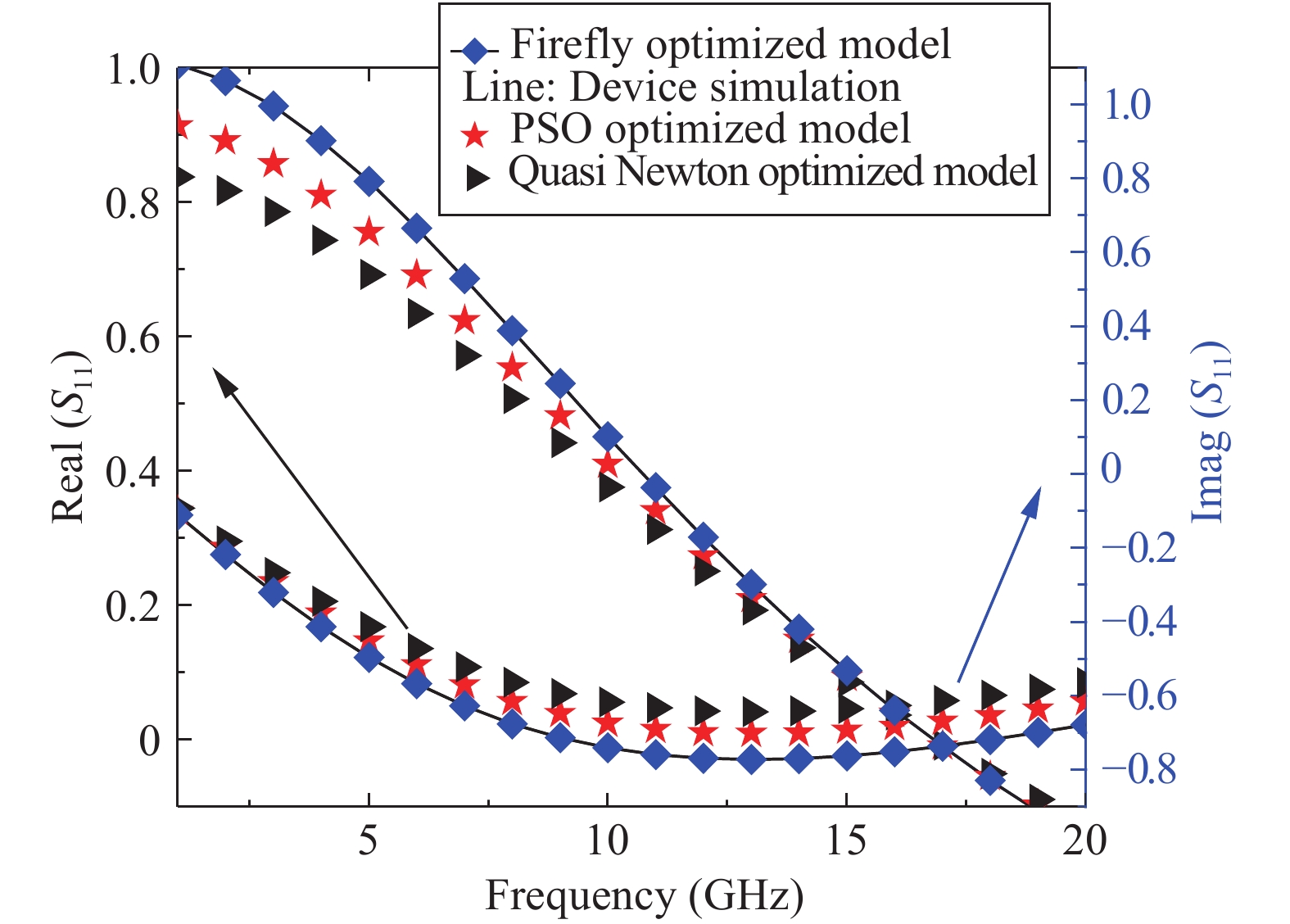
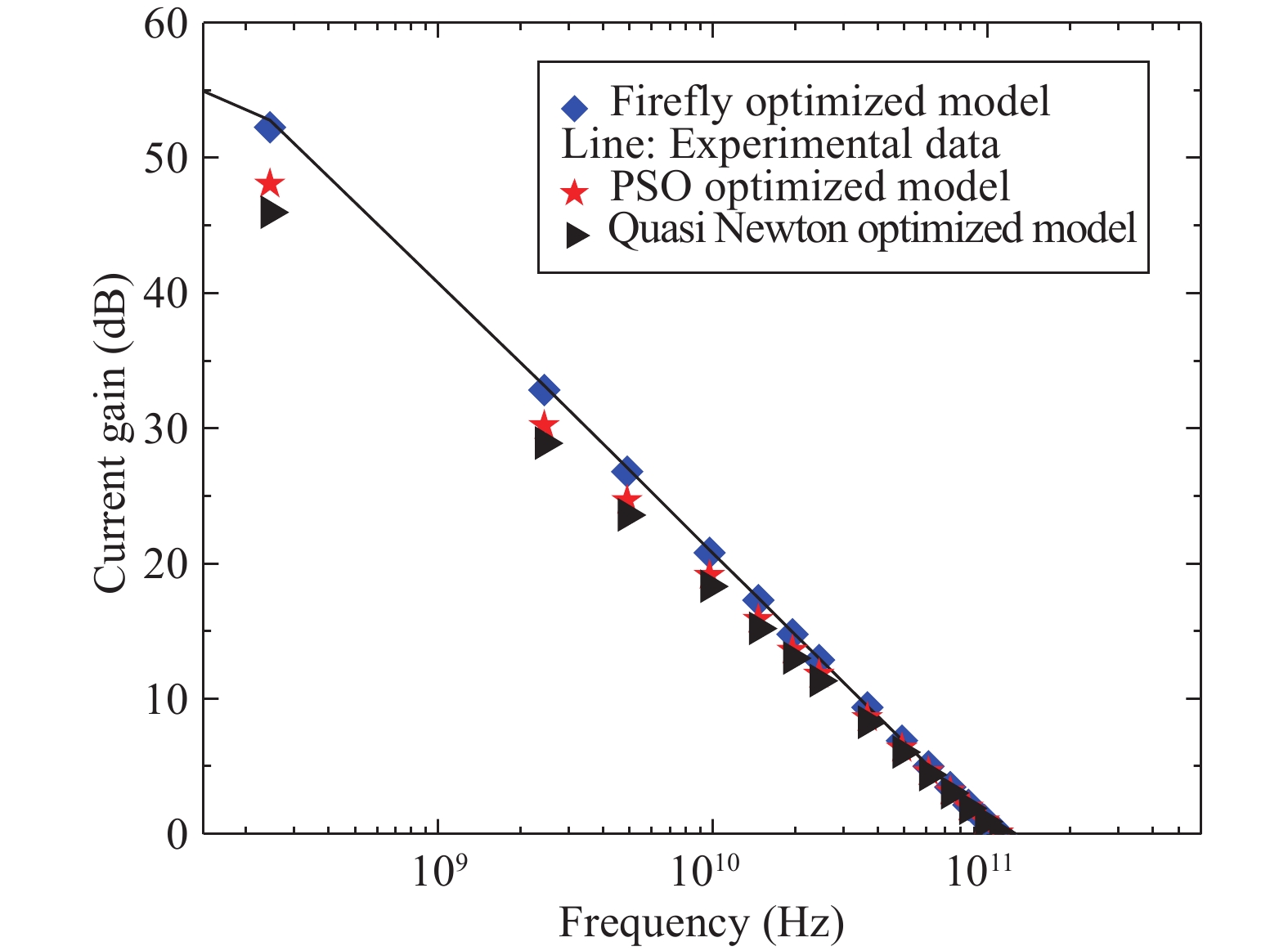
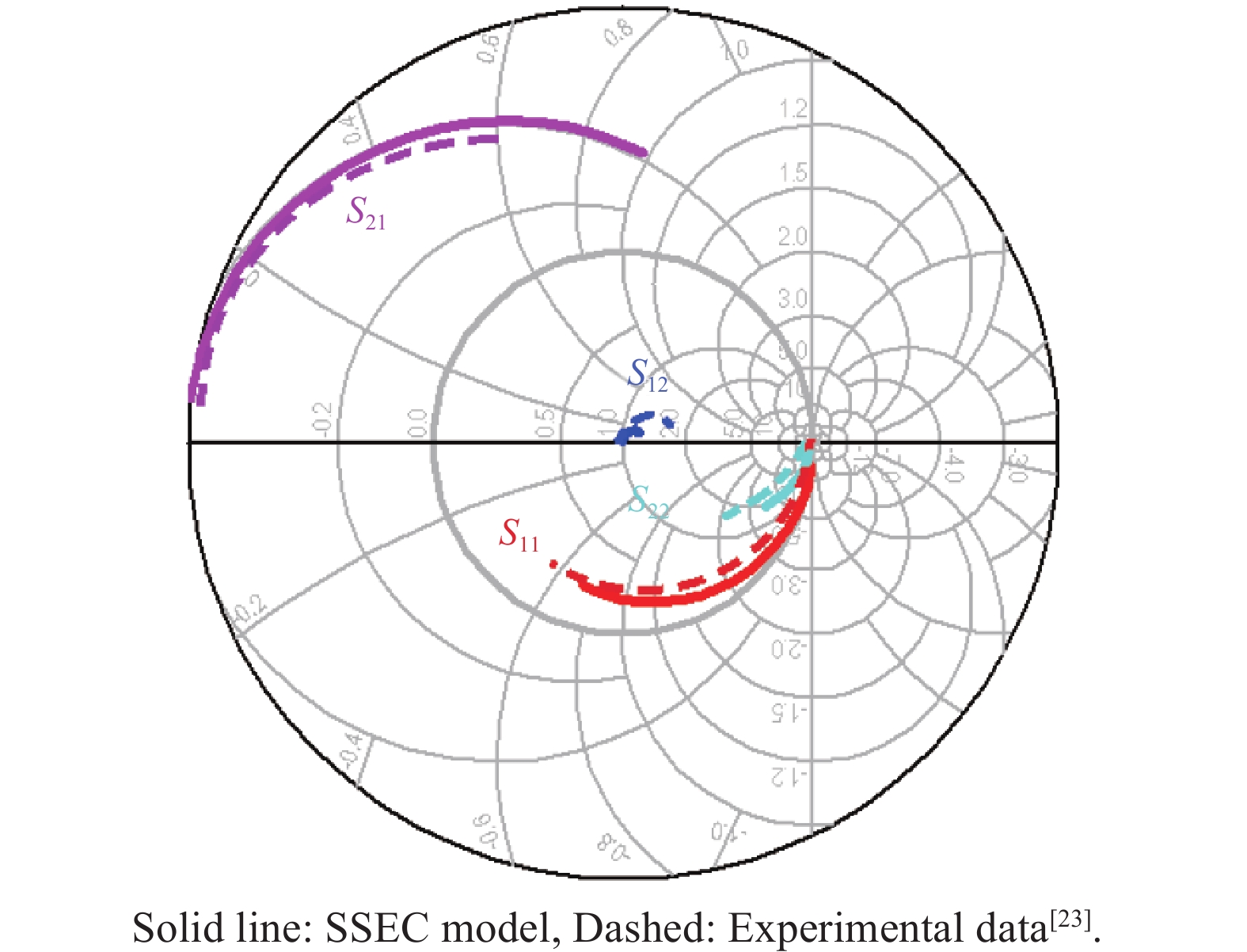
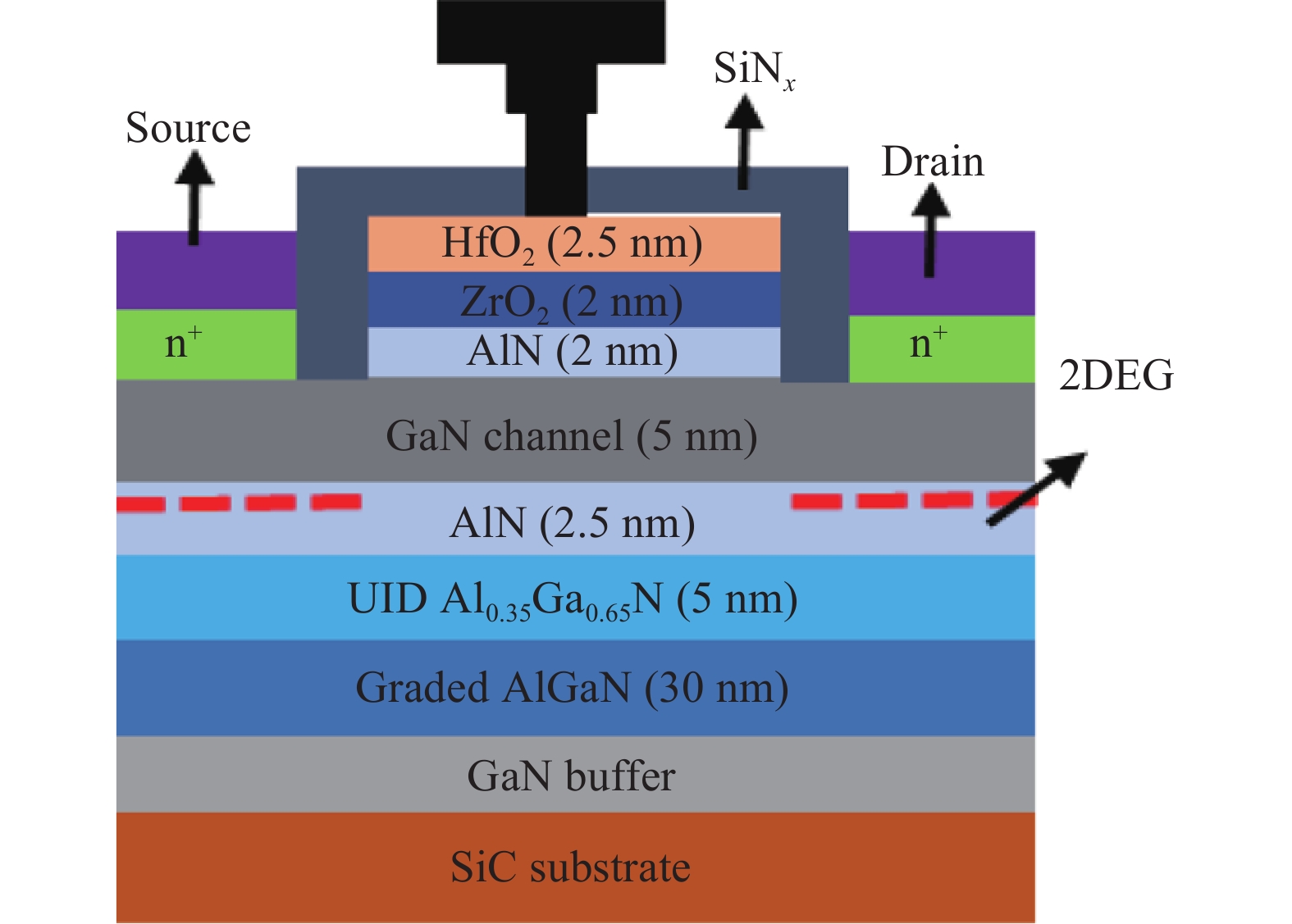
An improved small-signal parameter extraction technique for short channel enhancement-mode N-polar GaN MOS-HEMT is proposed, which is a combination of a conventional analytical method and optimization techniques. The extrinsic parameters such as parasitic capacitance, inductance and resistance are extracted under the pinch-off condition. The intrinsic parameters of the small-signal equivalent circuit (SSEC) have been extracted including gate forward and backward conductance. Different optimization algorithms such as PSO, Quasi Newton and Firefly optimization algorithm is applied to the extracted parameters to minimize the error between modeled and measured S-parameters. The different optimized SSEC models have been validated by comparing the S-parameters and unity current-gain with TCAD simulations and available experimental data from the literature. It is observed that the Firefly algorithm based optimization approach accurately extracts the small-signal model parameters as compared to other optimization algorithm techniques with a minimum error percentage of 1.3%. -
References
[1] Panda D K, Lenka T R. Modeling and simulation of enhancement mode p-GaN Gate AlGaN/GaN HEMT for RF circuit switch applications. J Semicond, 2017, 38(6): 064002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/6/064002[2] Panda D K, Lenka T R. Oxide thickness dependent compact model of channel noise for E-mode AlGaN/GaN MOS-HEMT. AEU - Int J Electron Commun, 2017, 82: 467 doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2017.09.025[3] Jena K, Swain R, Lenka T R. Impact of barrier thickness on gate capacitance-modeling and comparative analysis of GaN based MOSHEMTs. J Semicond, 2015, 36(3): 034003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/3/034003[4] Panda D K, Lenka T R. Effects of trap density on drain current LFN and its model development for E-mode GaN MOS-HEMT. Superlattices Microstruct, 2017, 112: 374 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2017.09.045[5] Chen M. A 1–25 GHz GaN HEMT MMIC low-noise amplifier. IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon Lett, 20(10): 563[6] Sun H F, Alt A R, Benedickter H, et al. High-speed and low-noise AlInN/GaN HEMTs on SiC. Phys Status Solidi A, 2011, 208(2): 429 doi: 10.1002/pssa.201000518[7] Chen M Q, Sutton W, Smorchkova, et al. A 1–25 GHz GaN HEMT MMIC low-noise amplifier. IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon Lett, 2010, 20(10): 563 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2010.2059002[8] Sun H F, Alt A R, Benedickter H, et al. Low-noise microwave performance of 0.1 μm gate AlInN/GaN HEMTs on SiC. IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon Lett, 2010, 20(8): 453 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2010.2049008[9] Li B, Wei L, Wen C. Static characteristics and short channel effect in enhancement-mode AlN/GaN/AlN N-polar MISFET with self-aligned source/drain regions. J Semicond, 2014, 35(12): 124006 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/12/124006[10] Singisetti U, Wong M H, Speck J S, et al. Enhancement-mode N-polar GaN MOS-HFET with 5-nm GaN channel, 510-mS/mm gm, and 0.66- ohm·mm Ron’. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2012, 33(1): 6 doi: 10.1109/LED.2011.2178050[11] Essaadali R, Jarndal A, Kouki A B, et al. A new GaN HEMT equivalent circuit modeling technique based on X-parameters. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2016, 64(9): 2758 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2594234[12] Alt A R, Marti D, Bolognesi C R. Transistor modeling: robust small-signal equivalent circuit extraction in various HEMT technologies. IEEE Microwave Mag, 2013, 14(4): 83 doi: 10.1109/MMM.2013.2248593[13] Du J, Xu P, Wang K, et al. Small-signal modeling of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs with consideration of CPW capacitances. J Semicond, 2015, 36(3): 34009 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/3/034009[14] Crupi G, Schreurs D M M P, Caddemi A, et al. High-frequency extraction of the extrinsic capacitances for GaN HEMT technology. IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon Lett, 2011, 21(8): 445 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2011.2160525[15] Resca D, Raffo A, Santarelli A, et al. Scalable equivalent circuit FET model for MMIC design identified through FW-EM analyses. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2009, 57(2): 245 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2008.2011208[16] Snowden C M. Large-signal microwave characterization of AlGaAs/GaAs HBT's based on a physics-based electrothermal model. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 1997, 45(1): 58 doi: 10.1109/22.552033[17] Majumdar A, Chatterjee S, Chatterjee S, et al. Optimization of intrinsic elements from small-signalmodel of GaN HEMT by using PSO. IEEE Applied Electromagnetics Conference (AEMC), Guwahati, 2015: . 1[18] Kumar R, Rajan A, Talukdar F A, et al. Optimization of 5.5-GHz CMOS LNA parameters using firefly algorithm. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016: 1[19] Brady R G, Oxley C H, Brazil T J. An improved small-signal parameter-extraction algorithm for GaN HEMT devices. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2008, 56(7): 1535 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2008.925212[20] Dambrine G, Cappy A, Heliodore F, et al. A new method for determining the FET small-signal equivalent circuit. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 1988, 36(7): 1151 doi: 10.1109/22.3650[21] Jarndal A, Kompa G. A new small-signal modeling approach applied to GaN devices. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2005, 53(11): 3440 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.857332[22] Yanagawa S, Ishihara H, Ohtomo M. Analytical method for determining equivalent circuit parameters of GaAs FETs. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 1996, 44(10): 1637 doi: 10.1109/22.538954[23] Nidhi, Dasgupta S, Keller S, et al. N-Polar GaN/AlN MIS-HEMT with fMAX of 204 GHz for Ka-band applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2011, 32(12): 1683 doi: 10.1109/LED.2011.2168558 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: