| Citation: |
Wensi Cai, Zhigang Zang, Liming Ding. Self-assembled monolayers enhance the performance of oxide thin-film transistors[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(3): 030203. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/3/030203
****
W S Cai, Z G Zang, L M Ding, Self-assembled monolayers enhance the performance of oxide thin-film transistors[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(3): 030203. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/3/030203.
|
Self-assembled monolayers enhance the performance of oxide thin-film transistors
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/3/030203
More Information
-
References
[1] Park J W, Kang B H, Kim H J. A review of low-temperature solution-processed metal oxide thin-film transistors for flexible electronics. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30, 1904632 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201904632[2] Vijjapu M T, Surya S G, Yuvaraja S, et al. Fully integrated indium gallium zinc oxide NO2 gas detector. ACS Sens, 2020, 5, 984 doi: 10.1021/acssensors.9b02318[3] Fortunato E, Barquinha P, Martins R. Oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors: A review of recent advances. Adv Mater, 2012, 24, 2945 doi: 10.1002/adma.201103228[4] Nomura K, Ohta H, Takagi A, et al. Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature, 2004, 432, 488 doi: 10.1038/nature03090[5] Ho D, Jeong H, Choi S, et al. Organic materials as a passivation layer for metal oxide semiconductors. J Mater Chem C, 2020, 8, 14983 doi: 10.1039/D0TC02379E[6] Ide K, Nomura K, Hosono H, et al. Electronic defects in amorphous oxide semiconductors: A review. Phys Status Solidi A, 2019, 216, 1800372 doi: 10.1002/pssa.201800372[7] Park J S, Jeong J K, Chung H J, et al. Electronic transport properties of amorphous indium-gallium-zinc oxide semiconductor upon exposure to water. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92, 072104 doi: 10.1063/1.2838380[8] Cai W, Wilson J, Zhang J, et al. Significant performance enhancement of very thin InGaZnO thin-film transistors by a self-assembled monolayer treatment. ACS Appl Electron Mater, 2020, 2, 301 doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.9b00791[9] Zhong W, Li G, Lan L, et al. InSnZnO thin-film transistors with vapor- phase self-assembled monolayer as passivation layer. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2018, 39, 1680 doi: 10.1109/LED.2018.2872352[10] Zhong W, Yao R, Liu Y, et al. Effect of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) as surface passivation on the flexible a-InSnZnO thin-film transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2020, 67, 3157 doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.3004420[11] Lee S E, Na H J, Lee E G, et al. The effect of surface energy characterized functional groups of self-assembled monolayers for enhancing the electrical stability of oxide semiconductor thin film transistors. Nanotechnology, 2020, 31, 475203 doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/abad5e[12] Xiao P, Lan L, Dong T, et al. InGaZnO thin-film transistors modified by self-assembled monolayer with different alkyl chain length. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2015, 36, 687 doi: 10.1109/LED.2015.2431741[13] Bashir A, Wöbkenberg P H, Smith J, et al. High-performance zinc oxide transistors and circuits fabricated by spray pyrolysis in ambient atmosphere. Adv Mater, 2009, 21, 2226 doi: 10.1002/adma.200803584[14] Cai W, Zhang J, Wilson J, et al. Significant performance improvement of oxide thin-film transistors by a self-assembled monolayer treatment. Adv Electron Mater, 2020, 6, 1901421 doi: 10.1002/aelm.201901421 -
Proportional views





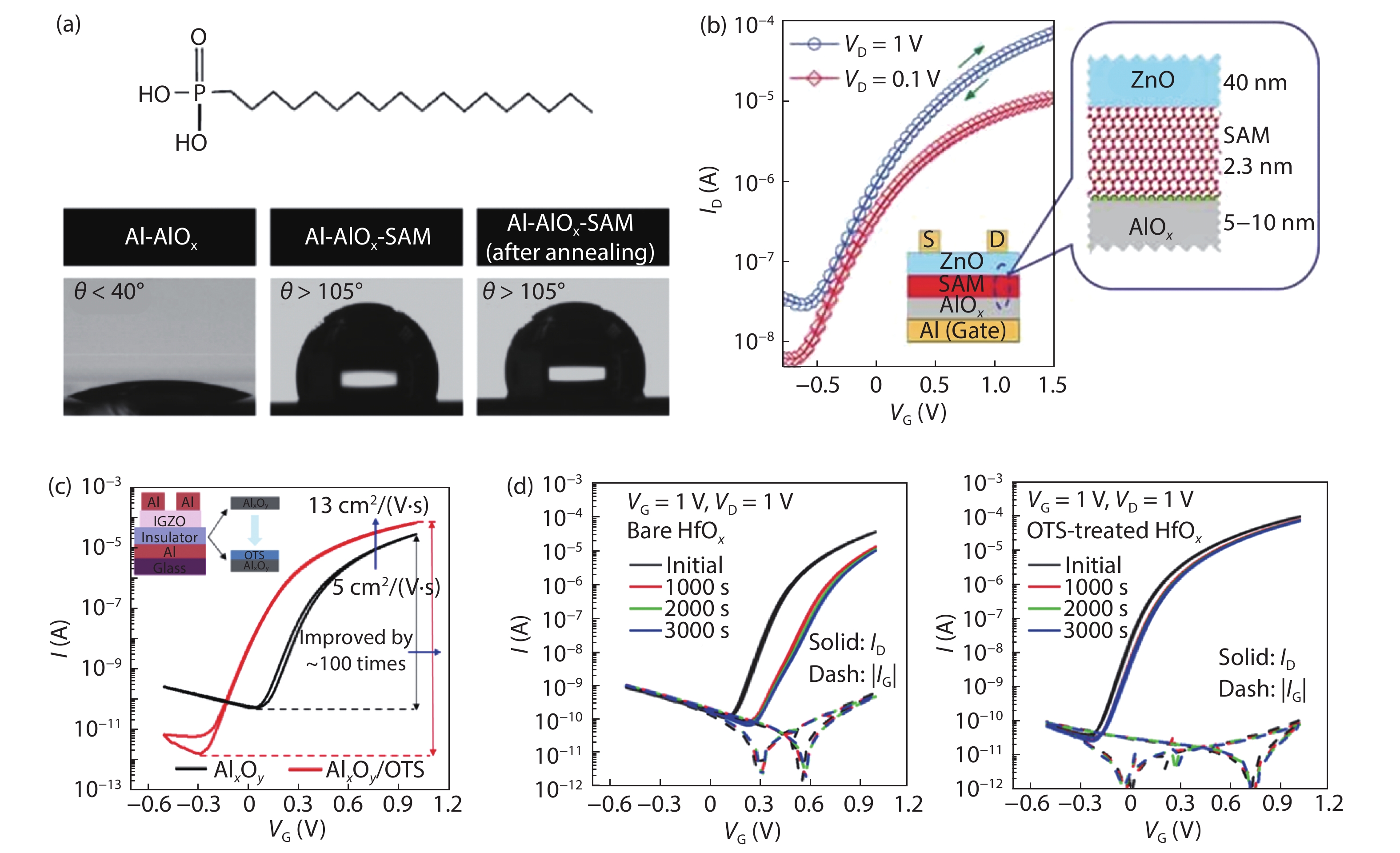
 DownLoad:
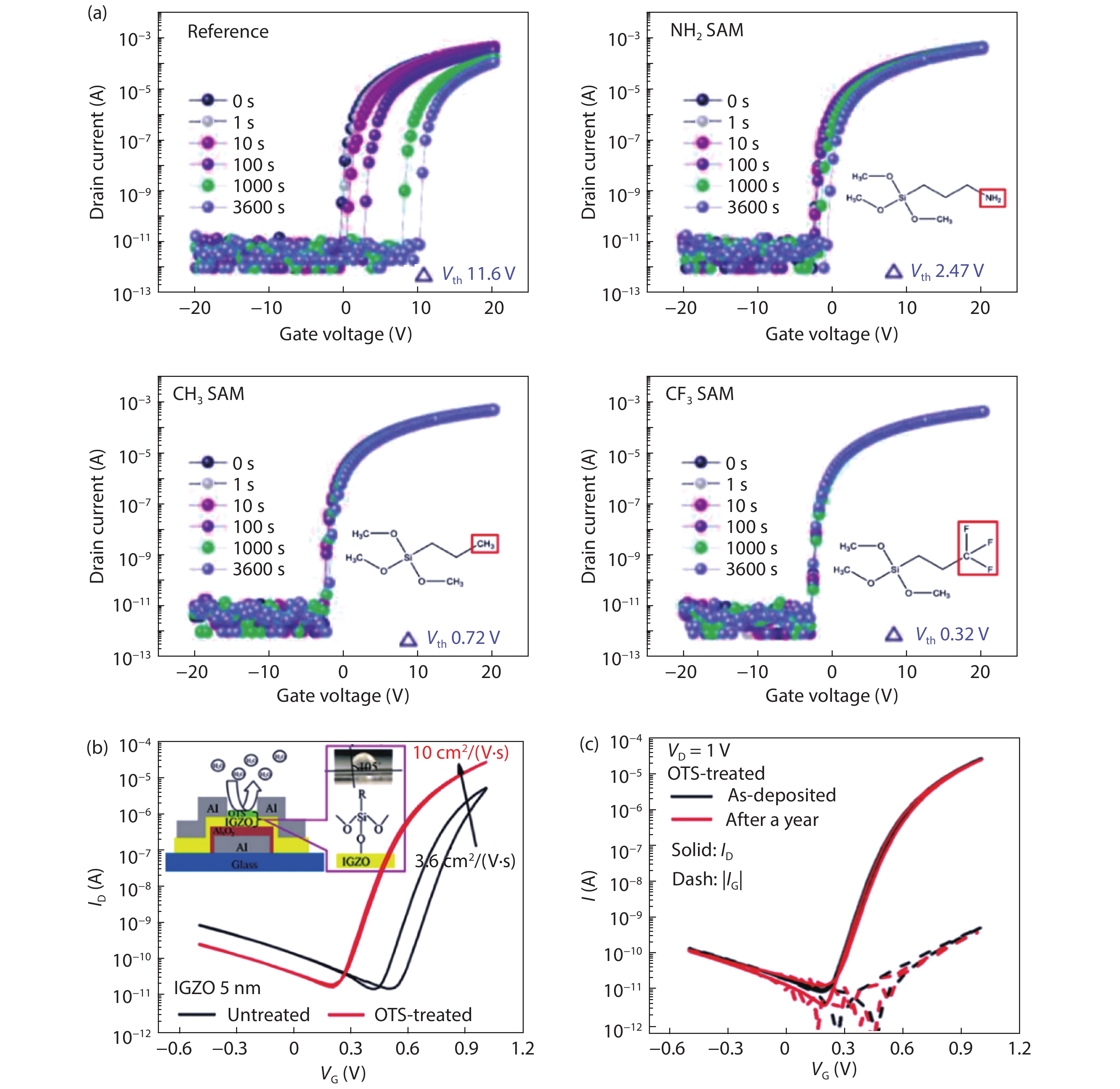
DownLoad: