| Citation: |
Xiaowen Zhang, Jiwen Xu, Hua Wang, Bin Wei, Huarong Zeng, Xueyin Jiang, Zhilin Zhang. Optimizing structure for constructing a highly efficient inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diode with stable electroluminescent spectra[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(2): 023002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/2/023002
****
X W Zhang, J W Xu, H Wang, B Wei, H R Zeng, X Y Jiang, Z L Zhang. Optimizing structure for constructing a highly efficient inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diode with stable electroluminescent spectra[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(2): 023002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/2/023002.
|
Optimizing structure for constructing a highly efficient inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diode with stable electroluminescent spectra
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/2/023002
More Information
-
Abstract
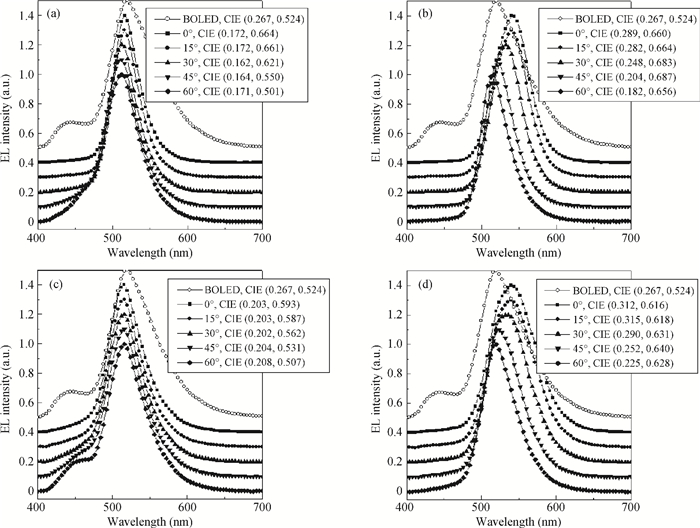
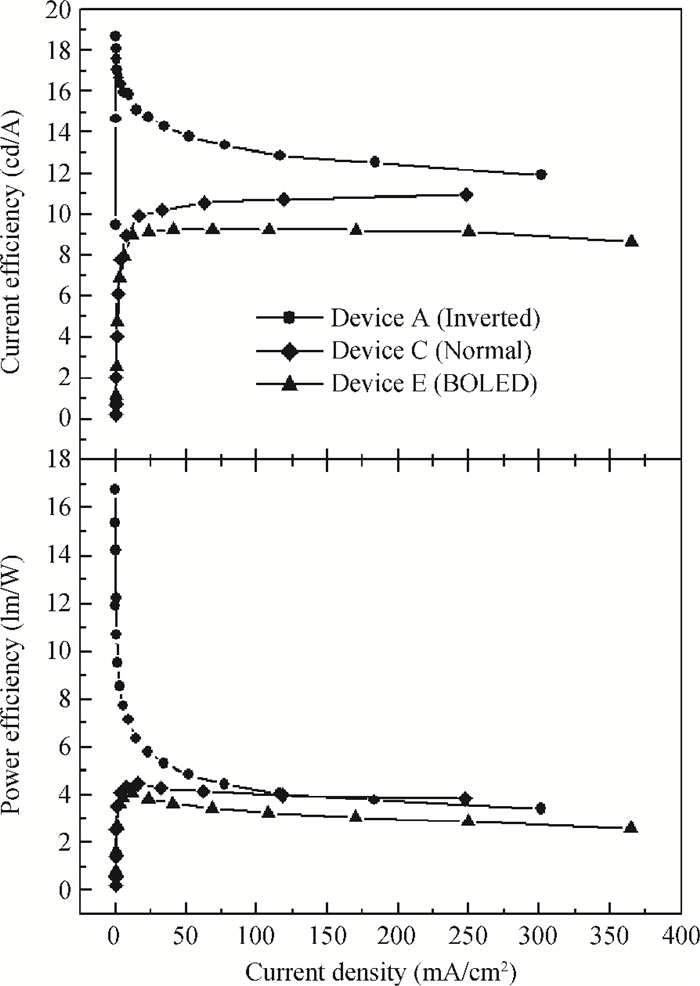
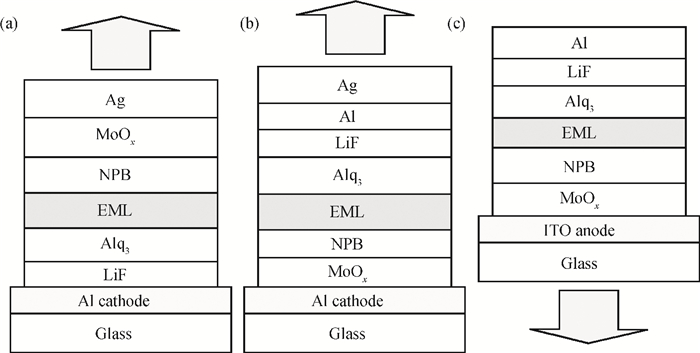
We demonstrate a highly efficient inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diode (TOLED) having stable electroluminescent spectra and color coordination with variation of viewing angles by simply tuning the resonance wavelength corresponding to the free emission of the emitter. Using a doped fluorescent emitting system, the inverted TOLED exhibits an enhanced maximum current efficiency of 19 cd/A and a power efficiency of 17 lm/W, which are much higher than those (11 cd/A and 5 lm/W) of the counterpart with normal structure, although both TOLEDs behave with similar stable electroluminescent spectra characteristics. The results indicate that we provide a simple and effective method of constructing an excellent inverted TOLED for potentially practical applications. -
References
[1] Flämmich M, Frischeisen J, Setz D S, et al. Oriented phosphorescent emitters boost OLED efficiency. Org Electron, 2011, 12:1663 doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2011.06.011[2] Zhang X W, Li J, Zhang L, et al. Top-emitting organic light-emitting device with high efficiency and low voltage using a silver-silver microcavity. Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518:1756 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2009.11.063[3] Liu X, Wei F X, Liu H. Spectrum study of top-emitting organic light-emitting devices with micro-cavity structure. Journal of Semiconductors, 2009, 30:044007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/30/4/044007[4] Hou J, Wu J, Xie Z, et al. Efficient inverted top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes using ultrathin MoO3/C60 bilayer structure to enhance hole injection. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95:203508 doi: 10.1063/1.3267084[5] Lim J T, Jeong C H, Lee J H, et al. High-luminance top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes using Cs/Al/Au as the semitransparent multimetal cathode. J Electrochem Soc, 2007, 154: J302 http://spl.skku.ac.kr/_res/pnpl/etc/2007-19.pdf[6] Li Y, Liu X Y, Wu C Y, et al. Tricolor microcavity OLEDs based on P-nc-Si:H films as the complex anodes. Journal of Semiconductors, 2009, 30:063005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/30/6/063005[7] D'Andrade B W, Forrest S R, Chwang A B. Operational stability of electrophosphorescent devices containing p and n doped transport layers. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83:3858 doi: 10.1063/1.1624473[8] Haq K, Khan M A, Jiang X Y, et al. Estimation of electron mobility of n-doped 4, 7-diphenyl-1, 10-phenanthroline using space-charge-limited currents. Journal of Semiconductors, 2009, 30:114009 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/30/11/114009[9] Wang Q, Deng Z, Ma D. Realization of high efficiency microcavity top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes with highly saturated colors and negligible angular dependence. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94:233306 doi: 10.1063/1.3153140[10] Yang C J, Liu S H, Hsieh H H, et al. Microcavity top-emitting organic light-emitting devices integrated with microlens arrays:simultaneous enhancement of quantum efficiency, cd/A efficiency, color performances, and image resolution. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91:253508 doi: 10.1063/1.2827182[11] Liu C C, Liu S H, Tien K C, et al. Microcavity top-emitting organic light-emitting devices integrated with diffusers for simultaneous enhancement of efficiencies and viewing characteristics. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94:103302 doi: 10.1063/1.3097354[12] Zhang X W, Liu L M, Li J, et al. The feasibility of using Cu as reflective anode in top-emitting organic light-emitting diode. Journal of Display Technology, 2011, 7:515 doi: 10.1109/JDT.2011.2154298[13] Yang C J, Lin C L, Wu C C, et al. High-contrast top-emitting organic light-emitting devices for active-matrix displays. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87:143507 doi: 10.1063/1.2081137[14] Lau K C, Xie W F, Sun H Y, et al. Contrast improvement of organic light-emitting devices with Sm:Ag cathode. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88:083507 doi: 10.1063/1.2172019[15] Chen S M, Yuan Y B, Lian J R, et al. High-efficiency and high-contrast phosphorescent top-emitting organic lightemitting devices with p-type Si anodes. Opt Express, 2007, 15:14644 doi: 10.1364/OE.15.014644[16] Xie Z Y, Hung L S. High-contrast organic light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84:1207 doi: 10.1063/1.1647689[17] Zhang X W, Jiang X Y, Zhu W Q, et al. Efficient fluorescence from 9, 10-bis(m-tolylphenylamino)anthracene doped into a blue matrix in Si-based top-emitting organic light-emitting diode. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519:6595 doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.04.126[18] Huang Q, Walzer K, Pfeiffer M, et al. Performance improvement of top-emitting organic light-emitting diodes by an organic capping layer:an experimental study. J Appl Phys, 2006, 100:064507 doi: 10.1063/1.2338145[19] Schubert E F, Hunt N E J, Micovic M, et al. Highly efficient light-emitting diodes with microcavities. Science, 1994, 265:943 doi: 10.1126/science.265.5174.943 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: