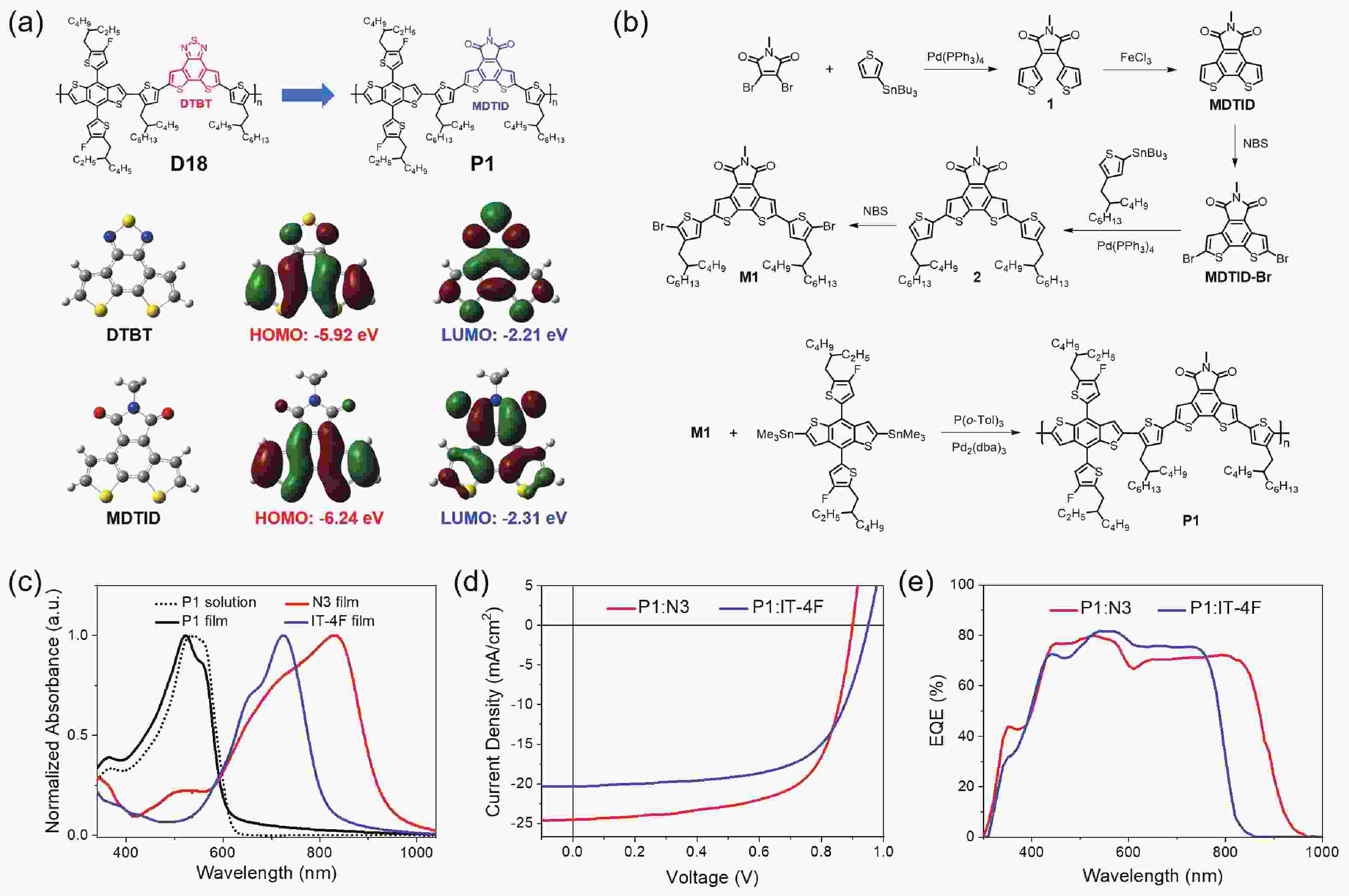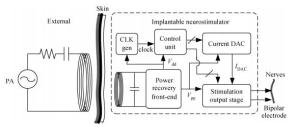
This paper present a highly-integrated neurostimulator with an on-chip inductive power-recovery frontend and high-voltage stimulus generator. In particular, the power-recovery frontend includes a high-voltage full-wave rectifier (up to 100 V AC input), high-voltage series regulators (24/5 V outputs) and a linear regulator (1.8/3.3 V output) with bandgap voltage reference. With the high voltage output of the series regulator, the proposed neurostimulator could deliver a considerably large current in high electrode-tissue contact impedance. This neurostimulator has been fabricated in a CSMC 1 μm 5/40/700 V BCD process and the total silicon area including pads is 5.8 mm2. Preliminary tests are successful as the neurostimulator shows good stability under a 13.56 MHz AC supply. Compared to previously reported works, our design has advantages of a wide induced voltage range (26-100 V), high output voltage (up to 24 V) and high-level integration, which are suitable for implantable neurostimulators.
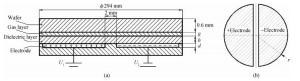
As one of the core components of IC manufacturing equipment, the electrostatic chuck (ESC) has been widely applied in semiconductor processing such as etching, PVD and CVD. The clamping force of the ESC is one of the most important technical indicators. A multi-physics simulation software COMSOL is used to analyze the factors influencing the clamping force. The curves between the clamping force and the main parameters such as DC voltage, electrode thickness, electrode radius, dielectric thickness and helium gap are obtained. Moreover, the effects of these factors on the clamping force are investigated by means of orthogonal experiments. The results show that the factors can be ranked in order of voltage, electrode radius, helium gap and dielectric thickness according to their importance, which may offer certain reference for the design of ESCs.
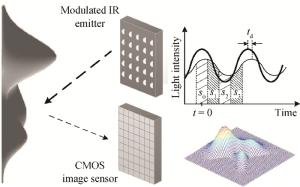
This paper presents an image sensor controller that is compatible for depth measurement, which is based on the continuous-wave modulation time-of-flight technology. The image sensor controller is utilized to generate reconfigurable control signals for a 256×256 high speed CMOS image sensor with a conventional image sensing mode and a depth measurement mode. The image sensor controller generates control signals for the pixel array to realize the rolling exposure and the correlated double sampling functions. An refined circuit design technique in the logic level is presented to reduce chip area and power consumption. The chip, with a size of 700×3380 μm2, is fabricated in a standard 0.18 μm CMOS image sensor process. The power consumption estimated by the synthesis tool is 65 mW under a 1.8 V supply voltage and a 100 MHz clock frequency. Our test results show that the image sensor controller functions properly.
A novel structure of a phase-locked loop (PLL) characterized by a short locking time and low jitter is presented, which is realized by generating a linear slope charge pump current dependent on monitoring the output of the phase frequency detector (PFD) to implement adaptive bandwidth control. This improved PLL is created by utilizing a fast start-up circuit and a slope current control on a conventional charge pump PLL. First, the fast start-up circuit is enabled to achieve fast pre-charging to the loop filter. Then, when the output pulse of the PFD is larger than a minimum value, the charge pump current is increased linearly by the slope current control to ensure a shorter locking time and a lower jitter. Additionally, temperature variation is attenuated with the temperature compensation in the charge pump current design. The proposed PLL has been fabricated in a kind of DSP chip based on a 0.35 μm CMOS process. Comparing the characteristics with the classical PLL, the proposed PLL shows that it can reduce the locking time by 60% with a low peak-to-peak jitter of 0.3% at a wide operation temperature range.
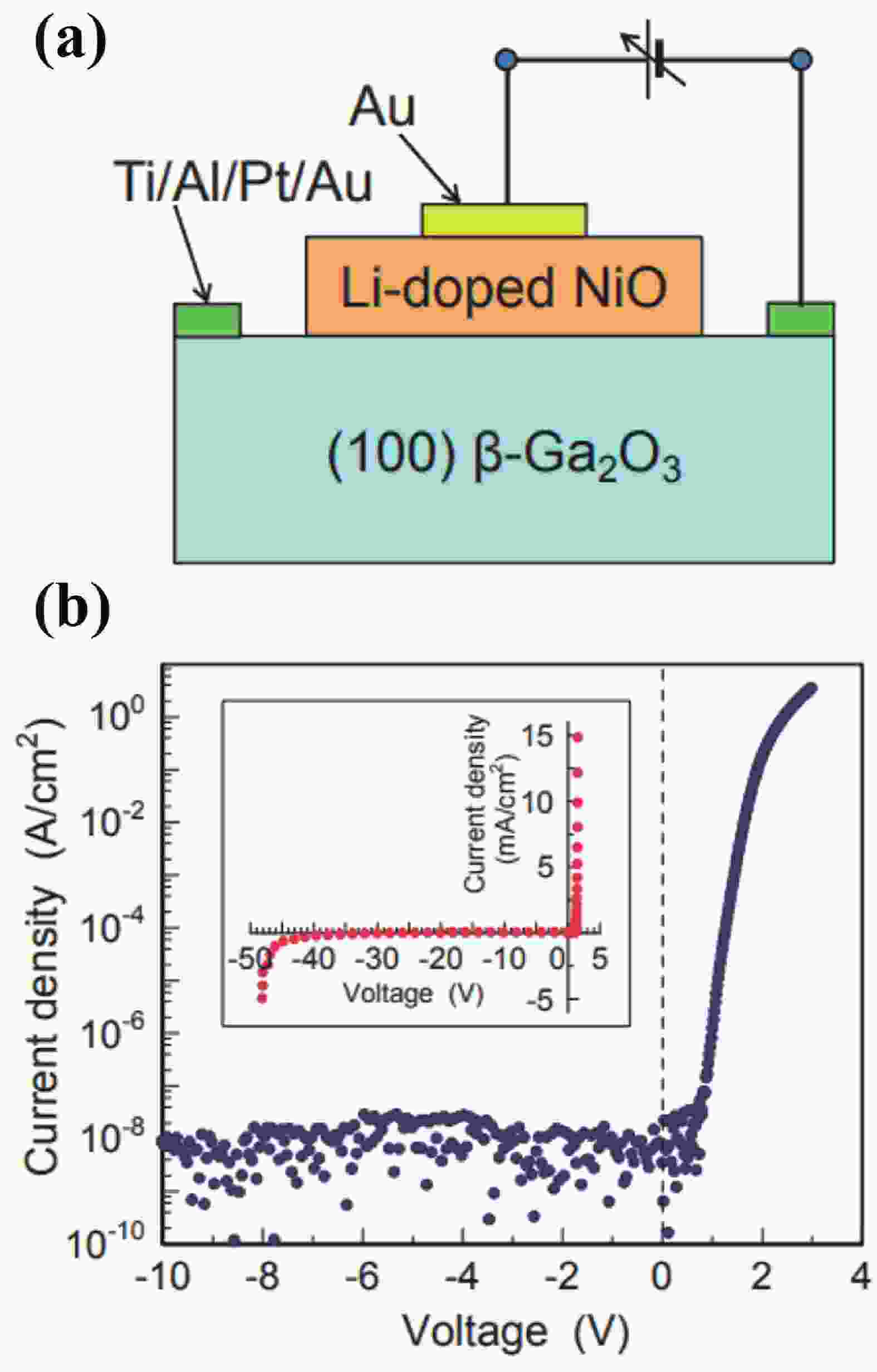
Beta gallium oxide (β-Ga2O3) has attracted significant attention for applications in power electronics due to its ultra-wide bandgap of ~ 4.8 eV and the large critical electric field of 8 MV/cm. These properties yield a high Baliga’s figures of merit (BFOM) of more than 3000. Though β-Ga2O3 possesses superior material properties, the lack of p-type doping is the main obstacle that hinders the development of β-Ga2O3-based power devices for commercial use. Constructing heterojunctions by employing other p-type materials has been proven to be a feasible solution to this issue. Nickel oxide (NiO) is the most promising candidate due to its wide band gap of 3.6–4.0 eV. So far, remarkable progress has been made in NiO/β-Ga2O3 heterojunction power devices. This review aims to summarize recent advances in the construction, characterization, and device performance of the NiO/β-Ga2O3 heterojunction power devices. The crystallinity, band structure, and carrier transport property of the sputtered NiO/β-Ga2O3 heterojunctions are discussed. Various device architectures, including the NiO/β-Ga2O3 heterojunction pn diodes (HJDs), junction barrier Schottky (JBS) diodes, and junction field effect transistors (JFET), as well as the edge terminations and super-junctions based on the NiO/β-Ga2O3 heterojunction, are described.
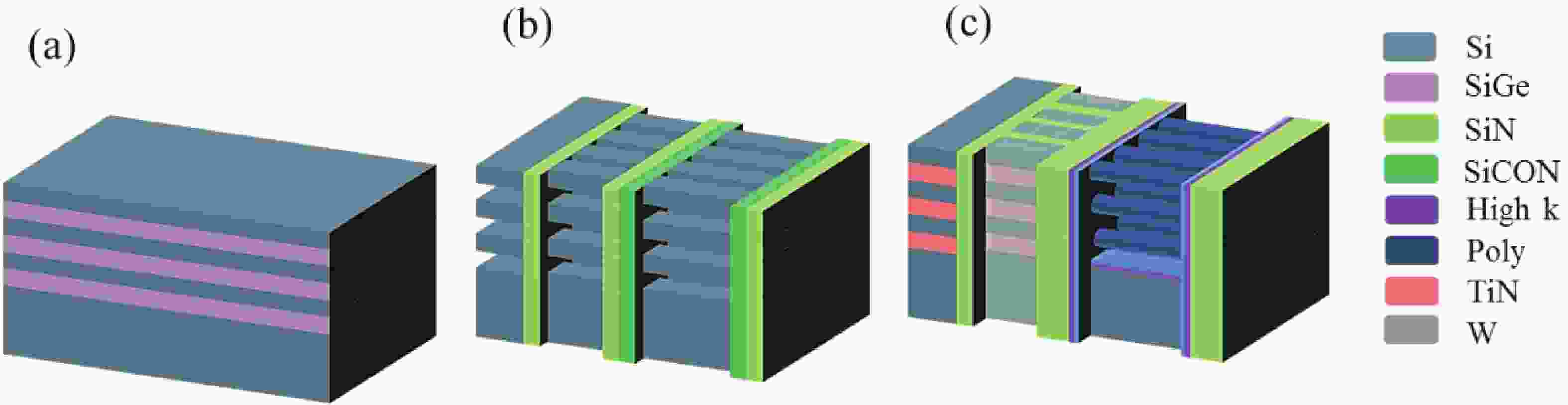
Fifteen periods of Si/Si0.7Ge0.3 multilayers (MLs) with various SiGe thicknesses are grown on a 200 mm Si substrate using reduced pressure chemical vapor deposition (RPCVD). Several methods were utilized to characterize and analyze the ML structures. The high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) results show that the ML structure with 20 nm Si0.7Ge0.3 features the best crystal quality and no defects are observed. Stacked Si0.7Ge0.3 ML structures etched by three different methods were carried out and compared, and the results show that they have different selectivities and morphologies. In this work, the fabrication process influences on Si/SiGe MLs are studied and there are no significant effects on the Si layers, which are the channels in lateral gate all around field effect transistor (L-GAAFET) devices. For vertically-stacked dynamic random access memory (VS-DRAM), it is necessary to consider the dislocation caused by strain accumulation and stress release after the number of stacked layers exceeds the critical thickness. These results pave the way for the manufacture of high-performance multivertical-stacked Si nanowires, nanosheet L-GAAFETs, and DRAM devices.
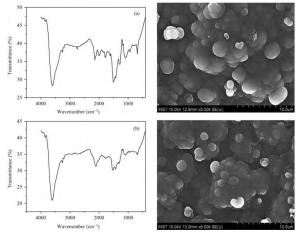
The optical properties of polypyrrole (Ppy) thin films upon 2 MeV electron beam irradiation changes with different doses. The induced changes in the optical properties for Ppy thin films were studied in the visible range 300 to 800 nm at room temperature. The optical band gap of the pristine Ppy was found to be 2.19 eV and it decreases up to 1.97 eV for a 50 kGy dose of 2 MeV electron beam. The refractive index dispersion of the samples obeys the single oscillator model. The obtained results suggest that electron beam irradiation changes the optical parameters of Ppy thin films.
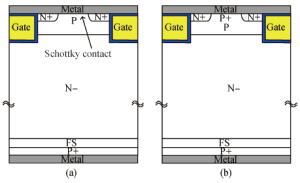
This letter proposes a high-conductivity insulated gate bipolar transistor (HC-IGBT) with Schottky contact formed on the p-base, which forms a hole barrier at the p-base side to enhance the conductivity modulation effect. TCAD simulation shows that the HC-IGBT provides a current density increase by 53% and turn-off losses decrease by 27% when compared to a conventional field-stop IGBT (FS-IGBT). Hence, the proposed IGBT exhibits superior electrical performance for high-efficiency power electronic systems.