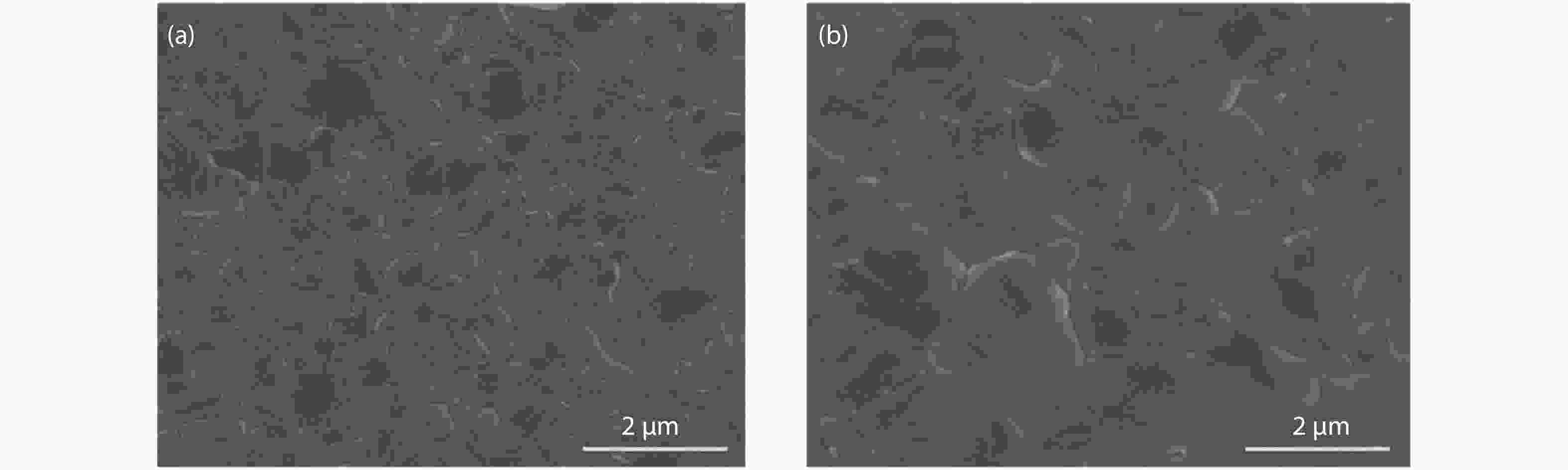
Although perovskite solar cells containing methylamine cation can show high power conversion efficiency, stability is a concern. Here, methylamine-free perovskite material CsxFA1–xPbI3 was synthesized by a one-step method. In addition, we incorporated smaller cadmium ions into mixed perovskite lattice to partially replace Pb ions to address the excessive internal strain in perovskite structure. We have found that the introduction of Cd can improve the crystallinity and the charge carrier lifetime of perovskite films. Consequently, a power conversion efficiency as high as 20.59% was achieved. More importantly, the devices retained 94% of their initial efficiency under 1200 h of continuous illumination.
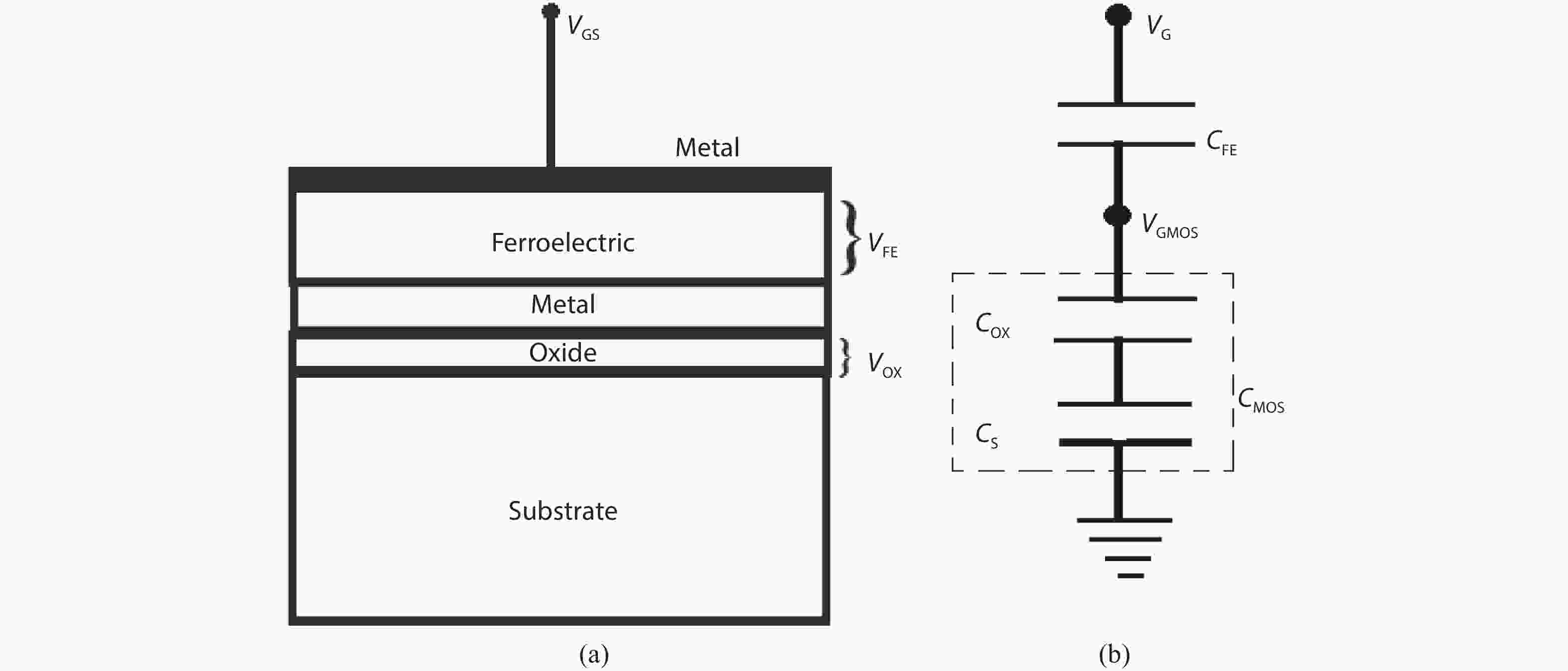
In this paper, we analytically study the relationship between the coercive field, remnant polarization and the thickness of a ferroelectric material, required for the minimum subthreshold swing in a negative capacitance capacitor. The interdependence of the ferroelectric material properties shown in this study is defined by the capacitance matching conditions in the subthreshold region in an NC capacitor. In this paper, we propose an analytical model to find the optimal ferroelectric thickness and channel doping to achieve a minimum subthreshold swing, due to a particular ferroelectric material. Our results have been validated against the numerical and experimental results already available in the literature. Furthermore, we obtain the minimum possible subthreshold swing for different ferroelectric materials used in the gate stack of an NC-FET in the context of a manufacturable semiconductor technology. Our results are presented in the form of a table, which shows the calculated channel doping, ferroelectric thickness and minimum subthreshold for five different ferroelectric materials.
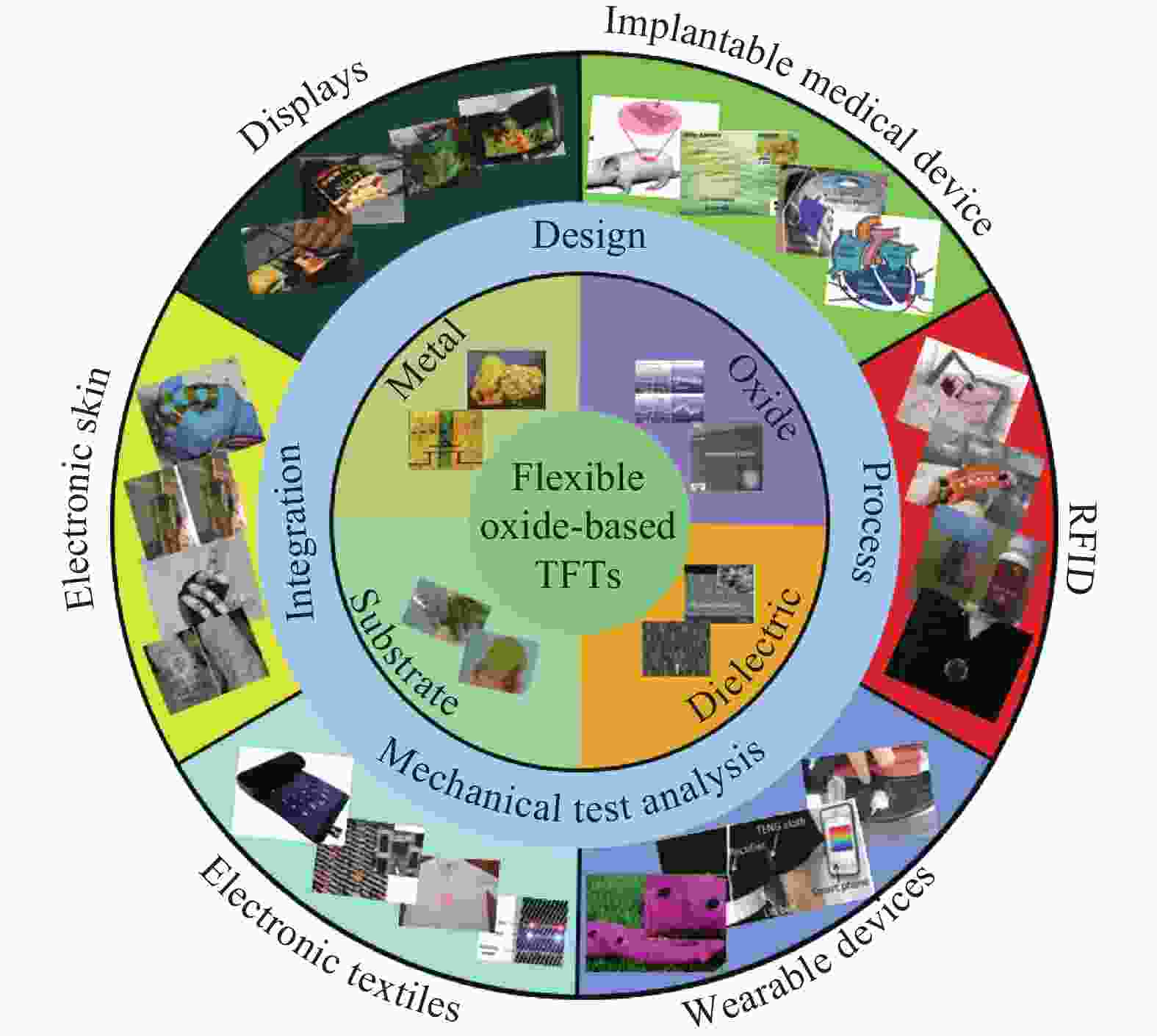
The continuous progress in thin film materials and devices has greatly promoted the development in the field of flexible electronics. As one of the most common thin film devices, thin film transistors (TFTs) are significant building blocks for flexible platforms. Flexible oxide-based TFTs are well compatible with flexible electronic systems due to low process temperature, high carrier mobility, and good uniformity. The present article is a review of the recent progress and major trends in the field of flexible oxide-based thin film transistors. First, an introduction of flexible electronics and flexible oxide-based thin film transistors is given. Next, we introduce oxide semiconductor materials and various flexible oxide-based TFTs classified by substrate materials including polymer plastics, paper sheets, metal foils, and flexible thin glass. Afterwards, applications of flexible oxide-based TFTs including bendable sensors, memories, circuits, and displays are presented. Finally, we give conclusions and a prospect for possible development trends.

The AC-electronic and dielectric properties of different phthalocyanine films (ZnPc, CuPc, FePc, and H2Pc) were investigated over a wide range of temperature. Both real and imaginary parts of the dielectric constant (ε=ε1-iε2) were found to be influenced by temperature and frequency. Qualitatively the behavior was the same for those compounds; however, the central atom, film thickness, and the electrode type play an important role in the variation of their values.The relaxation time, τ, was strongly frequency-dependent at all temperatures and low frequencies, while a weak dependency is observed at higher frequencies. The relaxation activation energy was derived from the slopes of the fitted lines of ln τ and the reciprocal of the temperature (1/T). The values of the activation energy were accounted for the hopping process at low temperatures, while a thermally activated conduction process was dominant at higher temperatures.The maximum barrier height, Wm, was found to be temperature and frequency dependent for all phthalocyanine compounds. The value Wm depends greatly on the nature of the central atom and electrode material type. The correlated barrier hopping model was found to be the appropriate mechanism to describe the charge carrier's transport in phthalocyanine films.
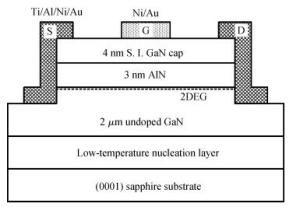
Using the measured capacitance-voltage and current-voltage characteristics of the rectangular AlN/GaN heterostructure field-effect transistors (HFETs) with the side-Ohmic contacts, it was found that the polarization Coulomb field scattering in the AlN/GaN HFETs was greatly weakened after the side-Ohmic contact processing, however, it still could not be ignored. It was also found that, with side-Ohmic contacts, the polarization Coulomb field scattering was much stronger in AlN/GaN HFETs than in AlGaN/AlN/GaN and In0.17Al0.83N/AlN/GaN HFETs, which was attributed to the extremely thinner barrier layer and the stronger polarization of the AlN/GaN heterostructure.
Silicon photonics is an emerging competitive solution for next-generation scalable data communications in different application areas as high-speed data communication is constrained by electrical interconnects. Optical interconnects based on silicon photonics can be used in intra/inter-chip interconnects, board-to-board interconnects, short-reach communications in datacenters, supercomputers and long-haul optical transmissions. In this paper, we present an overview of recent progress in silicon optoelectronic devices and optoelectronic integrated circuits(OEICs) based on a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor-compatible process, and focus on our research contributions. The silicon optoelectronic devices and OEICs show good characteristics, which are expected to benefit several application domains, including communication, sensing, computing and nonlinear systems.
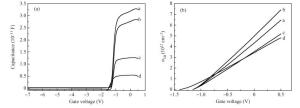
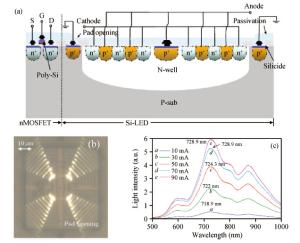
Based on the measured capacitance-voltage (C-V) curves and current-voltage (I-V) curves for the prepared differently-sized AlN/GaN heterostructure field-effect transistors (HFETs), the I-V characteristics of the AlN/GaN HFETs were simulated using the quasi-two-dimensional (quasi-2D) model. By analyzing the variation in the electron mobility for the two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) with the channel electric field, it is found that the different polarization charge distribution generated by the different channel electric field distribution can result in different polarization Coulomb field (PCF) scattering. The 2DEG electron mobility difference is mostly caused by the PCF scattering which can reach up to 899.6 cm2/(V·s) (sample a), 1307.4 cm2/(V·s) (sample b), 1561.7 cm2/(V·s) (sample c) and 678.1 cm2/(V·s) (sample d), respectively. When the 2DEG sheet density is modulated by the drain-source bias, the electron mobility for samples a, b and c appear to peak with the variation of the 2DEG sheet density, but for sample d, no peak appears and the electron mobility rises with the increase in the 2DEG sheet density.
The optoelectronic properties of heterojunction thin film devices with ITO/CuPc/C60/Al structure have been investigated by analyzing their current–voltage characteristics, optical absorption and photocurrent. In this organic photovoltaic device, CuPc acts as an optically active layer, C60 as an electron-transporting layer and ITO and Al as electrodes. It is observed that, under illumination, excitons are formed, which subsequently drift towards the interface with C60, where an internal electric field is present. The excitons that reach the interface are subsequently dissociated into free charge carriers due to the electric field present at the interface. The experimental results show that in this device the total current density is a function of injected carriers at the electrode–organic semiconductor surface, the leakage current through the organic layer and collected photogenerated current that results from the effective dissociation of excitons.
The fabrication and photoelectrical characteristics of suspended ZnO nanowire (NW) field-effect transistors(FETs) are presented. Single-crystal ZnO NWs are synthesized by a hydrothermal method. The fabricated FETs exhibit excellent performance. When Vds = 2.5 V, the peak transconductance of the FETs is 0.396 µS, the average electron mobility is 50.17 cm2/(V·s), the resistivity is 0.96 × 102 Ω·cm at Vgs = 0 V, and the current on/off ratio (IonIoff) is approximately 105. ZnO NW-FET devices exposed to ultraviolet radiation (2.5 µW/cm2) exhibit punchthrough and threshold voltage (Vth) shift (from –0.6 V to +0.7 V) and a decrease by almost half of the source–drain current (Ids, from 560 nA to 320 nA) due to drain-induced barrier lowering. Continued work is underway to reveal the intrinsic properties of suspended ZnO nanowires and to explore their device applications.
An asymmetric MOSFET-C band-pass filter (BPF) with on chip charge pump auto-tuning is presented. It is implemented in UMC (United Manufacturing Corporation) 0.18 µm CMOS process technology. The filter system with auto-tuning uses a master-slave technique for continuous tuning in which the charge pump outputs 2.663 V, much higher than the power supply voltage, to improve the linearity of the filter. The main filter with third order lowpass and second order high-pass properties is an asymmetric band-pass filter with bandwidth of 2.730–5.340 MHz. The in-band third order harmonic input intercept point (IIP3) is 16.621 dBm, with 50 Ω as the source impedance. The input referred noise is about 47.455 µVrms. The main filter dissipates 3.528 mW while the auto-tuning system dissipates 2.412 mW from a 1.8 V power supply. The filter with the auto-tuning system occupies 0.592 mm2 and it can be utilized in GPS (global positioning system) and Bluetooth systems.