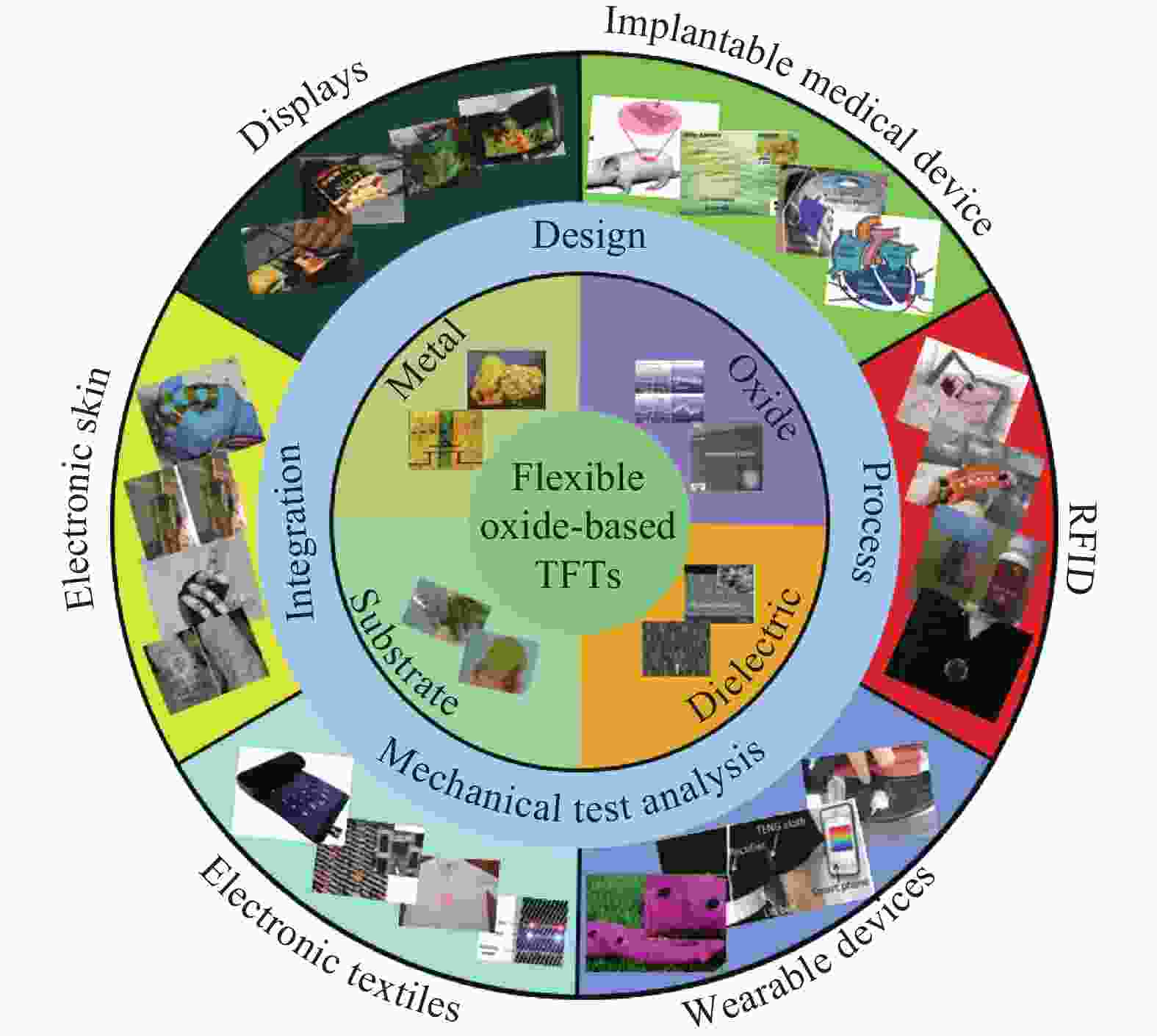
The continuous progress in thin film materials and devices has greatly promoted the development in the field of flexible electronics. As one of the most common thin film devices, thin film transistors (TFTs) are significant building blocks for flexible platforms. Flexible oxide-based TFTs are well compatible with flexible electronic systems due to low process temperature, high carrier mobility, and good uniformity. The present article is a review of the recent progress and major trends in the field of flexible oxide-based thin film transistors. First, an introduction of flexible electronics and flexible oxide-based thin film transistors is given. Next, we introduce oxide semiconductor materials and various flexible oxide-based TFTs classified by substrate materials including polymer plastics, paper sheets, metal foils, and flexible thin glass. Afterwards, applications of flexible oxide-based TFTs including bendable sensors, memories, circuits, and displays are presented. Finally, we give conclusions and a prospect for possible development trends.
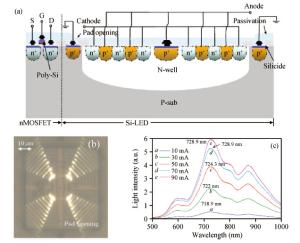
Silicon photonics is an emerging competitive solution for next-generation scalable data communications in different application areas as high-speed data communication is constrained by electrical interconnects. Optical interconnects based on silicon photonics can be used in intra/inter-chip interconnects, board-to-board interconnects, short-reach communications in datacenters, supercomputers and long-haul optical transmissions. In this paper, we present an overview of recent progress in silicon optoelectronic devices and optoelectronic integrated circuits(OEICs) based on a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor-compatible process, and focus on our research contributions. The silicon optoelectronic devices and OEICs show good characteristics, which are expected to benefit several application domains, including communication, sensing, computing and nonlinear systems.
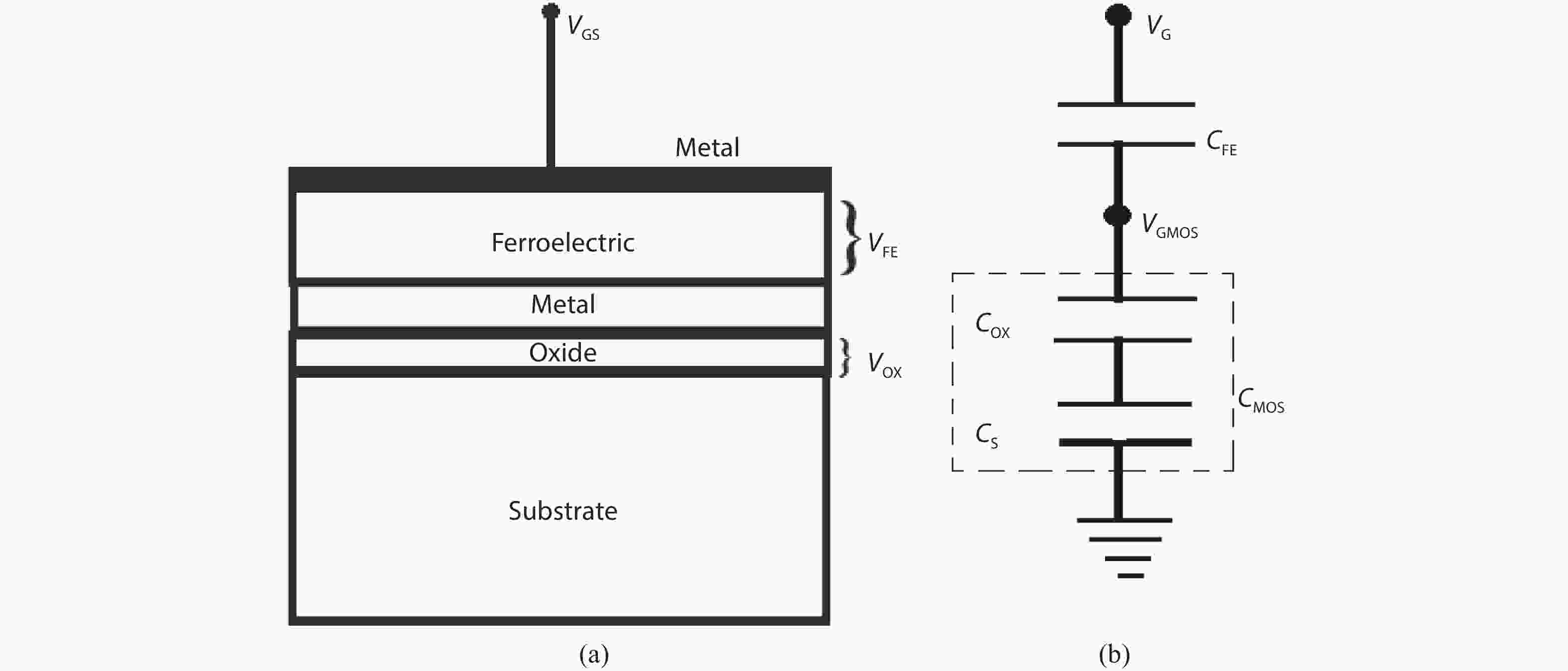
In this paper, we analytically study the relationship between the coercive field, remnant polarization and the thickness of a ferroelectric material, required for the minimum subthreshold swing in a negative capacitance capacitor. The interdependence of the ferroelectric material properties shown in this study is defined by the capacitance matching conditions in the subthreshold region in an NC capacitor. In this paper, we propose an analytical model to find the optimal ferroelectric thickness and channel doping to achieve a minimum subthreshold swing, due to a particular ferroelectric material. Our results have been validated against the numerical and experimental results already available in the literature. Furthermore, we obtain the minimum possible subthreshold swing for different ferroelectric materials used in the gate stack of an NC-FET in the context of a manufacturable semiconductor technology. Our results are presented in the form of a table, which shows the calculated channel doping, ferroelectric thickness and minimum subthreshold for five different ferroelectric materials.
Although perovskite solar cells containing methylamine cation can show high power conversion efficiency, stability is a concern. Here, methylamine-free perovskite material CsxFA1–xPbI3 was synthesized by a one-step method. In addition, we incorporated smaller cadmium ions into mixed perovskite lattice to partially replace Pb ions to address the excessive internal strain in perovskite structure. We have found that the introduction of Cd can improve the crystallinity and the charge carrier lifetime of perovskite films. Consequently, a power conversion efficiency as high as 20.59% was achieved. More importantly, the devices retained 94% of their initial efficiency under 1200 h of continuous illumination.
Two-dimensional (2D) materials with unique properties have received a great deal of attention in recent years. This family of materials has rapidly established themselves as intriguing building blocks for versatile nanoelectronic devices that offer promising potential for use in next generation optoelectronics, such as photodetectors. Furthermore, their optoelectronic performance can be adjusted by varying the number of layers. They have demonstrated excellent light absorption, enabling ultrafast and ultrasensitive detection of light in photodetectors, especially in their single-layer structure. Moreover, due to their atomic thickness, outstanding mechanical flexibility, and large breaking strength, these materials have been of great interest for use in flexible devices and strain engineering. Toward that end, several kinds of photodetectors based on 2D materials have been reported. Here, we present a review of the state-of-the-art in photodetectors based on graphene and other 2D materials, such as the graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides, and so on.
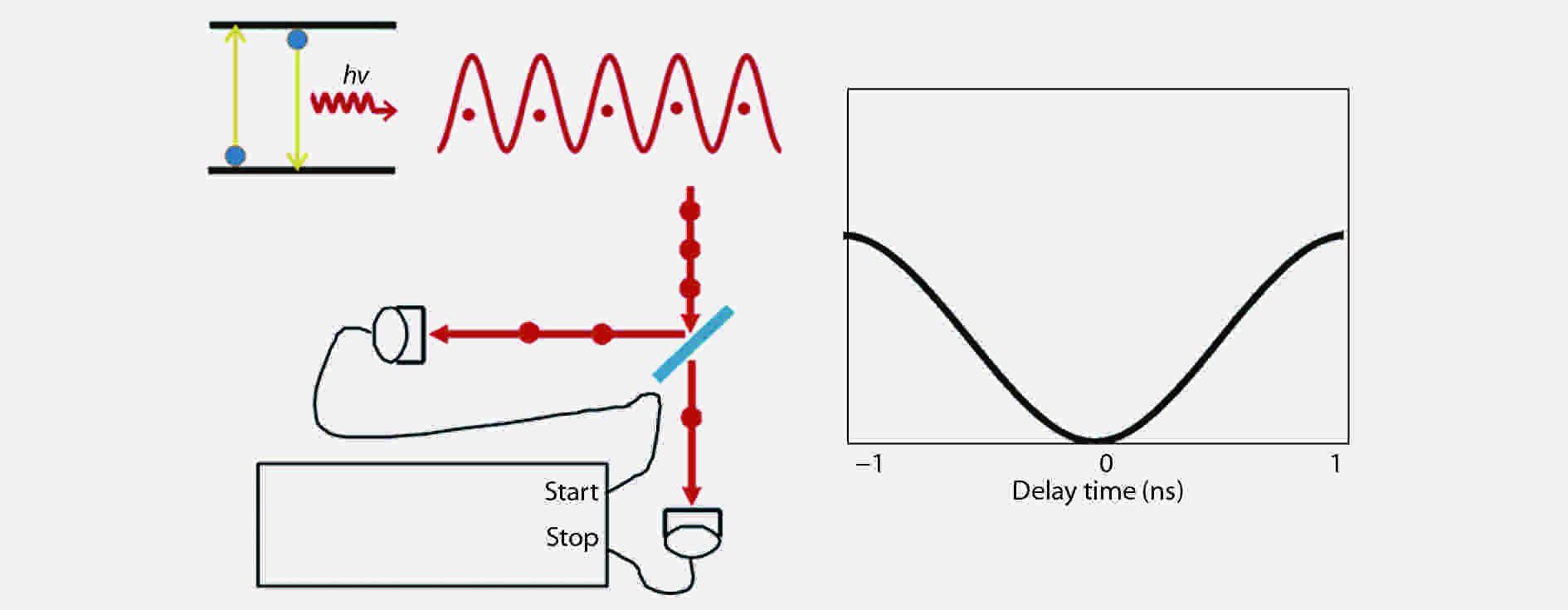
A brief introduction of semiconductor self-assembled quantum dots (QDs) applied in single-photon sources is given. Single QDs in confined quantum optical microcavity systems are reviewed along with their optical properties and coupling characteristics. Subsequently, the recent progresses in In(Ga)As QDs systems are summarized including the preparation of quantum light sources, multiple methods for embedding single QDs into different microcavities and the scalability of single-photon emitting wavelength. Particularly, several In(Ga)As QD single-photon devices are surveyed including In(Ga)As QDs coupling with nanowires, InAs QDs coupling with distributed Bragg reflection microcavity and the In(Ga)As QDs coupling with micropillar microcavities. Furthermore, applications in the field of single QDs technology are illustrated, such as the entangled photon emission by spontaneous parametric down conversion, the single-photon quantum storage, the chip preparation of single-photon sources as well as the single-photon resonance-fluorescence measurements.
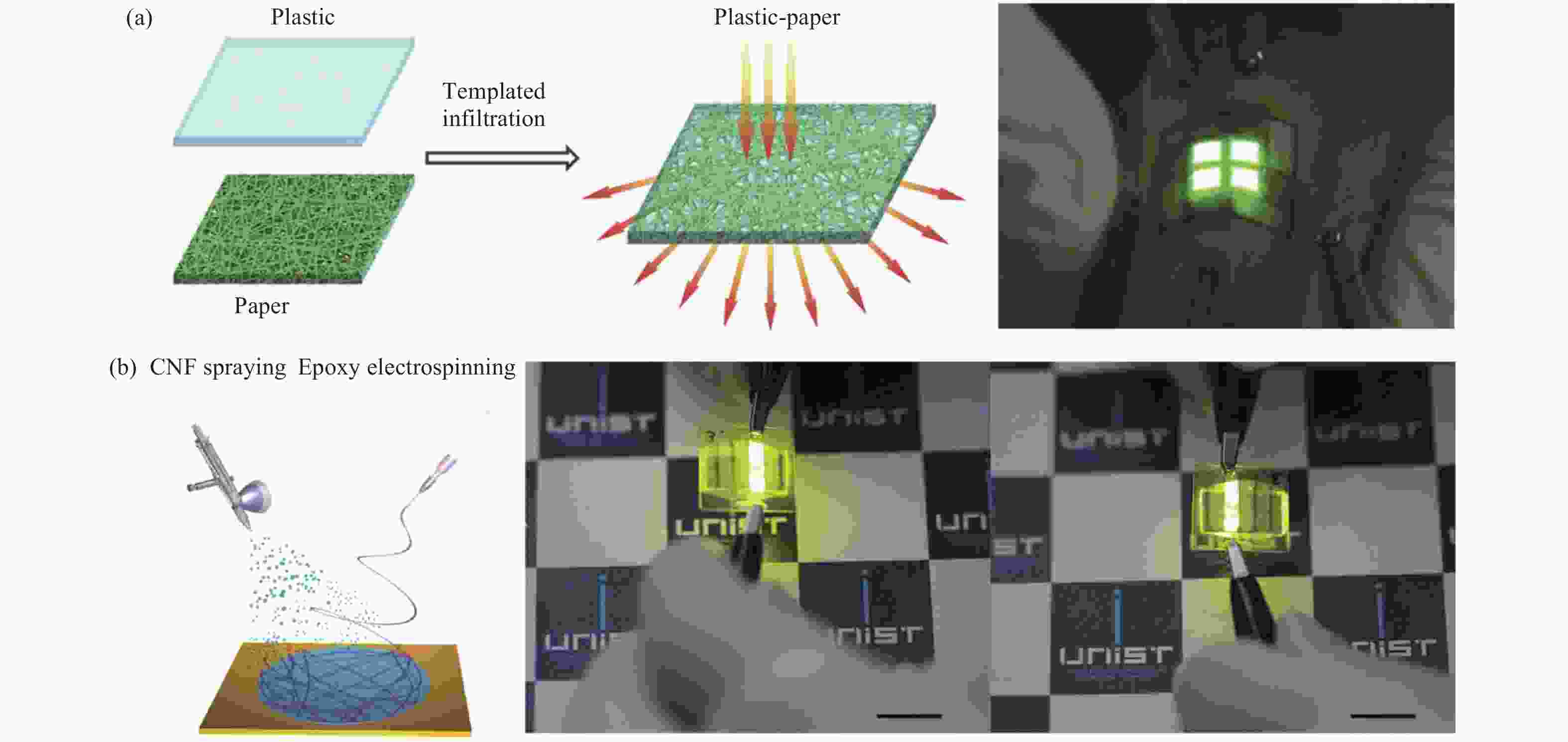
Flexible and wearable optoelectronic devices have been developing to a new stage due to their unique capacity for the possibility of a variety of wearable intelligent electronics, including bendable smartphones, foldable touch screens and antennas, paper-like displays, and curved and flexible solid-state lighting devices. Before extensive commercial applications, some issues still have to be solved for flexible and wearable optoelectronic devices. In this regard, this review concludes the newly emerging flexible substrate materials, transparent conductive electrodes, device architectures and light manipulation methods. Examples of these components applied for various kinds of devices are also summarized. Finally, perspectives about the bright future of flexible and wearable electronic devices are proposed.
A high efficiency charge pump circuit is designed and realized. The charge transfer switch is biased by the additional capacitor and transistor to eliminate the influence of the threshold voltage. Moreover, the bulk of the switch transistor is dynamically biased so that the threshold voltage gets lower when it is turned on during charge transfer and gets higher when it is turned off. As a result, the efficiency of the charge pump circuit can be improved. A test chip has been implemented in a 0.18 μm 3.3 V standard CMOS process. The measured output voltage of the eight-pumping-stage charge pump is 9.8 V with each pumping capacitor of 0.5 pF at an output current of 0.18 μA, when the clock frequency is 780 kHz and the supply voltage is 2 V. The charge pump and the clock driver consume a total current of 2.9 A from the power supply. This circuit is suitable for low power applications.

In a recent article, Chen et al. [Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 130: 279] presented their fabrication and characterization results on a graphene/n-Si solar cell where the Au nanoparticles were inserted in graphene to increase its optical and electrical properties. The higher efficiency of the device was attributed to increased conductivity of graphene after doping with Au nanoparticles. However, the knowledge in the field of Schottky diode solar cells relates this to increased band bending at the junction. Also, to explain the instability behaviour, they concluded that the growth of silicon oxide on the Si surface or oxygen adsorption on the window layer resulted in the device performance increasing initially and decreasing in the end. However, this instability seems to be due to variation in series resistance reduced at the beginning because of slightly lowered Fermi level and increased at the end by the self-compensation by deep in-diffusion of Au nanoparticles into n-Si layer. We also propose that inserting a very thin p-type layer at the junction will enhance the carrier collection and performance of this device.
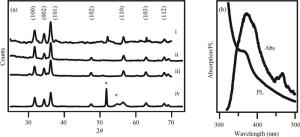
The fabrication of zinc oxide (ZnO) from inexpensive solution-processing techniques, namely, electrochemical deposition and electrospinning were explored on various conducting and mesoporous semiconducting surfaces. Optimised conditions were derived for template-and self-assisted nano/micro structures and composites. ZnO thin films were annealed at a fixed temperature under ambient conditions and characterised using physical and optical techniques. The photocurrent response in the UV region shows a fast rise and double decay behaviour with a fast component followed by a slow oscillatory decay. Photocurrent results were correlated with surface chemical analysis from X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Various characterisation details reveal the importance of fabrication parameter optimisation for useful low-cost optoelectronic applications.